Hysterectomy - Glossary
Abdominal: Relating to the abdomen, that part of the body that contains all of the structures between the chest and the pelvis.Benign: A noncancerous growth A benign tumor does not invade surrounding tissue or spread to other parts of the body.
Biopsy: The removal of a sample of tissue for purposes of diagnosis.
Cancer: An abnormal growth of cells, which tend to proliferate in an uncontrolled way and, in some cases, to metastasize, to spread to distant organs.
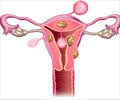
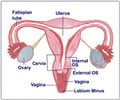
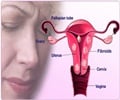
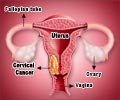
Cervix: The cervix is the lower, narrow part of the uterus . The uterus, a hollow, pear-shaped organ, is located in a woman's lower abdomen, between the bladder and the rectum. The cervix forms a canal that opens into the vagina, which leads to the outside of the body.
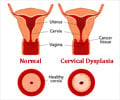
Cervical dysplasia: Changes in the cells lining the cervix. Cervical dysplasia involves a sequence of cellular changes from mild to severe that are not yet cancerous but constitute the prelude to cancer of the cervix.
Endometrial cancer: Cancer of the inner lining of the uterus. Endometrial cancer occurs most often in women between the ages of 55 and 70 years. It accounts for about 6% of cancer in women.
Endometriosis: In endometriosis, the endometrial cells that normally grow inside the uterus grow outside the uterus.
Fibroids: Fibroids are common, benign tumors of smooth muscle in the uterus. Uterine fibroids are the most common reason for performing a hysterectomy.
Hormone: A chemical substance produced in the body that controls and regulates the activity of certain cells or organs.
Lithotomy position: Position in which the patient is on their back with the hips and knees flexed and the thighs apart. The position is often used for vaginal examinations and childbirth
Oophorectemy: The removal of one or both ovaries by surgery. Also known as ovariectomy.
Ovary: The female gonad, the ovary is the reproductive gland in women. They are two in number and are located in the pelvis, one on each side of the uterus. Each ovary is about the size and shape of an almond. The ovaries produce eggs (ova) and female hormones. During each monthly menstrual cycle, an egg is released from one ovary. The egg travels from the ovary through a fallopian tube to the uterus. The ovaries are the main source of female hormones, which control the development of female body characteristics, such as the breasts, body shape, and body hair. They also regulate the menstrual cycle and pregnancy.
Pap Smear: A screening test for cervical cancer based on the examination under the microscope of cells collected from the cervix. The cells are smeared on a slide and can help study premalignant (before cancer) and malignant (cancer) changes as well as changes due to noncancerous conditions such as inflammation from infections.
Postmenopausal: After the menopause. Postmenopausal is defined formally as the time after which a woman has experienced twelve (12) consecutive months of amenorrhea, which is lack of menstruation.