Mitral Valve Stenosis And Mitral Valve Replacement - Glossary
Aortic Stenosis – Narrowing of the aortic valve.Atrial fibrillation - A disorder of heart rhythm in which the normally regular contractions of the atria of the heart are replaced by rapid and random twitching, resulting in irregular and usually faster than usual contractions of the ventricles.
Atrial Septal defect - Abnormal breach in the fibrous membrane separating the atrium [upper chambers of the heart]
Auscultation – To listen to the sounds made by the internal organs of the body for diagnostic purposes. For example, nurses and doctors auscultate the lungs and heart of a patient by using a stethoscope placed on the patient's chest.
Carcinoid – A type of tumor usually found in the gastrointestinal system (most often in the appendix), and sometimes in the lungs or other sites. Carcinoid tumors are usually benign.
Cardiac output – The amount or volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle per minute.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease - Emphysema, bronchitis, asthma or other diseases in which the lungs' ability to exchange air is impaired.
Coarctation of the aorta - Congenital narrowing of a segment of the aorta that impedes blood flow to the lower part of the body.
Congenital - Congenital is a term, which denotes Acquired by birth.
Coumadin - A medication that reduces clotting of the blood by inhibiting the body's production of coagulation factors.
Emphysema - Pulmonary emphysema is a disorder affecting the alveoli (tiny air sacs) of the lungs. The transfer of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs takes place in the walls of the alveoli. In emphysema, the alveoli become abnormally inflated, damaging their walls and making it harder to breathe. People who smoke or have chronic bronchitis have an increased risk of emphysema.
Endocarditis - Inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, usually the heart valves; typically caused by an infection
Endotracheal tube - A plastic tube that is fed down into the trachea through the mouth or nose to supply oxygen to a person who is not breathing properly
Heart Failure - Condition caused when the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the needs of the body; also characterized by fluid collecting in various parts of the body (such as legs, lungs, liver).
Hemodynamics - the forces involved during circulation of the blood.
Hypertrophy - Enlarged in size, rather than in the number of components.
Left Ventricular hypertrophy - Left ventricle muscle overgrowth that may impede blood flow into and out of the heart.
Lupus erythromatus – SLE is a chronic inflammatory connective tissue disease marked by skin rashes, joint pain and swelling, inflammation of the kidneys, inflammation of the fibrous tissue surrounding the heart (i.e., the pericardium), as well as other problems. Not all affected individuals display all of these problems. May be referred to as lupus.
Murmur - Heard through a physician's stethoscope, it is the sound of turbulent blood passing through the heart. Heart murmurs are possible indications of abnormal blood flow and may be caused by a disorder of a heart valve (structure which opens to allow blood to flow away from the heart, and closes to prevent back flow into the heart). Many murmurs are benign (of no significance).
Myxoma - A non-cancerous tumour made of mucous material and fibrous connective tissue
Prosthetic/ Prosthesis - An artificial replacement of a part of the body.
Pulmonary hypertension - Increased blood pressure in the arteries supplying blood to the lungs; caused by increased resistance to blood flow in the lungs, usually a result of a lung disease
Stenosis - The narrowing or closure of an opening or passageway in the body.
Streptococcus - The most common disease-causing bacteria in humans, which can be treated with antibiotics. If left untreated, some types of streptococcal bacteria may give rise to more serious diseases.
Supravalvular – Located above the valve.
Systole - The portion of the heart cycle during which the heart muscle is contracting.
Thrombus - Blood clot.
Vegetation – a growth in the heart.
Ventricular Diastole – The relaxation phase of the ventricles, when the blood fills in from the atrium. It is also the interval between two heartbeats.
Ventricular Septal defect - Hole in the wall separating the two ventricles.







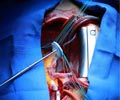




Patients undergoing mitral valve replacement are susceptible to the following risks. Bleeding, infection, complex reaction to anesthetic. The risk involved in most cases can be determined by the physician and it depends on a variety of factors such as the patient’s age, general condition, specific medical problems and heart functions.
Alternative treatment is Balloon valvuloplasty.Balloon valvuloplasty is performed using a catheter, i.e. a very thin flexible tube which can be inserted into the body, with a balloon at the end. The balloon is put inside the valve and is expanded thus stretching the valve and bringing it back to its normal size. For more info: heart-consult.com/articles.
can you pl guide me what to do i have mitral valve balooning twice after gap of 10 years and presently,I am only 30 years old.I am on acitrom 2 mg [Anticoagulant], metolar 25 mg and Penicilin 10 lacs once in three weeks.I am having feeling of irregular heart beating and sometimes irregular palpitations.I had undergone check up in 2008 june last time everything was ok and there was no need of balloning that time.Is it possible that there may be severe damage only in these two yaers that is between 2008 to 2010.Pl suggest and what could be the situation.
hallo, i am suffering from mitral valve stenosis for about 3.5jear. am like you help me without operation.
My mother had sucessive surgery. I flew her to NYC to see Dr David Adams ..the worlds greatest in mitral valve repair and replacement. His entire team at Mount Sinai is fabulous. He see patients from around the world.
i am suffering from Mitral stenosis(Moderate-severe)and Mitral regurgitation(Mild-moderate).The disease surfaced some 5/6 months back.i am intrested in the latest non surgical treatment.please guide/help me.thanks with regards,waiting for your reply.