- Peripheral neuropathy - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/peripheral-neuropathy/symptoms-causes/syc-20352061)
- About Nerve Injuries - (http://www.assh.org/handcare/hand-arm-injuries/nerve)
- Numbness - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/numbness/basics/causes/sym-20050938)
- Bladder and Bowel Dysfunction - (https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/healthlibrary/conditions/kidney_and_urinary_system_disorders/bladder_and_bowel_dysfunction_134,113)
- Nerve injury - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/nerve_injury)
- Nerve pain (neuralgia) - (https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/nerve-pain)
- Steps to Prevent or Delay Nerve Damage - (http://www.diabetes.org/living-with-diabetes/complications/neuropathy/steps-to-prevent-or-delay.html)
- Diabetic Neuropathy - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems/nerve-damage-diabetic-neuropathies)
Introduction to Nervous System
The nervous system includes central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system includes brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of the long nerves which connect the central nervous system with the body parts. The main function of the nervous system is to transmit the signals via the nerves, to and from the body parts in order to coordinate their proper functioning.
What are the Types of Nerves in the Body?
- Sensory nerves: They carry the sensory input from the skin and muscles to the brain and spinal cord. The sensory input is processed in the brain which helps to perceive the sensations like pain, touch, position, vibration and temperature sensations.
- Motor nerves: They control the movements of the body by transmitting the information from the brain and spinal cord to the muscles of the limb and face.
- Autonomic nerves: They control the involuntary body functions like digestion, heart rate, blood pressure and temperature regulation.
What are the Causes of Nerve Damage?
Nerve damage can occur due to a variety of illnesses and include the following
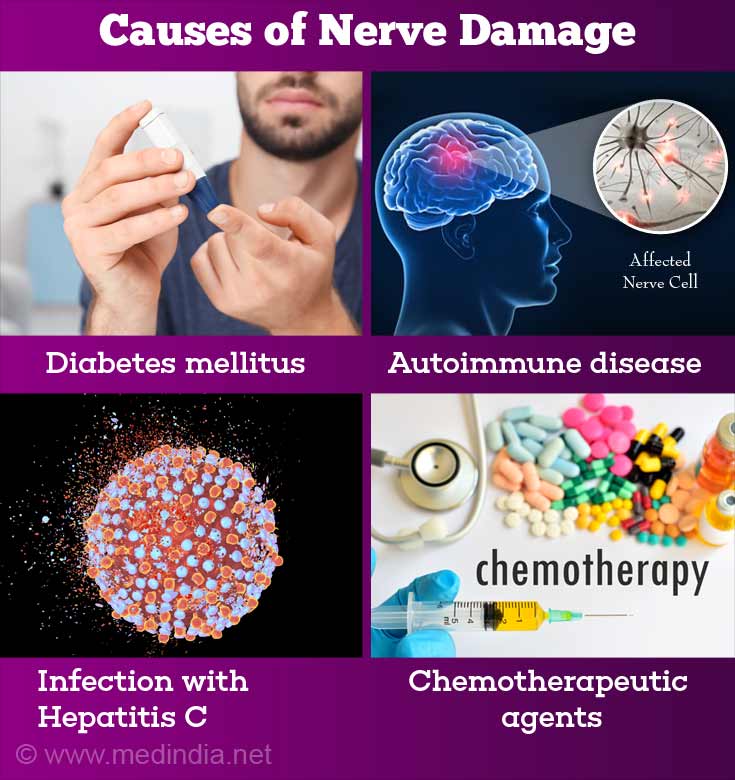
Diabetes mellitus:
Diabetic neuropathy is due to nerve damage from diabetes. High blood glucose levels and triglycerides due to diabetes can cause nerve damage.
Autoimmune diseases:
Autoimmune diseases can cause nerve damage and cause nerve pain. Autoimmune diseases like multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, inflammatory bowel disease and Guillain-Barre disease can cause nerve damage.
Cancer:
Cancer can cause nerve damage in various ways. They can compress the nerve or infiltrate the nerve. Cancer can cause nutritional deficiency which can lead to nerve damage. Cancer treatment like radiation treatment and chemotherapy can damage the nerves.
Trauma or compression:
Direct trauma or compression of the nerves or nerve roots (in spinal cord) can cause nerve damage with resulting disability.
Infections:
Some infections affect the nerves. Infection with Hepatitis C, HIV, herpes etc., can involve the nerves.
Metabolic causes:
Diabetes mellitus is a major cause of metabolic neuropathy. Thyroid diseases, hypoglycemia, renal failure and alcohol neuropathies are also metabolic neuropathies.
Drug side effects:
Chemotherapeutic agents, drugs used for tuberculosis and HIV can cause nerve damage.
Toxins:
Heavy metals like mercury, lead and arsenic on accidental consumption can cause nerve damage.
Nutritional deficiency:
Vitamin B12, folic acid, vitamin E, B1 and B6 are important for nerves. Their deficiency can cause nerve damage.
Motor neuron disease:
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is a motor neuron disease which causes a progressive motor nerve damage and ultimately death.
What are the Symptoms & Signs of Nerve Damage?
Nerve damage can result in the aberrant transmission of nerve signal and leads to dysfunction of the body parts. The symptoms and signs due to nerve injury or damage vary depending on the extent of damage and the type of nerve involved. There are various manifestations of the nerve damage. If they are identified earlier and found to have a treatable cause, the symptoms can be relieved.
The symptoms are due to the involvement of
- Motor nerves
- Sensory nerves or/and
- Autonomic nerves

The symptoms due to the sensory nerve involvement are:
- Pain: Pain due to the involvement of nerves is called as neuropathic pain or nerve pain. It is a common symptom due to nerve injury or damage. The pain may be shooting, stabbing or burning type. Nerve pain can be sudden and sharp like an electric shock. Its distribution is in the nerve course and most specifically at the site of injury. The course and distribution of pain may help in the diagnosis.
- Loss of sensations/numbness: The sensations are due to the sensory nerves, which transmit the sensory input to the brain. Injury or damage to the sensory nerves can lead to a loss of sensation of the respective area. The location and the type of sensation that is lost can help in localizing the lesion and finding the cause. A common cause of peripheral sensory nerve damage is diabetes mellitus
- Burning Sensation: Nerve damage can cause burning sensation in the area involved, which may be associated with pain, tingling and numbness.
- Tingling and pricking: Nerve damage can cause tingling and pricking sensation which can be associated with pain, numbness or burning sensation.
The symptoms due to motor nerve damage include
- Twitching: Muscle twitch or fasciculation is an involuntary contraction and relaxation of a muscle. It is visible under the skin. Involvement of the motor neurons can cause twitching. Sometimes it occurs even in normal conditions.
- Weakness or Paralysis: A loss in the function of the muscles is called weakness or paralysis.
Motor nerve damage can result in the paralysis. The causes of paralysis are spinal cord injury, stroke, poliomyelitis, multiple sclerosis, etc. It may be associated with sensory loss. Muscle paresis is partial loss of function or partial paralysis. When there is paralysis of one side of the body it is called hemiplegia. When both the lower limbs are paralyzed it is called paraplegia.
- Muscle Atrophy: A decrease in the muscle bulk is called muscle atrophy. It may be seen due to restricted movement and in bedridden patients. Partial or complete wasting is observed. Muscle atrophy can occur in patients with conditions like cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, renal failure, AIDS etc. Neurogenic atrophy of muscle is due to nerve damage. Neurogenic atrophy is the most severe form with a sudden onset. Neurogenic atrophy is due to nerve injury, motor neuron disease or infections.
- Abnormal Posture or Gait: Muscle weakness and pain due to the associated nerve damage, can cause an abnormal gait and posture.
The symptoms due to autonomic nerve damage are
- Bowel and bladder dysfunction: The urinary bladder and bowel function depend on the muscle and sphincter function which are regulated by the nerves. Nerve damage to those supplying the bladder and bowel muscle and sphincter can result in symptoms such as diarrhea, constipation, incontinence.
- Alterations in blood pressure: Alterations in the blood pressure is seen when the autonomic nerves are damaged.
- Miscellaneous Symptoms -
- Lightheadedness
- Excessive or less sweating
- Sexual dysfunction
- Heart rhythm abnormalities
- Early satiety
Treatment of nerve damage:
Treatment to prevent further nerve damage by treating the cause includes:
- In patients with diabetes, regular monitoring of the glucose levels and treatment of diabetes is essential.
- Treat if there is any underlying nutritional deficiency eg B12 injections
- Identifying and treating the infections causing nerve damage.
- Treatment of autoimmune diseases
Treatment to reduce nerve pain includes:
- Analgesics such as paracetamol, tramadol
- Antidepressants: Tricyclic antidepressant like amitriptyline helps to alleviate the pain.
- Physiotherapy
- Electrical stimulation
- Relaxation techniques
Tips to Prevent Nerve Damage
- Prevention of nerve damage plays an essential role in patients with diabetes. The following are precautions in such patients
- Regular monitoring of the glucose
- Good care of the feet
- Report early to the doctor when symptoms are present
- Follow a good diabetic diet
- Stop smoking
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Exercise: it helps to strengthen the muscles
- Keep body weight in check
- Avoid lifting heavy objects