Glossary
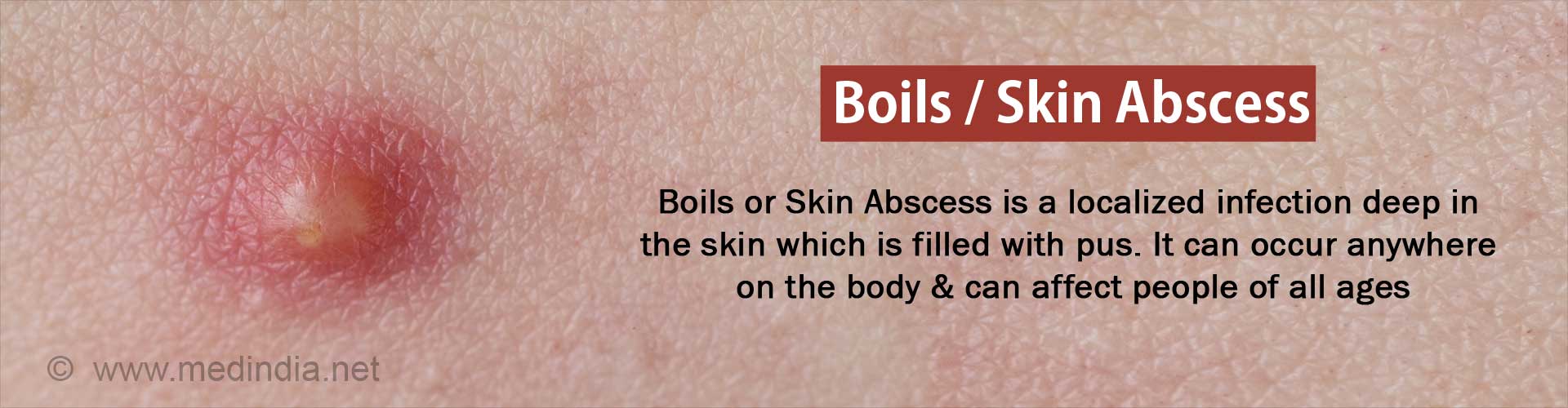
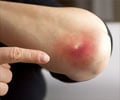
Abscess: Medical term for a common boil, a collection of pus beneath the skin.
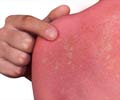
Carbuncle: Painful localized bacterial infection. A circumscribed inflammation of the skin and deeper tissues that terminates in a slough and suppuration and is characterized by a painful node, at first covered by tight reddened skin which later becomes thin and perforates, discharging pus through several openings.
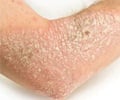
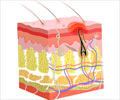
Furuncle: An acute circumscribed inflammation of the subcutaneous layers of the skin, gland or hair follicle.
Cyst: A closed sac or capsule, usually filled with fluid or semisolid material.
Antibiotic: A substance that inhibits the growth of or destroys bacteria or other microorganisms.
Pus: A thick whitish-yellow fluid which results from the accumulation of white blood cells (WBCs), liquified tissue and cellular debris. Pus is commonly a site of infection or foreign material in the body.
Gangrene: A necrosis, or death of tissue, usually due to deficient or absent blood supply.
Osteomyelitis: Inflammation of the bone due to infection, by the bacteria salmonella or staphylococcus.
Pleura: The thin covering that protects and cushions the lungs. The pleura is made up of two layers of tissue that are separated by a small amount of fluid.