- Bruises - (http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/bruises.html)
What is a Bruise?
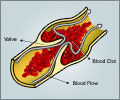
A Bruise is a discoloration of the skin as a result of accumulation of blood under the superficial layer of the skin. This can happen due to rupture of small vessels under the skin without a tear in the skin.
Causes of Bruises
- Accidents and bumps
- Ageing – With age the skin becomes thinner and blood vessels lose strength, hence rupture easily.
- Bleeding disorders – Deficiency of clotting factors. It can also present with gum bleeding, nasal bleeding and internal bleeding in the abdomen.
- High intensity sports like weight lifting, athletics
Types of Bruises
- Subcutaneous – Just beneath the skin
- Intramuscular – Inside the muscle
- Periosteal – Bruise to the bone
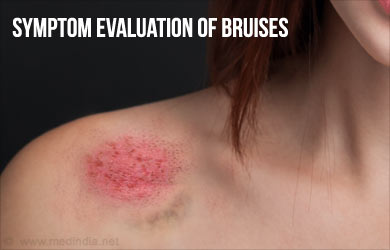
Symptoms associated with Bruises
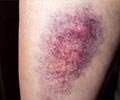
- A fresh bruise is usually reddish. Over days, there can be a gradual change of color of the bruise from red to bluish black and then to yellowish green.
- Pain or tenderness that usually subsides as the bruise fades with time
- Swelling at the area of the bruise
- Nosebleeds or bleeding gums associated with bruises may point to an underlying bleeding disorder.

Healing of bruise takes up to 4 weeks or more. In case the swelling persists for more than 4 weeks, further evaluation must be done to look for underlying cause like bleeding disorders.
Healing of a bruise undergoes various phases like the initial swelling with redness followed by bluish black discoloration and then the final stage of healing which is yellowish white color of the skin.
A bruise with severe swelling and pain should alert a more serious problem like a fracture of bone. Recurrent bruising in a certain pattern should raise suspicion of physical abuse.
Easy and recurrent bruising in various parts of the body along with bleeding from nose and in gums raises suspicion of a bleeding disorder.
Bruising can be seen in various conditions like:
- Injuries – Injuries can happen due to motor vehicle accidents, blunt injuries, sports or due to falling. A bruise after an injury is spongy or lumpy due to sudden collection of blood in that area. By the nature of the accident or assault it can be categorized either into injury or abuse. X-rays and abdomen ultrasound are useful in assessing the extent of injury.
- Alcohol abuse – It causes dehydration, loss of Vitamin C and a tendency of brittle capillaries. All these factors increase the chances of easy bruising in alcoholics.

- Ageing – Due to ageing the upper layer of the skin becomes thin and the soft tissues are unable to provide adequate support to the capillaries leading to easy bruising even for simple forces applied.
- Aplastic anemia – It is a condition affecting the bone marrow, inhibiting the production of blood cells. It can be caused by radiation therapy, exposure to chemicals, autoimmune disorders, certain medications and viral infections. Complete blood count with bone marrow biopsy is useful in concluding on the cause.
- Autoimmune diseases - It is a group of disorders happening due to abnormal response of the immune system to the body’s own cells causing various symptoms. Bruising in autoimmune diseases usually happen due to damage to the blood vessels or bone marrow.
- Cushing’s disease – It is a condition that develops due to abnormal production of high levels of cortisol by the adrenal glands in the body. It can happen due to the use of synthetic corticosteroids as a part of the treatment for various conditions or due to tumors in the adrenal glands. It presents with easy bruising, thin skin, reddish purple marks on the thighs, stomach, buttocks, arms and legs, weight gain and decreased libido. Estimating cortisol levels in the blood helps in arriving at a diagnosis.
- Hemophilia – It is a genetic disorder, causing abnormal bleeding in various organs of our body due to insufficient or complete loss of clotting factors (either factor 8 or 9). Excessive bleeding from injuries or surgical procedures, pain, stiffness and swelling in joints, deep bruises, nasal bleeding, blood in urine/stool etc. Tests like prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, factor 8 and factor 9 levels estimation helps in concluding on the cause for bruising.
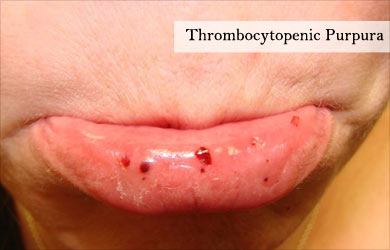
- Thrombocytopenic purpura – It is an autoimmune condition causing unexplained bruises with gum/nasal bleeding. It is usually triggered by a viral infection. It leads to formation of small clots causing the platelets to decrease in number. Platelet count and bone marrow examination are useful in arriving on the diagnosis.
- Vitamin C deficiency – Deficiency of Vitamin C leads to a condition called Scurvy. It presents with Perifollicular hyperkeratotic papules, perifollicular purpura, splint hemorrhages on the nails, conjunctival hemorrhages, gum bleeding and weight loss. Vitamin C is not synthesized by our body and needs to be included in the diet to avoid deficiency. Foods rich in Vitamin C include tomatoes, broccoli, cabbage, sprouts and sweet potatoes. Vitamin C levels testing and capillary fragility test are useful in concluding on the diagnosis.
- Von Willebrand’s disease – It happens due to deficiency of clotting factor 8. It is a hereditary disease affecting both males and females. Easy and profuse bleeding and bruising from various sites in the body are common with this condition. Estimation of factor 8 is useful in confirming the cause for easy bruising. Desmopressin is helpful in managing this condition.
Complications due to Bruises
- Brain hematoma or contusion leading to coma. Brain hematomas can happen due to blunt injury to the head especially in infants, children, elderly and alcoholics. They present initially with a bruise and develop other symptoms a few hours later when the hematoma progresses in size.
- Hypovolemic shock due to hematomas in liver and spleen. Hypovolemic shock occurs due to severe blood loss.
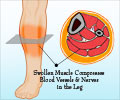
- Compartment syndrome - It occurs due to an increase in pressure in the muscle compartment as a result of bleeding in the muscle. Bleeding in the muscle can occur due to injury.
- Risk of fracture
Diagnosis of a regular bruise is made with physical examination. In case of severe pain and swelling, X –rays of that region are performed to rule out fractures. Easy bruising requires blood investigations to check for clotting time. Depending upon the cause of the bruise, tests can be ordered accordingly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which doctor treats a bruise?
A regular bruise due to injury is often treated by a general physician, unless it is accompanied by serious injuries like bone fracture etc which is treated by an orthopedician.
2. Is it serious to have a bruise?
Most often it is not serious. Most commonly it occurs due to trauma or physical assault, in that case it depends upon the severity of the injury. In certain cases bruising happens due to defective clotting process. In such a situation it is often accompanied by bleeding internally, especially in the abdomen or brain, which can be life threatening.
3. How long does it take to heal for a bruise?
A normal bruise heals with in 2-4 weeks of time. If it is taking more than this period it could be due to a severe injury like bruise to the bone.