- What causes diarrhoea? - (http://www.healthdirect.gov.au/what-causes-diarrhoea)
- Evaluating the Patient With Diarrhea: A Case-Based Approach - (http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mayocp.2012.02.015)
- Diarrhea - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diarrhea/basics/definition/con-20014025)
What is Diarrhea?
Diarrhea means loose, watery stools which occur frequently. It occurs when the intestines fail to absorb the liquids or when excess fluid leaks into the lumen.
The symptoms that may be associated with diarrhea include abdominal pain abdominal cramps, fever, bloating, blood in stool and fever. Depending on the cause, diarrhea may last for a day to several days.
If diarrhea lasts for less than 2 weeks, it is acute diarrhea. If it lasts longer than 4 weeks, it is called chronic diarrhea.
The causes of diarrhea include infection, medications, endocrine-related conditions, digestive disorders or malignancy.
Diarrhea is a frequent cause of death due to dehydration among children. Infections are the main cause of diarrhea in underdeveloped and developing nations.

What are the Causes of Diarrhea?
The causes of diarrhea are:
Infections due to bacteria, virus and parasites can cause diarrhea. The patient gives a history of intake of possible contaminated food or water and may suffer from vomiting, fever and pain in the abdomen as well.
Bacterial Causes of Diarrhea
- Bacteria causing diarrhea are Salmonella, Shigella, E.coli, Vibrio cholera, Campylobacter and Clostridium difficile. The type of stools and associated symptoms may give a clue on the type of infection.
- Vibrio cholerae produces watery diarrhea and causes severe dehydration.
- Clostridium difficile produces watery and sometimes bloody stools. The patient may give a history of prior antibiotic use or hospitalization.
- Shigella produces dysentery with mucus and/or blood in the stools.
- Some patients with diarrheal infections with organisms like Salmonella, Campylobacter, Shigella and Yersinia may develop reactive arthritis where the patient shows features of arthritis, sore or pink eyes, and inflammation of the urethra.
- Infection with enterohemorrhagic E coli and Shigella can result in kidney failure due to hemolytic uremic syndrome.
Viral Causes of Diarrhea
The viral causes of diarrhea include Norwalk virus, viral hepatitis and Cytomegalovirus. Rotavirus is the common causative agent of diarrhea among the children. Cytomegalovirus often causes diarrhea in patients with reduced immunity. Viral diarrhea is usually self-limiting and does not require antibiotics.

Parasitic Causes of Diarrhea
Giardia lamblia and Cryptosporidium are some of the parasites which cause diarrhea. Entamoeba histolytica produces dysentery.
Diarrhea due to Medications
Diarrhea can be a side effect of almost all oral medications. There are certain drugs which cause diarrhea by various mechanisms.
Drugs like citrates, sulfates, phosphates, magnesium containing laxatives and mannitol cause diarrhea due to osmotic water release into the lumen of the intestine.
- Antibiotics like amoxicillin, antiarrhythmic drugs like quinine, colchicine, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, prostaglandins and biguanides cause diarrhea due to increased secretion.
- Drugs like erythromycin, metoclopramide and laxatives cause diarrhea due to the increased intestinal motility.
- Drugs like acarbose and aminoglycosides cause diarrhea due to malabsorption
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics disturb the normal gut flora. This leads to the infection with Clostridium difficile causing pseudomembranous enterocolitis, which causes diarrhea.
A history of intake of the medications should be obtained from a patient with diarrhea. Diarrhea often reduces when the medication is stopped and replaced with a different medication.
Intestinal Disorders
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): It is functional diarrhea that can cause watery stools. IBS causes symptoms of crampy abdominal pain along with either diarrhea or constipation. The abdominal discomfort is relieved by defecation. It is more common among women and in developed nations. Emotional stress, eating and infections exacerbate IBS. The tests are normal in IBS.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) manifests in two forms, ulcerative colitis or Crohn’s disease. Ulcerative colitis involves colon, rectum and causes diarrhea, blood in stool and pain in abdomen. Crohn’s disease initially involves ileum and later involves the whole gastrointestinal system. Crohn’s disease causes diarrhea, pain in the abdomen and fever.
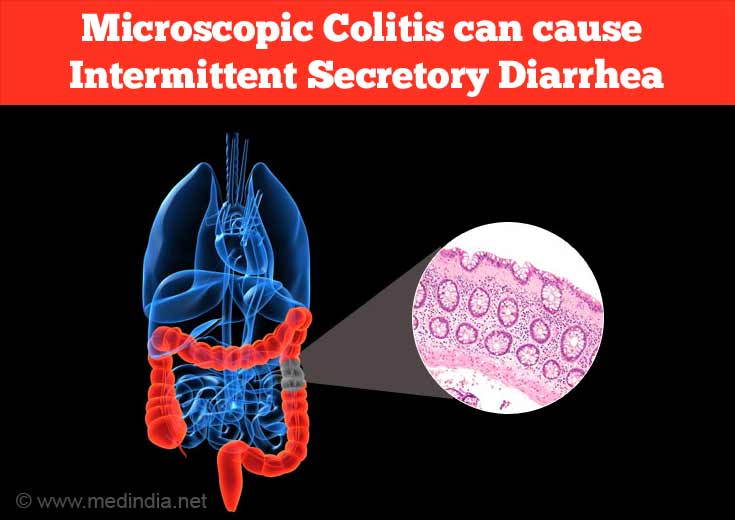
- Microscopic Colitis is due to microscopic inflammation of the colon. It causes intermittent secretory diarrhea.
- Malabsorptive Diarrhea is seen in intestinal malabsorption conditions like celiac disease, Whipple’s disease and mesenteric ischemia. Celiac disease is due to the hypersensitivity of the small intestine to gluten leading to malabsorption. Malabsorption of fat results in greasy, foul-smelling and difficult to flush stools. The patient may suffer from other nutrient deficiencies and weight loss.
- Lactose Intolerance is characterized by an inability of the intestines to digest lactose due to lack of the enzyme lactase. It causes chronic diarrhea, bloating and pain in abdomen. Diarrhea improves on avoiding lactose-containing foods.
Neoplastic Diarrhea
Cancers like colon carcinoma and villous adenocarcinoma can cause diarrhea. The patient may give a history of severe weight loss.
Endocrine Causes of Diarrhea
- Hyperthyroidism: High thyroid hormone levels increase the motility of the gut and cause diarrhea. Other symptoms of hyperthyroidism like increased heart rate, hand tremors and easy fatigue may be noted in these patients.
- Gastrinoma is a gastrin-secreting tumor of the pancreas or duodenum. Increased secretion of gastrin causes excessive release of hydrochloric acid into the gut and increases the gut motility to cause diarrhea. The patient suffers from stomach ulcers which do not respond to treatment.
- VIPoma is a tumor in the pancreas. The tumor secretes excess Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide (VIP) leading to diarrhea. The tumor results in large volumes of watery stools that can cause dehydration and electrolyte abnormalities.
- Addison’s Disease is due to adrenal gland insufficiency. Diarrhea is a common symptom in the patients with Addison’s disease.
- Mastocytosis is a disorder of the mast cells, which are often involved in allergic and inflammatory reactions. Diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting are common in mastocytosis.
- Carcinoid Syndrome is seen when the substances like serotonin and kallikrein produced by a carcinoid tumor are released into systemic circulation. Watery diarrhea is common in carcinoid syndrome. The patient may also experience episodes of flushing, wheezing and breathlessness, and skin lesions.
Surgery-Related Causes
Diarrhea is common among patients after surgeries like gastrectomy (surgical removal of part or all of the stomach), cholecystectomy (gall bladder removal), vagotomy (removing part of the vagus nerve) and intestinal resection. A history of prior surgery is obtained from the patient. The surgical scar may be noted to confirm the cause of the diarrhea.
Other Causes
Diarrhea can also be caused due to anxiety, excess caffeine and alcohol consumption and radiotherapy.