- Eye Pain - (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/nbk216/)
- What Facts Should You Know About Eye Pain? - (http://www.emedicinehealth.com/eye_pain/page2_em.htm)
About
Eye pain usually follows trauma, infection or inflammation of the eye and the surrounding structures.
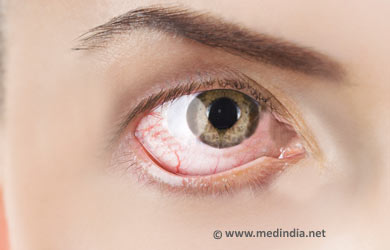
Eye pain is a distressing symptom often described in different ways depending on the cause. The pain arising from the superficial structures of the eye results in burning, or sharp and shooting pain. Pain due to conditions affecting the deeper structures feels like a throbbing, aching or stabbing pain.
The cause of eye pain can be diagnosed to some extent based on the description of the pain by the patient. For example:
- Pain in a single eye could be due to trauma. Pain affecting both the eyes may be due to infection or a systemic disease.
- A sudden onset of severe deep-seated eye pain could indicate glaucoma.
- Eye pain accompanied by purulent discharge indicates bacterial infection.
- Eye pain that is not accompanied by visual symptoms may indicate that the conjunctiva or eyelids are affected. Visual disturbances are usually caused if the cornea or deeper structures are involved.
- Mild pain may accompany a conjunctival infection.
- A history of use of contact lenses could indicate a corneal abrasion or infection.
- Eye pain that occurs in patients with conditions like rheumatoid arthritis may indicate infliction of the eyes by the disease.
In some cases like glaucoma or infection of the deeper structures, it is necessary to identify the cause and treat it early as possible to prevent permanent damage to vision.
Causes
Eye pain could be due to a cause in the superficial structures of the eye, the deeper structures or the structures surrounding the eye.
The causes of eye pain are listed below:
Conditions Affecting The Eyelids And Surrounding Structures: Conditions affecting the eyelids and surrounding structures that result in eye pain include:
- Sty: A sty is an inflammation of a blocked oil gland located at the edge of the eyelids. It causes an obvious lump, which is often red and painful to touch. The pain goes away once the obstruction is relieved.
- Blepharitis: Blepharitis is a condition where the eyelash follicles are inflamed. It causes pain around the eye. The eyelids appear red and irritated with attached scales. They may appear crusty, swollen and itchy.
- Sinusitis: Sinusitis is inflammation and sometimes infection of the sinuses of the face. It usually accompanies a respiratory tract infection and could result in pain around the eye.
- Migraine: Eye pain may occur during attacks of migraine. It is accompanied by other symptoms of migraine like headache, nausea, vomiting and visual disturbances.
Conditions Affecting The Conjunctiva: The conjunctiva is the membrane that lines the eyes and the inner surface of the eyelids. Conditions affecting the conjunctiva that could result in eye pain are:
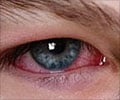
- Conjunctivitis: Conjunctivitis or sore eyes is one of the most common causes of eye pain. Conjunctivitis is a result of a viral or bacterial infection or an allergic reaction of the conjunctiva. Allergic conjunctivitis is associated with more itching than pain.
- Viral Conjunctivitis: Viral conjunctivitis is caused by viruses like adenovirus, herpes simplex virus, enterovirus, varicella zoster virus and Epstein Barr virus. Viral conjunctivitis spreads through direct contact with contaminated fingers or personal items. It is often associated with upper respiratory infection. The eye discharge is usually watery or mucoid. The eye pain in viral conjunctivitis is minimal. However, the pain may be more severe in the case of herpes zoster. In this case, the patient may experience pain in the area of distribution of the affected nerve. The presence of fluid-filled eruptions along the distribution of a nerve helps to diagnose the condition.
- Bacterial Conjunctivitis: Bacterial conjunctivitis is highly contagious and most commonly spreads through direct contact with contaminated fingers. Staphylococcus aureus causes acute bacterial conjunctivitis in adults whereas Streptococcus pneumoniae and H. influenzae are common causes of bacterial conjunctivitis in children. Mild-to-moderate pain with stinging sensation, red eye with foreign body sensation, mild-to-moderate purulent discharge with bilateral glued eyes upon awakening are some of the symptoms associated with bacterial conjunctivitis.
Conditions Affecting The Cornea: The cornea is the transparent surface in front of the eye through which the light enters. Conditions that affect the cornea that cause eye pain include:
- Corneal Abrasions and Ulcerations: Corneal abrasions occur from scratches to the surface of cornea by objects such as foreign body in the eye or contact lens. The abrasions expose nerves, which get stimulated and results in pain every time the patient blinks. Other symptoms of corneal abrasions are red and watery eyes, increased sensitivity to light and a foreign-body sensation. The abrasions could predispose to ulcerations.
- Keratitis: Keratitis or inflammation of the cornea causes severe eye pain. It could result from bacterial or viral infection, or corneal abrasion. It is accompanied by redness of the eye, reduced vision, abnormal sensitivity to light, a mucopurulent discharge and a foreign body sensation.
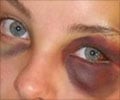
- Trauma: Trauma to the cornea and the deeper structures of the eye could be a result of a direct injury to the eye, contact with a foreign body, or a superficial burn caused by a chemical or intense light such as in welding. The patient complains of a severely painful and red eye with reduced vision when the cornea is involved. Trauma to the surrounding structures results in black eye.
Conditions Affecting The Sclera: The sclera is the white portion of the eye. Inflammation of the sclera can result in eye pain.
- Scleritis: Scleritis is a condition where the white part of the eye is inflamed. It usually occurs due to diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, Wegener’s granulomatosis, reactive arthritis, sarcoidosis, inflammatory bowel disease, syphilis and tuberculosis. The patient complains of severe, boring pain radiating to area around the eyeball. The pain increases with eye movements and is intense at night and upon awakening. In addition, the patient also complains of redness of the eye, watery discharge and increased sensitivity to light.
Conditions Affecting The Deeper Eye Structures: Conditions that affect the deeper eye structures that could give rise to eye pain are:
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma is a condition where the eye pressure is increased. If left untreated, it could lead to defects in vision and even blindness. The eye pain in glaucoma is acute in onset, and severe and throbbing. Other symptoms include blurred vision, halos around lights, nausea and vomiting. In some cases, glaucoma may be painless.
- Iritis: Iritis is an inflammation of the iris or colored part of the eye. It could be a consequence of a perforating wound, a corneal ulcer or autoimmune condition. The patient complains of constant eye pain that develops over hours and radiates to the brow or temple. Other symptoms include redness and watering of eyes, blurred vision and increased sensitivity to light.
- Optic neuritis: Optic neuritis is an inflammation of the optic nerve, the nerve that is responsible for vision. Optic neuritis may occur due to multiple sclerosis, viral or bacterial infections. Besides pain, symptoms include pressure behind the eye and alterations in vision.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which doctor should I visit in case I suffer from eye pain?
You should visit an ophthalmologist in case you suffer from eye pain.
2. When does eye pain indicate a serious problem?
Any eye pain accompanied by visual disturbances should be immediately investigated. Moreover, any eye pain should prompt a visit to the ophthalmologist to prevent any permanent damage to the eyes.
3. Does glaucoma always cause eye pain?
Glaucoma does not always cause eye pain. Open angle glaucoma, a condition where the pressure in the eye increases slowly is usually painless. On the other hand, angle closure glaucoma is associated with a sudden rise in eye pressure resulting in severe pain and blindness if not treated immediately.