- Papier A, Tuttle DJ, Mahar TJ. Differential Diagnosis of the Swollen Red Eyelid. Am Fam Physician. 2007 Dec 15;76(12):1815-1824.
About
Our eyelids are not merely organs meant for fluttering and denoting coyness, but they play a very significant role in protecting the eye. In addition, they also help to distribute tears on the surface of the eyes and maintain a tear film.
The eyelids consist of a thin muscle layer covered by skin on the outer aspect and conjunctiva on the inner aspect. They are supported internally by connective tissue called the tarsal plates. At the edge, they are lined by small hair called eyelashes. Also opening into the edge are small glands.
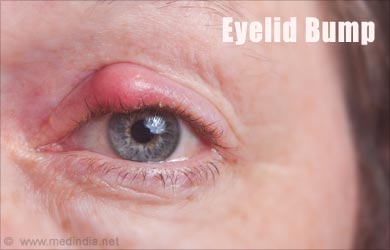
An eyelid bump is usually caused by a localized swelling of one of the eyelid glands. In this article, we will consider the causes of both, eyelid bump and generalized eyelid swelling that result in puffy eyes. A problem with the eyelid could have secondary effects on the eye below and therefore should be treated without delay.
Causes of Eyelid Bump
Causes of eyelid bumps include:
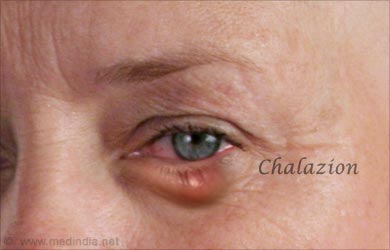
- Chalazion: A chalazion is a small eyelid nodule that arises due to obstruction of one of the eyelid glands called the meibomian gland. The swelling is usually painless, unless it gets infected. It is usually treated with warm compresses and sometimes local antibiotic. Excision may be necessary if it does not respond to medical treatment.
- Hordeolum: A hordeolum, commonly known as stye, is an infection of the eyelid glands by a bacterium that normally results in pus formation, Staphylococcal aureus. The infection may affect a meibomian gland or gland of Zeiss or Moll. It results in a painful swelling at the edge of the eyelid that is filled with pus. The skin over the eyelid is red and inflamed. It is treated with warm compresses and antibiotic drops.
- Viral infections: Viral infections of the eyelid like herpes simplex and herpes zoster may produce small swellings which are often fluid filled. Similar swellings may be present in other parts of the body. They are treated with antiviral medications.
- Malignant Tumors: Cancers that affect the skin like basal cell cancer, squamous cell cancer and melanoma, or those affecting glands like sebaceous carcinoma can also affect the eyelid. Among these, basal cell cancer is the most common cancer affecting the eyelids. Cancers of the eyelid grow and spread rapidly, and may ulcerate.
Causes of Generalized Eyelid Swelling
Causes of generalized eyelid swelling include:
- Allergies: Allergies commonly cause eyelid swelling, giving a puffy appearance to the eyes. The allergy may result due to a local cause or a systemic cause. Allergy to a local cause may be due to eye or face makeup, eye drops or hair dye. A general allergic reaction affecting the body also manifests in the eyelids resulting in swelling. Thus, eyelid swelling may be seen in an anaphylactic reaction, food allergy etc. It may also accompany seasonal conjunctivitis, in which case the underlying condition will be obvious. The eyelid allergy is often accompanied by redness and tearing of the eyes.

- Blepharitis: Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelid margin that may arise due to an infection, dysfunction of a meibomian gland or seborrhea. The eyelid margins are swollen along with scaling or crusting. The patient may complain of burning or itching. It is treated with warm compresses, antibiotics and regular cleaning of the eyelids.
- Ocular rosacea: Ocular rosacea is a condition that results in small swellings and dilated blood vessels over the eyelids. It is usually accompanied by similar features on other parts of the face which makes the condition easy to diagnose.

- Conditions affecting the eye: Conditions that affect the eye are often associated with swelling of the eyelid. These include herpes simplex or herpes zoster ophthalmicus, bacterial or viral infection affecting the eye etc. The eye should therefore be checked for any sign of disease in those individuals presenting with an eyelid problem.
- Cellulitis: Cellulitis is an infection of the subcutaneous tissue. It spreads very fast and should be treated as an emergency. It could follow a surgery, trauma, insect bite, or spread from the neighboring structures. The eyelids are red, swollen and it may be difficult for the patient to open the eye.

- Systemic Disorders: Conditions that affect other parts of the body could produce swelling of the eyelids. These include hypothyroidism, kidney disease, congestive heart failure and angioneurotic edema.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which doctor should I visit in case of swelling of the eyelids?
You could visit an eye specialist or an ophthalmologist for swelling of the eyelids. You may be referred to another specialist depending upon the cause of the swelling.
2. How is swelling of the eyelid diagnosed?
Swelling of the eyelids is diagnosed based on
- Carefully taken medical history of the patient
- Physical examination of the eyelids, eyes, face and other parts of the body
- Diagnostic tests depending on the underlying cause
3. What is the treatment recommended for swelling of the eyelids?
Treatment of the underlying cause is the primary step towards treating eyelid swelling.
- Less serious conditions can be treated with proper eyelid hygiene and local medications.
- Surgery may be recommended in serious and malignant conditions affecting the eyelid.









