- Hoarseness: Frequently Asked Questions - (http://my.clevelandclinic.org/services/head-neck/diseases-conditions/hoarseness-frequently-asked-questions)
- Hoarseness - (http://www.entnet.org/content/hoarseness)
- What is hoarseness? - (https://www.nidcd.nih.gov/health/hoarseness)
- Feieraband RH, Malik SN. Hoarseness in Adults. Am Fam Physician. 2009 Aug 15;80(4):363-370
What is Hoarseness?
Hoarseness is a symptom where you experience a raspy, strained voice along with lowered volume. You may also feel some pain and irritation in your throat. Conditions that affect the larynx or voice box cause hoarseness. The larynx is located in the throat just below the tongue. It contains two muscular bands, whose movement and vibration causes sound.
Hoarseness which lasts more than two weeks without any other underlying cause like viral flu requires immediate investigation. Coughing up blood, problems with swallowing, a lump in the neck, trouble breathing or a total loss of voice warrants emergency treatment by a doctor.

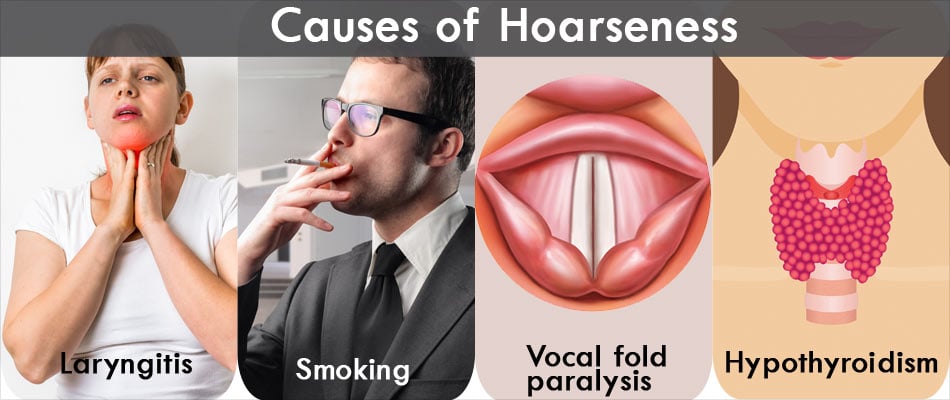
What Causes Hoarseness?
There are several underlying disorders which can cause hoarseness. These include:
- Laryngitis – Laryngitis refers to swelling of the vocal folds. It may occur due to:
Upper respiratory infections like common cold or strep throat. Affected patients also suffer from other symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infections like cough, sinusitis and sore throat. A strep throat can be treated with antibiotics.
Allergies, where the patient may also have symptoms like sneezing, or watery eyes and nose. Allergies are treated with anti-allergy medications e.g. antihistamines
Voice strain from excessive use (for example, in teachers, public speakers, singers and dramatists). The hoarseness in these cases may be due to a bleed into the vocal cords during the moment of screaming. The patients give a history of excessive loud speaking. The doctor may ask then to rest the voice for a couple of days. Some patients may be asked to undergo voice therapy to learn optimal voice modulation.
- Smoking – Smoking is a major cause of change in voice. Prolonged smoking makes the voice hoarse and husky. Quitting smoking usually helps to reduce this type of hoarseness.
- GERD (Gastrointestinal reflux) – GERD causes stomach acids to rise up to the throat irritating the vocal cords and larynx and making the voice hoarse. Since GERD occurs more commonly in the lying down position, the hoarseness is usually worse on getting up in the morning. The hoarseness may or may not be accompanied by heartburn. People experiencing hoarseness due to GERD often feel an obstruction in the throat making them frequently spit. Treating GERD with antacids and other medications usually helps to reduce hoarseness.
- Benign growth – Benign growths like vocal nodules, polyps and cysts on the vocal folds also cause hoarseness. Vocal nodules usually appear in people who strain their voice excessively. These can be diagnosed on examination by the doctor. These can be treated with rest, voice therapy or surgery to remove the unwanted tissue. The removed tissue is sent for pathological examination to rule out cancer.
- Vocal fold paralysis – Vocal cord paralysis is a voice disorder which occurs when the one or both vocal folds do not close or open correctly due to a problem to the nerves that supply the cords. This is usually due to injury to neck or head including following thyroid surgery or certain types of cancers in the neck or head like thyroid cancer. People with neurological disorders like multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease and rare disorders like spasmodic dysphonia also experience vocal cord paralysis. In patients with myasthenia gravis, the hoarseness worsens later during the day. In some cases, a brain stroke also causes vocal fold paralysis.
- Cancers – Certain types of cancers affecting the larynx primarily begin with the symptom of hoarseness. Lymphomas can also begin with this symptom. Thyroid or lung cancer can also spread to the larynx and present with an initial symptom of nagging hoarseness which does not subside.
- Hormonal disorders: Low thyroid hormone (hypothyroidism) levels can cause hoarseness, along with outer symptoms like weight gain, lethargy and puffiness. A blood test for thyroid hormone levels can diagnose the condition. Treatment is with tablets of thyroxine hormone. Acromegaly, a condition due to high growth hormone levels, can also cause hoarseness.
- Other conditions: Other conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, amyloidosis and sarcoidosis can also affect the larynx and cause hoarseness. Other symptoms of these conditions will also be present.
- Trauma to the vocal cords: Trauma of the vocal cords may occur during surgical procedures like endotracheal intubation often used during surgery. In this procedure, a tube is passed into the airways to facilitate breathing. Endotracheal intubation can also cause paralysis of the vocal cords.
- Medications: Inhaled corticosteroids, drugs commonly used to treat asthma, can cause hoarseness of voice. The patient is advised to gargle after every inhalation to prevent local side effects of the medication on the mouth and throat.
Ways to Prevent Hoarseness
- Quit smoking and keep off second hand smoke
- Avoid excess consumption of tea, coffee and other dehydrating agents
- Keep yourself well-hydrated with plenty of tepid water (not cold)
- Protect yourself from pollutants and allergy-causing agents. Use a face mask if possible
- Humidify your home to avoid excess dust
- Avoid rich and spicy foods to keep away acid reflux
- Use a microphone if you need to speak to a large audience
- Never overuse your voice if you are already hoarse







