- What is the digestive system? - (https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/digestive-diseases/digestive-system-how-it-works)
- 5 Foods That Can Increase Your Body Odor - (http://www.nextavenue.org/5-foods-can-increase-your-body-odor/)
- Fingernail Changes in IBS, Gluten Sensitivity and Celiac Disease - (http://celiaccommunity.org/2016/fingernails-ibs-gluten-celiac/)
- Failure to thrive - (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/failure_to_thrive)
- Unexplained Weight Loss - (http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/unexplained-weight-loss/basics/causes/sym-20050700)
- Risk factors for sebaceous gland diseases and their relationship to gastrointestinal dysfunction in Han adolescents. - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18837699)
- Iron Deficiency Anemia - (http://www.giassoc.org/iron-deficiency-anemia.html)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease - (http://www.arthritis.org/about-arthritis/types/inflammatory-bowel-disease/)
- Food Allergy - (https://www.allergyuk.org/food-intolerance/what-is-food-intolerance)
- Struch, F., Schwahn, C., Wallaschofski, H., Grabe, H. J., Völzke, H., Lerch, M. M., Kocher, T. (2008). Self-reported Halitosis and Gastro-esophageal Reflux Disease in the General Population. Journal of General Internal Medicine, 23(3), 260–266.
What is Digestion?
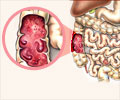
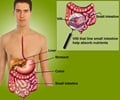
Digestion is the process of breaking down complex food into simpler nutrients that are necessary for body growth, cell repair and energy production. The digestive system includes the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus (including the stomach, small intestine and large intestine) and organs like the liver, pancreas and gall bladder.
Digestion of food takes place in the gastrointestinal tract. When we start chewing the food present in the mouth, the saliva and the food get mixed together to form a substance called the bolus. The amylase in the saliva helps in the breakdown of starch. Swallowing helps the bolus to move to the stomach via the esophagus (food pipe). The stomach secretes gastric juice which has hydrochloric acid and pepsin which can break the proteins in the food. The mechanical food mixing occurs due to the muscle contractions in the stomach, which help in mixing the digestive juices and the food very well. After 1-2 hrs of digestion in the stomach, the digested matter becomes a thick liquid which is called chyme. Chyme is released into the duodenum where the digestive juices from pancreas and liver are released.
The pancreatic juice contains enzymes to break down the fats, proteins and starches. The bile acids released from the liver help in the break down of the lipids. The chyme passes down the small intestine by peristaltic movement or the rhythmic contraction of muscles. When digestion is complete the nutrients are absorbed into the blood vessels in the walls of the small intestine. In the large intestine, the water and minerals are absorbed. Waste products are eliminated by the process of defecation through the anus.
The following are a few uncommon signs of digestive issues.
- Body Odor:
Body odor is the smell due to fermentation of the sweat and oil secreted by the skin glands. It is genetically determined. Some foods also increase body odor. Broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, fish and red meat increase body odor. Impaired food digestion can also cause body odor.
Body odor can be reduced by avoiding foods that enhance it or by parboiling the vegetables in water with sea salt.
- Halitosis (Bad Breath):
Halitosis is a common condition and has around 25% prevalence in the general population. It results in personal discomfort and social embarrassment.
It is often due to infection of the gums, bad oral hygiene, kidney failure, smoking, sinusitis, and eating certain foods like garlic and onions. It is essential to get an appropriate treatment for the underlying condition.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) can also cause halitosis. Anti-reflux treatment should be initiated to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.

- Failure to Thrive:
Failure to thrive is a condition in children where it is difficult to gain weight on par with children in the same age group.
There are many causes for failure to thrive but sometimes digestive issues are also the reasons behind the condition. Digestive issues like celiac disease, cystic fibrosis and parasitic infestation can cause impaired absorption and lead to difficulty in gaining weight.
Necessary investigations followed by appropriate treatment are essential.
- Anemia:
Anemia is a condition where the hemoglobin content in the red blood cells is low. In patients with gastrointestinal disorders, anemia, especially iron deficiency anemia may be present. Iron from the food is re-absorbed in the small intestine. In patients with gastrointestinal problems like celiac disease and Helicobacter pylori infection, iron absorption is impaired.
Iron deficiency anemia can also occur due to blood loss. Treating the cause and supplementing with iron is essential.
- Loss of Weight:
Weight loss can sometimes be due to digestive problems. Celiac disease, ulcerative colitis, peptic ulcer and cholecystitis can cause an unintentional weight loss.
Necessary investigations followed by appropriate treatment are essential.

- Nail Changes:
Nails can sometimes be indicators of digestive health. In patients with digestive issues like celiac disease and irritable bowel syndrome, nail changes are present. Nails may become brittle, flat or spoon like, with white spots, ridges or lines. Nail changes may occur due to impaired absorption of nutrients in patients with digestive issues.
Investigations to find the underlying cause are necessary before providing the appropriate care.
- Food Intolerance:
Food intolerance is a condition where some foods are not digested properly. It can be associated with symptoms like pain in the abdomen, diarrhea or bloating. Enzymes play an important role in the digestion of foods to a simpler form. Deficiency of an enzyme can lead to improper digestion. Deficiency of the enzyme lactase will cause intolerance to milk because the lactose in the milk is not properly digested.
Identifying the food that is causing indigestion is required to avoid unnecessary symptoms from their ingestion.

- Arthritis:
Inflammatory bowel disease is sometimes associated with arthritis known as enteropathic arthritis.
- Acne:
Acne can be associated with gastrointestinal dysfunction. The risk factors associated with acne are age, stress, spicy food, sweet food, constipation, bloating and anxiety. There is also an association between acne and gastrointestinal symptoms like halitosis, constipation, bloating and gastric reflux.
- Early Satiety:
Early satiety means the feeling of fullness after eating only a small amount of food. It presents in people with gastroparesis (paresis of the stomach), duodenal scars, gastric ulcer, gastroesophageal reflux, and gastric cancer.
Finding the underlying cause helps in the treatment of the symptoms and the condition.