- PJ Mehta. Practical Medicine 19th Edition
- Reasons for Gaining Weight Suddenly - (http://www.livestrong.com/article/275657-common-causes-of-weight-gain/)
About
An inadvertent increase in bodyweight indicates weight gain. Necessary care like intake of a balanced diet and adequate physical activity is required to maintain good health and fitness.

Various genetic, physiological and behavioral factors are involved in the regulation of body weight. When the total calorie intake is more than that burnt, the excess nutrients are stored in the adipose or fat tissue, which proportionately increases the body mass and body weight. As we age, our metabolism slows down and the ability of our body to burn down the excessive fat decreases. Hence, regular exercise is necessary to burn the excess energy.
Increase in food intake, intake of wrong foods, and a sedentary lifestyle contribute to unintentional weight gain. Various disease conditions especially endocrinal disorders and certain drugs also cause weight gain.
Obesity is associated with a number of health conditions like heart disease, diabetes and sleep apnea. It is therefore necessary to evaluate unintentional weight gain and treat the cause before the patient proceeds to an obese state.
The causes of unintentional weight gain are listed below:
- Pregnancy: Pregnancy is among the most common causes of weight gain in women. A woman normally puts on 8 to 14kg during pregnancy; this amount of weight gain is considered healthy for the pregnancy. The extra weight is mainly due to the fetus, amniotic fluid, placenta, enlarged uterus and increased blood volume. Lactation after delivery and mild exercise help to lose excess weight.
- Polycystic Ovaries: This condition is caused due to an ovarian dysfunction in women, and results in alteration in the levels of estrogen. The affected woman shows weight gain and irregular menstrual cycles.
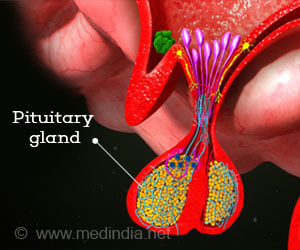
- Hormonal Disorders: Some hormonal diseases that cause weight gain include:
- Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism is a condition where thyroid gland does not produce sufficient amount of thyroid hormone. Deficiency of thyroid hormone decreases the rate of metabolism and results in accumulation of fat and fluid, which contribute to weight gain. Symptoms of hypothyroidism include lethargy, fatigue, decreased sweating, weakness, dry and coarse skin, swelling of face and around eyes and constipation. Blood tests are used to diagnose the condition.
- Cushing's Syndrome: Cushing's syndrome is a disorder that occurs due to the chronic exposure of the steroids. Major symptoms include moon face, upper body obesity with thin legs and arms, slow growth rate in children, repeated infections, buffalo hump and bone tenderness. The condition is diagnosed with blood tests which include ACTH stimulation test, dexamethasone suppression test, blood sugar levels and WBC count.
- Other endocrine disorders: Other endocrine disorders that are associated with weight gain are acromegaly, diabetes, and hypopituitarism. Most of these conditions are diagnosed based on blood tests.
- Heart, Liver and Kidney Failure: Conditions like heart, liver and kidney failure result in accumulation of fluid, which contribute to a sudden weight gain. Conditions that cause weight gain due to accumulation of fluid may be found at the link below:
http://medindia/newmedindia/symptoms/ankle-edema.htm
- Medications and Alcohol: Medications like birth control pills, tranquillizers, antidepressants, corticosteroids, diabetic medications and lithium may result in weight gain. A history of medication intake should be obtained from the person complaining of weight gain. Excessive alcohol intake also results in weight gain.
- Psychological Disorders: Psychological disorders like anxiety and stress cause weight gain. In addition, as mentioned above, medications used to treat psychological disorders are also associated with weight gain. Eating disorders like hyperphagia or polyphagia result in weight gain.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Which doctor should I visit in case I suffer from unintentional weight gain?
You should visit a general physician in case you suffer from unintentional weight gain. Your doctor will diagnose the cause of your weight gain based on your history and after conducting an examination and various tests.
2. Why should you consider unintentional weight gain as a serious problem?
Unintentional weight gain may indicate certain hormonal or metabolic disorders that need to be examined by a physician and treated at the earliest. Increase in weight reduces fitness of the body and leads to complications like heart disease, diabetes and sleep apnea.