Health Checks during antenatal visits
Periodic checks during the antenatal period along with blood and urine tests, help in monitoring the pregnancy and ensure safety of the mother and the baby.
Ultrasound scan of the uterus can show the progress of the baby’s development. The 3-D reconstruction can show the shape of the baby and make it look very real.
THE FIRST VISIT
Weight - Your weight will be taken and weight gain checked regularly at each visit. Majority of women gain about 8-12 kgs during their pregnancy.
During the first three months there is usually very little weight gain and you will put on only 1-2 kgs.
In the next six months however, you should expect to put on a little less than ½ kg a week. This is approximately how the weight gain might be distributed at the end of the pregnancy:
- Amniotic fluid-1 kg
- Baby’s weight – 3 kg
- Blood – 2 kg
- Breasts – 2 kg
- Mother’s body fat (stored for use during breast-feeding period) – 2 kg
- Placenta – 1 kg
- Uterus – 1 kg
If you find that you are losing weight during the first trimester you shouldn’t be alarmed. This is generally because of the vomiting due to Morning sickness. However if you gain a lot of weight suddenly, you should consult your doctor. The cause of this could be several factors from fluid retention to signs of pre-eclampsia.
Blood Pressure – Your Blood pressure will be checked at every visit from the time you are pregnant. The average blood pressure during this time should be 120 over 70. (Blood pressure may vary as it is also dependent on the age of the mother.)
Urine Test – During your first antenatal check up, a sample of urine will be asked. You will be instructed to collect a mid-stream sample. For this you will be required to pass the fist few drops of urine into the toilet bowl and then collect some midstream urine into a sterile container. You can then finish urinating into the toilet.
Doctors will ask the mother to bring a morning sample of urine at every antenatal check- up to ensure a healthy mother and baby.
The urine test is done to examine a few things:
- Sugar (for evidence of diabetes)
- Protein (for evidence of pre – eclampsia or urinary tract infection)
- Pus cells ( to rule out urinary tract infection)
Blood Test – A standard routine of prenatal blood tests are carried out on all pregnant women. A blood sample will be taken and tested. This is to check for:
(1) Blood Group and Rhesus (Rh) Antibodies – A blood test is carried out to determine your blood group, which could be A, B or O and your Rhesus (Rh) blood group ( positive or negative). This is partly for the records, in case a transfusion should ever be needed. If the lab finds you Rh Negative you will be tested for Rh compatibility with your baby.
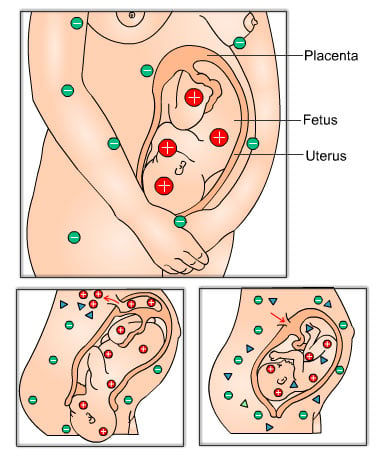
If the child as seen in the picture is Rh positive and the mother Rh negative this can cause rhesus disease.
During the first pregnancy the chances of any problems occurring due to this for the baby are small. However, in case the baby’s Red Blood Cells pass through into the mother’s system during labor then her body will respond by producing anti-Rhesus antibodies. She now becomes Rh Sensitized and carries these antibodies in her immune system for life.
During the mother’s second pregnancy, these anti-Rhesus antibodies will attack and destroy the blood cells of her next Rhesus positive baby. This can cause jaundice, hemolytic disease or mild to possible fatal anemia.
To ensure the safety of future pregnancies, an Anti-D injection (Rh immune globulin) will be given within 48 hours of the birth of the 1st baby.
The Mother can become Rh sensitized usually when the baby’s RBC cross into the mother's system via the placenta. It can also happen –
- Through a fall or accident
- An amniocentesis procedure
- During a miscarriage
- Elective abortion, or ectopic (tubular) pregnancy
- After delivery when the placenta is removed
What are blood groups and RH factor?
Blood Groups are divided into several different types such as A negative, B positive, AB positive or negative, O positive and so on. All these different blood types have red blood cells (RBCs), which help to transport oxygen around the body.
Everyone’s RBCs contain different groups of proteins which are inherited from our parents either outside or inside the cell itself. It is these elements in our Red Blood Cells that act like a thumb print making our blood different from any body else’s.
Rh factor, are groups of proteins which are found only on the surface of the red blood cell. If you fall in this category your blood will be classified as Rh positive. However, if Rh factor is absent from your blood then it is classified as Rh negative.
(2) Total & Differential blood count including Hemoglobin – This is to check whether you are anemic. The normal level of your hemoglobin should be between 12 to 14 grams. If the test shows your hemoglobin level as below 10 grams, you may be given treatment for anemia. It is hence essential to eat a healthy iron rich diet.
(3) Immunity – Immunity to Rubella (German Measles) and Hepatitis B. There will also be checks to see if you have any genetic disorders or sexually transmitted disease such as syphilis. This will help doctors to determine the course of treatment required.
(4) Toxoplasmois Infection: Toxoplasma is a parasite which can be picked up from poorly cooked lamb, pork and the faeces of cats. This infection can be fatal for the baby in the mother’s womb. The infection can cause blindness, epilepsy and development delays in the baby. You would have to ask for this blood test specifically to be taken and it is strongly advised if you have pets in your house.
Height – If you are small usually it may mean that your pelvic inlet and outlet are small. Generally your baby will match your physical build. However, this information is necessary to help with the planning of the delivery of your child.
Breasts – Your breasts are checked for the formation of any Lumps and the conditions of your nipples inspected.
Ultra Sound Scan – This is a routine antenatal test which uses sound waves to build up a picture of the baby in the womb. An ultrasound scan is essential to check on your baby’s position and general well being. It can help to detect many abnormalities, particularly of the head and spine. The scan can be done at any stage of pregnancy, though usually your fist scan is done at about 12/13 weeks and a second scan at 18/20 weeks. All women have an ultrasound scan at least once in their pregnancy.
Your first Ultrasound is an extremely thrilling moment. It will be the first chance for both you and your partner to witness the baby in your womb. The scan will take generally 15 to 20 minutes and is totally pain-free. You may be asked by your doctor to drink approximately a pint of water and come to the clinic on a full bladder. This helps to provide a clearer picture of the baby on the ultrasound monitor as the uterus lies behind the bladder and the water works like a window to see the pregnant uterus.
At the clinic you will be asked to lie down on a bed. Your top half is lifted up and the abdomen is exposed. The doctor will rub an oil or jelly on to your abdomen and the ultrasound transducer is moved over the lower abdomen area. The echoes produced by the sound waves help to form a picture of your baby on the ultrasound machine.
The ultrasound helps doctors to keep an eye on the development of the fetus and warn you of any abnormalities or complications that could be expected during pregnancy. The sex of the baby as well can be determined by this period. However, in certain countries like India the sex of the fetus cannot be disclosed to the parents as per the Indian law and doing so is a punishable offence. This is in order to prevent parents from resorting to a sex- selective abortion.
Cervical Smear Test – This will probably be done if the cervix covering looks abnormal. Otherwise it is usually done during the postnatal check up (check up after the birth of your baby).
You may have an Internal Vaginal Examination.
How often would you need to be checked? - Most women go for three first check-up around the 8th to 12th week of pregnancy. After that, they would need to go every 4-6 weeks until 28 weeks of gestation and then every week until the baby arrives (usually at 40 weeks).
Tests - If the pregnancy is uneventful during all the visits you will have only your weight, blood pressure and urine checked. The abdomen will be felt to check for the baby’s position, growth and heart beat.
Amniocentesis -In this a needle is used to tap some of the amniotic fluid from your pregnant uterus. This test is only done if there is any suspicion of abnormalities in the fetus. This test is not done often. It is only done in certain cases:
- for older women (over 35 years) for whom there is a risk of having a baby with Down’s syndrome.
- when there is a family history of hemophilia, muscular dystrophy or other genetic abnormalities.
- for women whose blood sample has shown a raised level of a substance called alpha feto protein.
Amniocentesis - Surgical Procedures