The Science behind Botox
Botox inhibits the release of the neuro transmitter, acetylcholine, which is responsible for muscular contractions which leads to the formation of wrinkles.
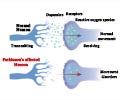
In a normal muscle, the place where a nerve ends is called the ‘muscle- end- plate’. A gap is present between the nerve ending and the muscle surface. The stimulated nerve releases a
So what is the role of botulinum toxins in muscle contraction or in its prevention?
The most significant symptom of botulism is paralysis, which can sometimes prove to be fatal. This is caused when the toxins released by the bacteria attach themselves to the nerve endings and inhibits the release of acetylcholine that is responsible for muscle contraction.
Certain proteins such as VAMP, Syntaxin and Snap-25 are required to bring about the release of acetylcholine. Botox acts by attacking Snap-25, thereby preventing the release of the neurotransmitter. When muscle contraction is inhibited, wrinkling is also prevented.
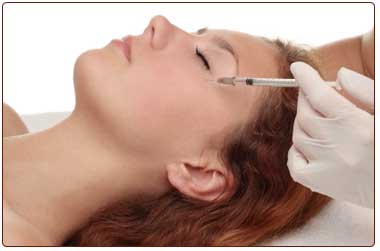
Botox temporarily arrests nerve impulses and paralyses the muscles into which it is injected thereby imparting a smoother, softer and rejuvenated appearance to the skin.