- Drugs Approved for Prostate Cancer - (https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/treatment/drugs/prostate)
- New drugs in prostate cancer - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/pmc4916061/)
- Screening for prostate cancer - (https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/prostate-cancer/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20353093)
- Prostate Cancer Foundation - (https://www.pcf.org/c/treatment-options/)
- Hormone Therapy for Prostae Cancer - (https://www.cancer.org/cancer/prostate-cancer/treating/hormone-therapy.html)
Drugs for Treatment of Prostate Cancer
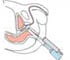
Prostate cancer generally affects elderly men and after skin cancer is the commonest cancer among men. In many instances there are minimum symptoms and the cancer manifests only once it has spread to adjoining areas or other organs. In this situation medical treatment using drugs is advised and there are currently many options depending on the patients and the stage of the disease.
The prostate gland is dependent on the male hormones called androgen for its growth, hence suppressing the hormone can control the growth of the cancer. This may involve using either injections or daily tablets. Most of these injections may require to be given only once in a month or three months or sometimes even at 6 months interval.
There are other therapeutic options which includes drugs that can destroy the cancer cells these are called chemotherapy drugs. These include Docetaxel, Mitoxantrone or cabazitaxel. Usually these are combined with a steroid called prednisone. These drugs are given as injections. Another new drug that can be taken orally called Abiraterone acetate is now approved to be used with prednisone. The drug has shown promising results and has improved the survival of patients with prostate cancer.
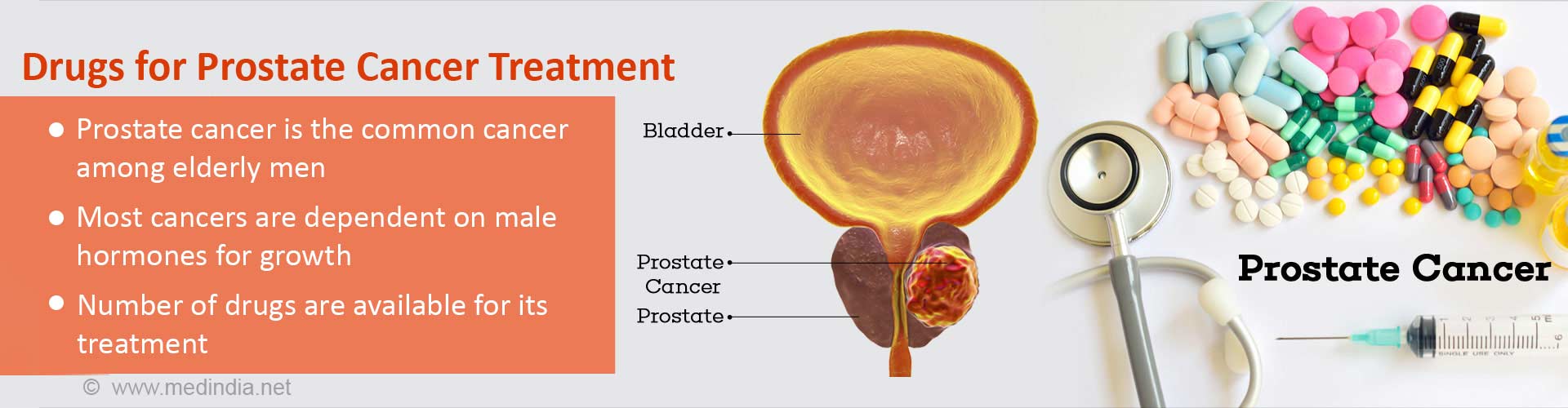
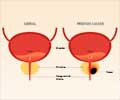
What is Prostate Gland and What are the Symptoms of Prostate Cancer?
The prostate is a small gland in the pelvic region, found in only males. It makes prostatic fluid, which is part of the semen.
Prostate cancer usually develops very slowly and one may not observe any symptoms for many years. In such cases, the individual may not even know he has been suffering from prostate cancer. In its later stages, it may lead to problems during urination, e.g. frequent urination, weak flow, difficulty in passing urine, dribbling of urine and blood in urine.
What are the Treatment Options for Prostate Cancer?
The treatment options for prostate cancer include:
Local treatment:
- Surgery - Surgery involves removal of the prostate gland and surrounding tissue. Surgery may also be used to remove the testes, which produce male sex hormones called androgens
- Radiation therapy - Newer radiation techniques are used which focus the radiation on the tumor and the normal cells are not affected, thereby increasing the effectiveness of radiation therapy and reducing the side effects
Systemic treatments - This involves prescribing drugs for prostate cancer. The drugs could be administered orally, intravenously or topically.
Medications for prostate cancer could be in the form of chemotherapy or hormonal therapy. Generally, hormone therapy is prescribed for advanced stages of prostate cancer. However, the patient stops responding to most hormonal treatments after about a period of 18 months as the cancer progresses to castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) . At this stage of CRPC, chemotherapy is started. Docetaxel is generally prescribed for metastatic CRPC, which has spread to distant sites.
Which Hormone Therapies are Used to Treat Prostate Cancer?
Hormone therapy used in the treatment of prostate cancer is also known as androgen-deprivation therapy. Androgens are male sex hormones which include testosterone and dihydrotestosterone. They play an important role in the normal development of males. However, when prostate cancer develops, the androgens support the tumor growth and proliferation. Hormone therapy is prescribed to stop the body from producing androgens, or block the effect of the androgens. This therapy is used in advanced cancer stages, to shrink the cancer and retard its growth. When prescribed to men suffering from early-stage cancer, hormone therapy help in shrinking the tumor before radiation therapy.
The options of hormone therapy include:
Drugs to lower androgen levels
- LHRH (Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone) agonists - These drugs act on pituitary gland to release LHRH, which reduces the amount of testosterone made by testicles. An initial rise in the testosterone level may be noted. This treatment is also known as chemical castration. The drugs include leuprolide, goserelin, triptorelin and histrelin.
- LHRH antagonist - Degarelix is a drug which blocks the effect of LHRH and reduces testosterone levels without causing an initial rise.
- CYP17 inhibitor - The CYP17 inhibitor prevents the prostate cancer cells and other cells from making androgens by inhibiting the enzyme CYP17. It is prescribed for men with advanced castration-resistant prostate cancer. Abiraterone is the CYP17 inhibitor that is usually administered with an LHRH agonist or antagonist, if the patient has not undergone surgical removal of the testes. Additional treatment with prednisone, a corticosteroid is needed when the patient takes the drug.
Drugs that stop the androgens from functioning - These drugs prevent testosterone from acting on the cancer cells, and therefore limit the growth of the cancer. These include flutamide, bicalutamide and nilutamide.
Enzalutamide is a newer drug under this category. It blocks the effect of the androgen at a point beyond its binding to its receptor or site of action on the cancer cells. It is prescribed for castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Which are the Chemotherapy drugs used to treat Prostate Cancer?
The chemotherapy drugs used to treat prostate cancer include the following:
- Cabazitaxel: Cabazitaxel, an antineoplastic agent, is prescribed along with the corticosteroid prednisone. It is prescribed in patients where disease has progressed in spite of consuming docetaxel.
- Docetaxel: Docetaxel is an anti-cancer agent used for the treatment of breast, stomach, ovarian and prostate cancer. It inhibits the growth and proliferation of cancer cells. It is usually the first chemotherapy drug that is used for the treatment prostate cancer.
- Mitoxantrone: Mitoxantrone was one of the first approved drugs for prostate cancer, however, it is not commonly used.
- Abiraterone acetate: Abiraterone acetate is prescribed in patients who have been previously prescribed docetaxel. It is used alone or with other medications like prednisone.
- Estramustine: Estramustine blocks the cell division of the prostate cancer cells, and has hormonal effects as well.

Which are the Other Drugs used in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer?
Other drugs used in the treatment of prostate cancer include the following:
For prostate cancer that has spread to the bones:
- Bisphosphonates: Bisphosphonates like zoledronic acid are used to treat prostate cancer that has spread to bones. They reduce the bone resorption caused by the prostate cancer, thereby improving bone strength, and reducing pain and the chances of fractures.
- Denosumab: Denosumab is a monoclonal antibody that prevents the formation of osteoclasts, which are involved in bone resorption. This helps in the strengthening of the bones.
- Radium-223, Strontium-89, Samarium-153: These drugs are called radiopharmaceuticals; when administered, they get concentrated on the cancer-affected bone sites and release radiation, which reduces pain caused by the cancer in the bones. They may cause reduced blood counts and symptoms related to the digestive tract like nausea, vomiting and diarrhea.
To reduce pain:
Pain associated with cancer can make life distressing for the patient. Therefore, every attempt should be made to relieve the pain. Acetaminophen and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen, diclofenac or ketorolac may be useful in patients with mild-to-moderate pain. Opioids may be required for more severe pain.
To improve Immunity against Prostate Cancer:
- Sipuleucel-T: Sipuleucel-T is a special type of vaccine used to treat patients with prostate cancer. Certain white blood cells are obtained from the patient, exposed to a protein called recombinant human fusion protein, PAP-GM-CSF, and then reintroduced into the patient. It is used to treat hormone-refractory prostate cancer that causes minimal or no symptoms, but unlike other vaccines, is not useful for the prevention of prostate cancer.
Which are the New Drugs for Prostate Cancer?
Several drugs are under investigation for the treatment of prostate cancer. Some of these include the following:
- Clinical trials with celecoxib, an anti-inflammatory drug, vitamin E and sulindac, are in progress to evaluate their effect on reducing the recurrence of the cancer.
- The traditional chemotherapy treatment has progressed to “smart drugs’, which work at specific molecular level and have minimal side effects. These are under clinical trials at various stages. Trials with imatinib mesylate, a smart drug, are in progress for checking its effect on growth of prostate cancer.
What are the Side effects of Drugs used in Prostate Cancer?
The side effects of prostate cancer drugs depend on the type of drug being administered, the dose prescribed and the length of the treatment.
The common side effects of hormonal treatments include:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Reduced sexual desire
- Depression
- Hot flashes
- Osteoporosis
The side effects of chemotherapy include the following:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Fatigue
- Sores in the mouth and throat
- Hair loss
- Diarrhea
- Blood disorders
- Appetite loss
- Peripheral neuropathy due to docetaxel and cabazitaxel
- Blood clots with estramustine

What Precautions or Health Checks could be recommended before starting Chemotherapy?
The health care provider or oncologist may suggest the following tests and precautions, before administering chemotherapy drugs for prostate cancer.
- Dental checkup – Chemotherapy can cause mouth sores and dry mouth. Hence, it is good to have thorough dental check before starting chemotherapy.
- Echocardiogram (ECG) – Some cancer drugs may cause affect the heart. ECG is recommended to know the state of heart and if the cancer medications can cause further harm.
- Reproductive health – Some anti-cancer drugs can reduce the fertility of men. Hence, if a patient wants children, it is better to inform the same to the healthcare provider. The treatment option would be considered accordingly.
- Blood counts – Chemotherapy affects blood counts; therefore, blood counts should be done at the beginning of the treatment and repeated during treatment.