- Myths and Facts About Hearing Aids - (http://www.asha.org/public/hearing/hearing-aid-myths-and-facts/)
- Hearing Aid Buying Guide - (http://www.consumerreports.org/cro/hearing-aids/buying-guide.htm)
- How to Shop for a Hearing Aid - (http://www.aarp.org/health/conditions-treatments/info-05-2011/getting-the-right-hearing-aid.html)
About
There are various factors that determine the type of hearing aid one requires. The process of hearing aid fitting starts with audiometry, to check the severity and the type of hearing loss. Hearing aids can be classified based on several parameters.
- Style of hearing aid:
Behind-the-ear
In-the-ear
In-the-canal
Completely-in-the-canal
- Type of hearing aid:
Analogue
Digital
Analogue and Digital Hearing Aids:
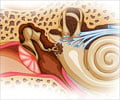
In analogue hearing aids, the sound is picked up by the microphone and converted into electrical signal. This electrical signal is amplified by the amplifier, and the speaker converts these amplified signals into sounds and sends it to the ear through the ear piece. Analogue hearing aids use telecoil that is compatible with the telephone receiver and the induction loop system.
A digital hearing aid has more advanced features. The microphone picks the sound and transmits to the silicon chip. The silicon chip that comprises of millions of electrical components that works together to process the incoming sound according to which it is programmed. The programming of the chip processes sounds of specified frequencies and converts the incoming sound into clearer and more audible sounds. These sounds are then released as specified amplification level into the ear. A digital hearing aid improves the clarity of speech for the user.
Digital hearing aids can be adapted to suit the hearing thresholds of the person with diminished hearing capacity. The volume can be moderated and programmed to filter out wind and other background noises so that speech is received clearly. Modern hearing aids come with Bluetooth that can be synchronized to the smart phone. Telecoils are also found in programmable hearing aids that can be used in some sports and concert venues.
Choosing the Right Hearing Aid
The first step in choosing a hearing aid is to check the hearing ability. Once the correctable or reversible conditions causing the hearing loss is ruled out, the audiologist measures the residual hearing ability in each of the specified frequencies. These thresholds help in programming digital hearing aids.
Recommendations while Consulting a Hearing aid Specialist:
Get a family member or friend to accompany you: A close family or friend will be able to understand the difference in your hearing ability while trying out a hearing aid or adjusting the programmable hearing aid.
Discuss with the specialist: You can discuss certain issues on hearing and ear with the specialist who helps you in choosing the right hearing aid. Some of the topics can be tinnitus (ringing in the ears), vertigo problems, pain in the ears, intolerance to loud sounds, etc.
Try before buying: A few hearing aids can be tried using disposable plugs and you can experience the new sounds and how it works. Try in noisy and quiet environments so that you get the feel of it.
Extra features: Some hearing aids have extra features like Bluetooth, telecoil and directional microphones. These features can be helpful in various situations, but choose them according to your own requirement.
Personalized care: The audiologist can provide a personalized consultation and counseling for the hearing aid. The professional understands how your hearing loss can affect your daily activities. The fitting session includes explanation of how to get accustomed to the hearing aid and its new sounds, how to take care of the hearing aids and the aftercare services.
Factors to be considered while fitting a Hearing Aid:
Amplification required: Based on the residual hearing ability, an audiologist selects a hearing aid type that can provide the required amplification at various frequencies. Digital hearing aids are programmed to amplify sounds at required frequencies.
Hearing aid style: Based on the requirement and personal choice of the user, an audiologist helps to choose among behind-the-ear, in-the-ear or completely-in-the-canal hearing aid types. Dexterity of the user is taken into consideration as the switches and volume control can be too tiny to handle. Some people prefer discreet models for cosmetic reasons and can be guided to get the smaller models. Hearing aids with remote control can be suggested to others.
One or Two hearing aids: Humans have two ears on either sides so that direction of the sounds can be understood. Similarly, if amplification is provided in both ears, the sound are more natural, the wearer experiences better sense of direction, improved understanding of speech in a background noise and a feeling of more balanced hearing ability. Binaural amplification, or amplification in both ears, can help avoid ‘lazy ear’, a condition in which the unused ear tends to deteriorate due to lack of use.
Requirement of an earmold: An earmold is a shoe for directing the receiver tube of a behind-the-ear hearing aid into the wearer’s ear and is custom-made to fit into the shape of the shell of the outer ear. An earmold is made of materials like acrylic and silicon. It is different in terms of shape, size and air vent provision, depending on the personal requirement of the wearer. Earmolds can also be made discreet for the wearer with minimum occlusion of the hollow part of the outer ear, though the hearing aid will be seated behind the ear.
Other lifestyle factors: Hearing aids come with several features like telecoils that help in public places with loop systems, water-proof coatings and add-on plug-in to be connected to public systems. Some hearing aids are ‘set and forget’ types where the wearer has to just use the on-off switches. Hearing aids with remote control can help the senior citizens handle the controls easily. The user can choose these features as per their own requirements.
Brand of hearing aid: Hearing aids are manufactured by various companies that provide service through service centers. So, after sales service is a very important factor while choosing a hearing aid. The user needs to choose a brand that has a service point accessible to his home or work place. Cost of the hearing aid is also an essential factor to be considered.
Steps in Hearing aid Fitting:
1. An audiologist will test the hearing ability.
2. Various hearing aids will be tried on. Digital hearing aids will be programmed to suit the hearing ability.
3. Trial of hearing aids will be done and the best suited model can be selected.
4. An impression of the shell of the pinna and ear canal will be taken. This is to customize the shape of the in-the-ear hearing aids or the earmold in case of behind-the-ear models.
5. Counseling is done about using the hearing aid and its controls, getting accustomed to the sounds and care and maintenance of hearing aids.
6. Follow-up sessions can be scheduled.