- IVF (In Vitro Fertilization) - (https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/treatments/22457-ivf)
- 1 in 6 people globally affected by infertility: WHO - (https://www.who.int/news/item/04-04-2023-1-in-6-people-globally-affected-by-infertility)
- In vitro fertilization (IVF) - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/007279.htm)
- A History of Developments to Improve in vitro Fertilization - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6140213)
- 5 steps of the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process - (https://www.piedmont.org/living-real-change/5-steps-of-the-in-vitro-fertilization-(ivf)-process)
- In Vitro Fertilization - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK562266/)
- Three-Parent IVF: Gene Replacement for the Prevention of Inherited Mitochondrial Diseases - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4005382/)
- In Vitro Fertilization - (https://ivf.org/treatments-and-services/vitro-fertilization-ivf)
About
Since 1978, over 5 million children worldwide have been conceived via IVF (1). Around 17.5% of the adult population – roughly 1 in 6 worldwide – experience infertility.Millions of infertile couples are benefiting from IVF.It would not be an exaggeration to call IVF “A Boon to Mankind” because it has allowed many couples who yearn for a child to become parents.Approximately 10% to 15% of couples have difficulties getting pregnant(1✔ ✔Trusted Source
IVF (In Vitro Fertilization)
Go to source), (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
1 in 6 people globally affected by infertility: WHO
Go to source).
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is the most common form of assisted reproductive technology and is used in the management of infertility. Invitro fertilization (IVF) involves fertilizing an egg with sperm outside the body, in a laboratory setting. Once the egg is fertilized and begins to develop, the resulting embryo is transferred into theuterus(3✔ ✔Trusted Source
In vitro fertilization (IVF)
Go to source).
Of the various options available for the treatment of infertility, none of the treatment procedures have an impact on the society as much as in vitro fertilization. The use of these reproductive techniques has generated tremendous interest, concern, and controversy in the recent years.
Brief History of In Vitro Fertilization
- 1950s-1960s: Early research in IVF began with scientists exploring the fertilization of animal eggs outside the body (in vitro). This set the stage for applying similar techniques in humans.
- 1978: Louise Brown's birth, often referred to as the first "test-tube baby," marked the beginning of successful human IVF reproduction in the United Kingdom.
- 1980s-1990s: Rapid advancements in IVF technology allowed the processbecome more accessible. Methods like embryo freezing, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) and preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD) were developed
- 2000s-Present: With improvements in genetic screening, embryo culture methods, and fertility medications, IVF has continued to develop, increasing success rates and enhancing safety. Millions of people have benefited from it as a common reproductive treatment provided globally(4✔ ✔Trusted Source
A History of Developments to Improve in vitro Fertilization
Go to source).
Indications of IVF
- Bilateral blocked Fallopian tubes
- Severe endometriosis
- Pelvic inflammatory disease with severe adhesion
- Premature Menopause
- Failed reversal of Vasectomy/ Tubectomy
- Obstructive azoospermia
- Genetic diseases
- Menopause
- Surrogacy (Traditional/ Gestational)
- Low sperm count or poor sperm motility
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome or uterine fibroid(6✔ ✔Trusted Source
In Vitro Fertilization
Go to source)
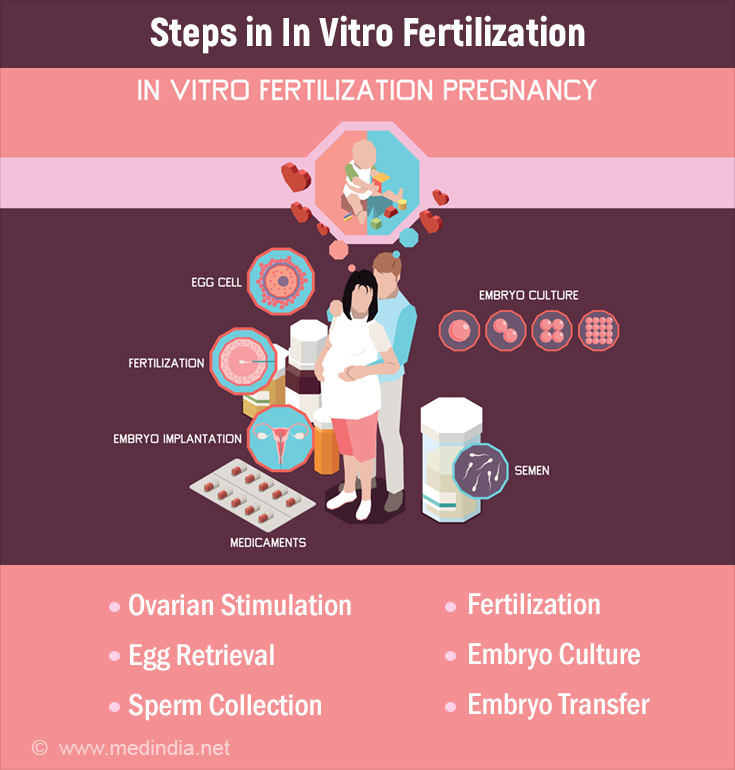
IVF Roadmap: From Oocyte Retrieval to Embryo Transfer
Step #1: Control Ovarian Hyperstimulation (COH)
The prospective mother is treated with gonadotrophic hormones or other forms of fertility medications to induce maturation of the oocyte. The dosage of the drug is adjusted according to age, weight, and development of the follicle(5✔ ✔Trusted Source
5 steps of the in vitro fertilization (IVF) process
Go to source).
The patient is also being monitored by transabdominal ultrasound regarding the development of the follicles. Particular care is taken to ensure that ovulation does not occur before the medical staff are ready for oocyte aspiration.
Step #2: Egg Retrieval
The following preparation is required before oocyte aspiration can be carried out. The patient is asked to fast for 5 hours. Different forms of anesthesia can be used. Shortacting intravenous sedatives and narcotics are popularly used. The vaginal area is cleaned with antiseptics and rinsed with saline to remove potential sources of contamination. Transvaginal ultrasound scan is carried out.
Under ultrasound guidance, oocytes are aspirated from both ovaries. The ultrasound probe is fitted with a needle. This needle pierces the vaginal wall and punctures the follicle. The aspirated follicular fluid is examined under a microscope to identify the oocyte/oocytes. The retrieved oocytes are then washed with appropriate solution and placed in a culture dish containing nutrient fluids. The dish is now kept in the incubator.
Step #3: Semen Preparation
The male partner is required to produce the semen sample at the same time as oocyte collection. Semen can be collected at the hospital or it can be collected at home, provided he will transport it to the hospital within 20 to 25 minutes.Different fluids and different techniques are used in preparing the sample.
Initially, a semen sample is collected and analyzed for sperm count, motility, morphology, and overall quality. The sample is then processed to separate healthy sperm from seminal fluid and other debris.Methods such as the swim-up technique or density gradient centrifugation are used.The processed sperm are concentrated and, if necessary, specific techniques like intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) are used to select a single sperm for injection into an egg. This method ensures that only the highest quality sperm are used, enhancing the chances of successful fertilization.
Step #4:Fertilization and Embryo Culture:
After egg retrieval, the eggs are combined with sperm in a laboratory setting to achieve fertilization.
This can be done by:
- Traditional insemination, where sperm and eggs are mixed and allowed to fertilize naturally, or
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), where a single sperm is directly injected into an egg.
The goal is to produce embryos from the fertilized eggs.In cases of male factor infertility, ICSI may be required, where one immobilized sperm is directly injected into the oocyte.
Embryo Culture:
Once fertilization occurs, the resulting embryos are cultured in a controlled environment within an incubator. The culture medium provides the necessary environment and nutrients for embryonic growth.
After observing the embryos' growth and development for a few days (usually three to five), embryologists evaluate their quality and choose the best ones for either cryopreservation (freezing) or transfer into the uterus.
Step #5: Assessing Embryo Quality
Embryo quality is assessed to determine which embryos can be transferred. On the transfer day, embryos are evaluated and photographed. Based on their development rate and appearance, decisions are made on the number and type of embryos to transfer.
Cleavage Stage (Day 3): Embryos at this stage have 4 to 8 cells. Quality is judged by cell number, symmetry, and fragmentation. Fragmentation occurs when the cells divide unevenly. An embryo with minimal fragmentation is ideal.
Blastocyst Stage (Day 5): The embryos increase in size and are more developed, with an expanded ball of cells and fluid.
A day-five embryo transfer in IVF may lead to quicker pregnancies and fewer miscarriages, while a day-three transfer allows for more embryos to be frozen and may reduce the risk of premature birth.
Step #6:Embryo Transfer
One or two healthy embryos are selected and transferred into the uterus. This is a non-surgical procedure usually performed through the cervix.
More than two embryos are usually transferred to improve the chances of success.
- 2-embryo transfer: 15 % success
- 3-embryo transfer: 25 % success
- 4-embryo transfer: 35 % success
This practice results in many multiple births about 20-25%, compared to just 1 % in the general population. This has raisedconcern about stillbirth, high infant mortality rates and the risk of delivering low birth weight babies.
For each month an attempt is made, only about 10 % eventually end up in a live birth. The major stumbling block in the IVF seems to be the failure of the embryo to implant after transfer to the recipient’s uterus.
Embryo Freezing
Majority of the clinics have now developed techniques for freezing and storing four to eight cell embryos. This also saves the trouble of repeat ovulation trigger and oocyte retrieval.
Freezing also reduces the risk of multiple births, because the physician can transfer just one or two fresh embryos, saving the remainder for successive attempts.
Exploring IVF Options: From Conventional to Advanced Techniques
Conventional IVF
This method involves using medications to generate a higher number of eggs. The eggs are fertilized with sperm in a laboratory dish, and the resulting embryos are transferred to the uterus. Conventional IVF is often recommended for women over 35, those with unexplained infertility, or those with blocked or damaged Fallopian tubes.
Natural Cycle IVF
In this approach,eggs are collected during a woman’s regular menstrual cycle without using stimulating medications. It is suitable for women who are still ovulating and prefer to avoid the use of fertility drugs and other complex treatments
Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI)
A single sperm is injected directly into an egg, typically used in male infertility issues.It is the type of IVF usually preferred when a man has a very low sperm count or poor sperm motility. In ICSI, a single chosen sperm is carefully injected into the selected egg for the IVF procedure.
Minimal stimulation IVF
Also known as mini-IVF or micro-IVF, this method uses lower doses of fertility medications to produce fewer but higher-quality eggs. The approach is similar to conventional IVF but with reduced stimulation.
Assisted Embryo Hatching
Assisted hatching is performed during an IVF cycle before the embryo transfer on day 3. An embryologist uses a laser to thin the zona pellucida (the outer layer of the embryo) to help the embryo break through its shell more easily and implant in the uterus(8✔ ✔Trusted Source
In Vitro Fertilization
Go to source).
Donor Egg IVF
In donor egg IVF, eggs from a donor are fertilized and transferred into the recipient’s uterus, when the recipient cannot produce viable eggs herself. The donor undergoes ovarian stimulation and egg collection, after which donor eggs are fertilized with the male partner’s sperm. The resulting embryos are then transferred into the recipient’s womb. This approach often has a higher success rate, approximately 60 percent, due to the use of younger, high-quality donor eggs.
Three-parent IVF
It is an advanced reproductive technique designed to prevent the transmission of certain genetic disorders from mother to child. It involves the use of DNA from three individuals: the mother, the father, and a healthy female donor. The technique replaces defective mitochondrial DNA in the mother's egg with healthy mitochondria from the donor's egg.The resulting embryo carries nuclear DNA from the mother and father, but has healthy mitochondrial DNA from the donor, reducing the risk of mitochondrial diseases(7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Three-Parent IVF: Gene Replacement for the Prevention of Inherited Mitochondrial Diseases
Go to source).
Frozen Embryo Transfer (FET)
Embryos from a previous IVF cycle are frozen and later thawed for transfer into the uterus.
Preimplantation Genetic Testing (PGT)
Embryos are genetically screened for abnormalities before being transferred, helping to prevent genetic disorders.
Facts About Invitro Fertilization
- Egg quality is often more important than quantity for successful IVF.
- Advanced techniques like time-lapse imaging helps to select the most viable embryos for transfer.
- Lifestyle factors such as diet and weight significantly influence IVF success rates.
- Children conceived through IVF generally do not facelong-term health risks.
- Natural Cycle IVF uses the body’s ovulation cycle without hormonal stimulation, though success rates are lower.
- Cultural attitudes toward IVF vary widely, impacting its acceptance in different societies.
- IVF can facilitate surrogacy arrangements for individuals or couples.
- Laws regulating IVF practices differ by country, affecting embryo transfer and donor use.
- Many clinics offer mental health support to help couples cope with the emotional challenges of IVF.
- It is possible to select embryos of a specific gender before implantation.
- Genetic testing of embryos can be done to prevent the transmission of certain genetic disorders.
- IVF can be used to preserve fertility for individuals undergoing medical treatments like chemotherapy or those who wish to delay childbearing for personal reasons.IVF is not limited to heterosexual couples. It is an option for same-sex couples and individuals who wish to become parents, often involving the use of donor eggs or sperm.
Myths vs Fact About IVF
1. Myth: IVF is a guarantee of pregnancy.
Fact: IVF increases the chances of pregnancy but does not guarantee success. The success rate depends on various factors, including age, overall health, and the quality of the embryos.
2. Myth: IVF is only for older women or those with severe fertility issues.
Fact: IVF can be used for various fertility issues, including male factor infertility and age-related factors. It is not limited to older women.
3. Myth: IVF treatments are always successful on the first try.
Fact: Success rates for IVF vary, and it may take multiple cycles for a successful pregnancy. The process can be different for each individual or couple.
4. Myth: IVF can lead to multiple births in all cases.
Fact: While IVF can increase the chance of multiple births due to the transfer of multiple embryos, many IVF pregnancies are single births. Advances in IVF techniques have also reduced the incidence of multiple births.
5. Myth: IVF will always result in a child with health problems.
Fact: The majority of children born through IVF are healthy. However, some studies suggest a slightly increased risk of certain conditions, but this risk is generally small.
6. Myth: IVF is a one-time procedure.
Fact: IVF often involves multiple steps, including ovarian stimulation, egg retrieval, fertilization, embryo culture, and transfer. It may require several cycles to achieve pregnancy.