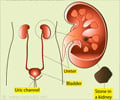
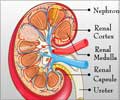
Diagnosis
The following are the methods by which kidney stones are diagnosed-
- Medical history and physical examination of the patient
- Urinalysis to evaluate the presence of blood or micro organisms in the urine
- Blood tests for complete blood count and to check for creatinine and calcium levels
- Ultra sound can be done but is not sensitive enough to pick up small stones. It is usually the first radiological investigation and the preferred method for pregnant woman.
- Abdominal X-ray helps to obtain images of the urinary system and to identify a kidney/urinary stone. This test is not completely reliable.
- Intravenous Pyelogram or Urogram (IVP or IVU ) can be carried out to precisely locate kidney stones. The procedure is done by injecting a contrast medium intravenously and by taking a series of X-rays to detect the blockage. Some patients may be allergic to the contrast medium or the dye.
- Plain non-contrast spiral computerized tomography (CT) scan uses X-ray beams to produce two-dimensional images of body organs. It can detect small kidney stones that cannot be revealed by ordinary X-rays or the usual CT scans.
CT urogram- like in IVU, a contrast medium containing iodine is injected intravenously into the patient and a CT scan of the kidneys, bladder and ureters is taken. This test which is done rarely, helps to study the functioning of the kidneys.