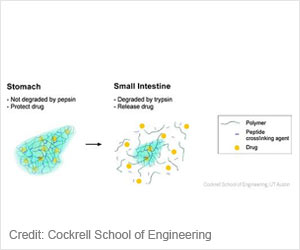
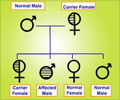
Hemophilia B is a rare single gene disorder. It is also known as Factor IX deficiency or Christmas disease. This disorder tends to run in families for generations as it only affects males because it is X- linked disorder (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hemophilia B: Medlineplus
Go to source).
Due to the deficiency of an important clotting factor called factor IX, blood clot formation following an injury may not be proper, and so following an accident, hemophiliacs can suffer from excessive bleeding, as it takes longer to heal, in comparison to normal individuals.