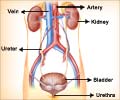
What is Bladder Cancer?
Bladder cancer occurs when there is abnormal cell growth in the urinary bladder. About 90-95% of the cancers begin from the inner lining of the bladder (urothelium or transitional epithelium) and hence they are known as urothelial or transitional cell carcinoma (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Bladder Cancer
Go to source).
Bladder Cancer Facts
Statistics on Bladder Cancer
- About 75 percent of bladder cancer cases are detected in the superficial stage. One-third when the cancer is in the deeper layers but still within the bladder and the remaining only when it has spread to other tissues and lymph nodes (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Superficial Bladder Cancer
Go to source). - Cancers detected after they have spread to distant parts of the body comprise only 4% of the total bladder cancers.