What is Pneumonia?
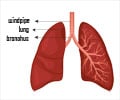
Pneumonia is a lung infection that can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi. It causes inflammation in the lung’s air sacs, which can swell with fluid, making it difficult to breathe.
The symptoms and signs of pneumonia are chest pain, cough, fatigue, fever, nausea, vomiting, shortness of breath, confusion, and changes in the mental health (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pneumonia
Go to source).
Facts on Pneumonia
The importance of Pneumonia as a major health concern may be gleaned by the following facts about this disease.
Pneumonia Statistics
- Worldwide, it is the leading cause of mortality in children under age of 5, accounting for 14% of deaths in this age group. In the US, it is the primary cause of hospital admissions among children (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pneumonia in children
Go to source). - Over 1,400 cases of pneumonia per 100,000 children occur every year worldwide. Where South Asia (2,500 cases per 100,000 children) and West and Central Africa (1,620 cases per 100,000 children) are the greatest incidence (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Pneumonia
Go to source). - An estimated 18 million more health workers are needed by 2030 to prevent, diagnose, and treat pneumonia and also to reach the development goal targets (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Pneumonia
Go to source). - Around 2 billion children aged 0-17 years are live in areas where outdoor air pollution exceeds international guideline limits (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
About Pneumonia
Go to source). - Around 24% of adults aged over 18 who were received a pneumococcal vaccination (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Information About Pneumonia
Go to source). - In the United States, pneumococcal pneumonia causes 150, 000 hospitalization every year (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pneumococcal Disease
Go to source). - Children under the age of 5 and those aged 5 to 18 years should receive PCV13 or PCV15. Also, children aged 2 to 18 years should receive PPSV23 (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pneumococcal Disease
Go to source). - Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) and CURB-65 are the most commonly used clinical scoring tools for severity assessment and mortality prediction of pneumonia (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Prognostic factors for mortality due to pneumonia among adults from different age groups in Singapore and mortality predictions based on PSI and CURB-65
Go to source).
History of Pneumonia
- Hippocrates gives a written account of pneumonia in approximately 460-370 BC. He calls the old disease 'peripneumonia' and describes its recognizable symptoms (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Know More About Pneumonia
Go to source).
Risks of Pneumonia
- Individuals hospitalized for other illnesses are also at risk of developing pneumonia. This is due to the fact that they may be already immunocompromised, and the hospital environment is a breeding ground for various organisms. Such infections are termed nosocomial or hospital acquired infections (8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hospital-Acquired Infections
Go to source). - The elderly have a higher risk of developing pneumonia, due to their weakened immune systems, and presence of chronic underlying conditions such as heart disease and diabetes. They are also less likely to realize that they have pneumonia and seek medical attention, before it is too late and the infection has spread to other parts of the body (9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Community-acquired pneumonia in elderly patients
Go to source). - Among the elderly, hospitalization for pneumonia is associated with a higher mortality rate compared to other admission reasons.
- Interestingly, viral pneumonia is the leading cause of hospitalization of infants. In fact, the WHO has allotted top priority for development of newer drugs and vaccines for these pneumonia, that by and large don’t have any drugs or vaccines that can be used.
Advertisement
Outbreak of Pneumonia
- Recently, emerging infections such as avian flu epidemics and pandemics, severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), coronavirus, Middle Eastern Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) are also associated with pneumonia. Environmental reservoirs such as Legionella can cause localized outbreaks. Anthrax, considered a bio-weapon can also cause pneumonia (10✔ ✔Trusted Source
Emerging respiratory infections: The infectious disease pathology of SARS, MERS, pandemic influenza, and Legionella
Go to source).
Treatment for Pneumonia
- The rapid emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains poses a significant challenge for effective pneumonia treatment, primarily due to the widespread misuse of antibiotics. This has occurred largely due to misuse of antibiotics, both in the community as well as the hospital setting. There is an urgent need for the development of newer and more effective antibiotics to combat this situation (11✔ ✔Trusted Source
Antibiotic resistance
Go to source).