|
Drugs and Non-Communicable Diseases (NCDs)  In 7 member countries, kidney dialysis, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are available in public health system. Nicotine replacement and oral morphine are least available. In 7 member countries, kidney dialysis, radiotherapy and chemotherapy are available in public health system. Nicotine replacement and oral morphine are least available.Health Financing  Through a government annual budget, fund allocation is needed for NCD prevention and control; all member countries have such allocation. Through a government annual budget, fund allocation is needed for NCD prevention and control; all member countries have such allocation. Except Maldives and Sri Lanka in all other member countries government revenue is the main source of funding for NCD management. International donors are helping to these 2 countries. Except Maldives and Sri Lanka in all other member countries government revenue is the main source of funding for NCD management. International donors are helping to these 2 countries.Trends in smoking prevalence and excise tax, Thailand, 1990-2010 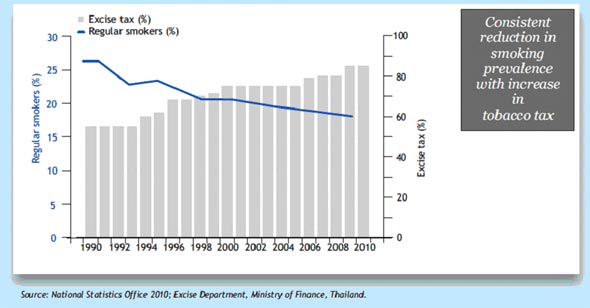  Revenue from tobacco through “sin tax” and alcohol is used for health promotion in Thailand. Revenue from tobacco through “sin tax” and alcohol is used for health promotion in Thailand. The main funding source in India is out of pocket expenditure. The main funding source in India is out of pocket expenditure. Funding covers treatment, control, prevention, health promotion, surveillance, monitoring and evaluation. Funding covers treatment, control, prevention, health promotion, surveillance, monitoring and evaluation. Only in 5 countries health insurance is available for NCD management. Only in 5 countries health insurance is available for NCD management.  Sri Lanka and Thailand have full insurance coverage for whole population. In India it is only 20% and in Indonesia and Maldives it is estimated to be 20%–50%. Sri Lanka and Thailand have full insurance coverage for whole population. In India it is only 20% and in Indonesia and Maldives it is estimated to be 20%–50%. In DPR Korea, Myanmar, Thailand home care is available for people who are affected by end stage diseases. In DPR Korea, Myanmar, Thailand home care is available for people who are affected by end stage diseases.Partnerships and Collaboration  Either other sectors involvement or integration with health sector will be very useful for people to choose appropriate choice to get better healthcare. Either other sectors involvement or integration with health sector will be very useful for people to choose appropriate choice to get better healthcare. NCD prevention and control have to be multisectoral and multidisciplinary and should act at multiple levels. NCD prevention and control have to be multisectoral and multidisciplinary and should act at multiple levels. Through appropriate mechanisms, private sector helps to determine the consumption of tobacco, alcohol and dietary items. Through appropriate mechanisms, private sector helps to determine the consumption of tobacco, alcohol and dietary items. In member countries, governments are proceeding to establish intersectoral coordination mechanism. In member countries, governments are proceeding to establish intersectoral coordination mechanism. As per report, for implementing key activities related to NCDs, member countries have partnerships or collaborations between various departments or sectors. As per report, for implementing key activities related to NCDs, member countries have partnerships or collaborations between various departments or sectors. Cross-departmental or ministerial committees and interdisciplinary committees are the key mechanisms used for such collaboration. Cross-departmental or ministerial committees and interdisciplinary committees are the key mechanisms used for such collaboration. |
| Stakeholders Involvement | |
| Number of Countries | Agency Type |
| All countries | Government Ministries |
| Except Indonesia | UN agencies |
| 9 Countries | International agencies |
| 10 Countries | Academic institutions and nongovernmental organizations |
| 8 Countries | Private Sector |
Subscribe to our Free Newsletters!