Last Updated on Dec 01, 2023
Endocrine Glands
-
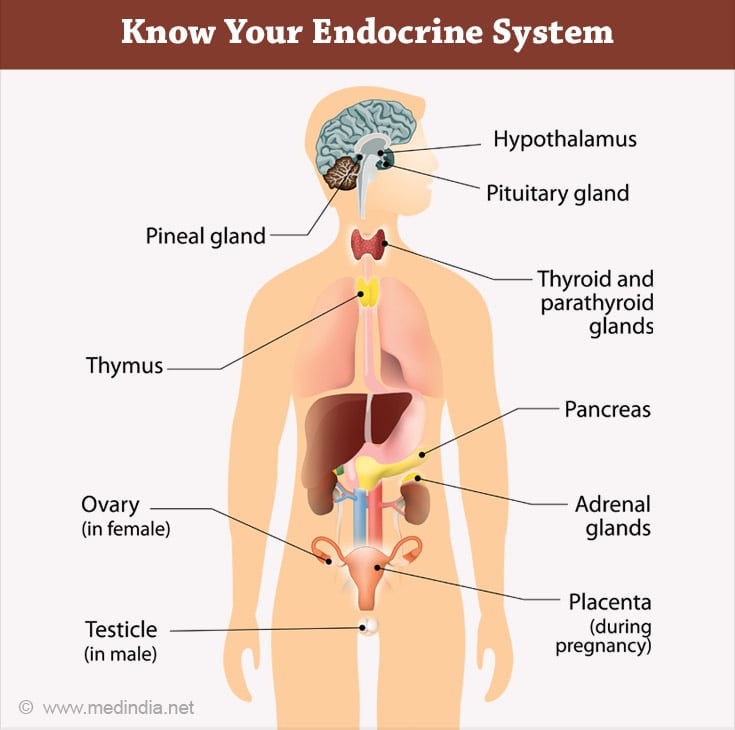
The major endocrine glands in the human body are the pineal, pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, thymus, adrenals, pancreas, ovaries (female), and testes (male).
Hormones
-
The human body contains 50 amazing hormones, which regulate activities like sleep, body temperature, hunger, growth and development, and managing stress in times of crisis (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Overview of the Endocrine System
Go to source). -
The term "hormone" was introduced in 1905, and "endocrinology" was introduced in 1909 (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Emergence of the concept of endocrine function and endocrinology
Go to source).
Neuroendocrine System
-
The endocrine system works together with the nervous system to regulate growth, reproduction, and metabolism. They are called the neuro endocrine system (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Endocrine disorders and the neurologic manifestations
Go to source).
Stress and Hormones
-
The endocrine system produces cortisol and other steroid hormones that help the body respond to stress (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Stress Reaction
Go to source). -
Physical and emotional stress causes the endocrine system to produce more hormones.
Hormones of the Hypothalamus
-
The hypothalamus produces hormones that help to regulate body temperature, heart rate, sleep, sex drive, hunger, and thirst (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Hypothalamus
Go to source). - Hormones secreted by the hypothalamus are gonadotropin-releasing hormone, growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), oxytocin, somatostatin, corticotropin-releasing hormone, vasopressin, dopamine, and thyrotropin-releasing hormone.
Ductless Gland
-
The endocrine glands do not have any ducts and transfer hormones directly into the bloodstream. They are referred to as the ductless glands.
Pituitary Gland
-
The pituitary gland is a small, pea-sized gland located at the base of the brain and controlled by the hypothalamus (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Pituitary Gland
Go to source). - The pituitary gland is referred to as the body’s master gland as it controls the activity of most other hormone-secreting glands (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Pituitary gland and hormones
Go to source).
Pancreas
-
The pancreas is a small organ that has both exocrine and endocrine functions. It helps with digestion and regulates blood sugar.
Advertisement
Thyroid Gland
-
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located in the lower part of the neck (8✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Exocrine Gland
Go to source). -
Thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin are the hormones produced by the thyroid gland (9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Histology, Thyroid Gland
Go to source). -
Iodine is an essential element for the production of thyroid hormones (10✔ ✔Trusted Source
The role of iodine in human growth and development
Go to source). -
Thyroid function will decrease with age (11✔ ✔Trusted Source
Hypothyroidism in the older population
Go to source).
Adrenal Gland
-
The adrenal gland is a small, triangular-shaped gland found on both sides of the kidney. This gland is composed of two parts: the medulla and the cortex (12✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Adrenal Gland
Go to source). -
Adrenal hormones help regulate the immune system, blood pressure, metabolism, and the body's salt and water balance.
-
Adrenaline or epinephrine is a hormone produced by the adrenal glands that plays a vital role in the fight or flight response.
Pineal Gland
-
The pineal gland is a small, tiny cone-shaped gland located in the center of the brain. It is also known as the "Seat of the Soul" and the "Third Eye" (13✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology of the Pineal Gland and Melatonin
Go to source). -
Melatonin is a natural hormone produced by the pineal gland that helps control the circadian cycle of sleep and wakefulness (14✔ ✔Trusted Source
Melatonin, the Hormone of Darkness: From Sleep Promotion to Ebola Treatment
Go to source).
References:
- Overview of the Endocrine System - (https://www.epa.gov/endocrine-disruption/overview-endocrine-system)
- Emergence of the concept of endocrine function and endocrinology - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15492974/ )
- Endocrine disorders and the neurologic manifestations - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4316409/ )
- Physiology, Stress Reaction - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541120/)
- Physiology, Hypothalamus - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535380/)
- Physiology, Pituitary Gland - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459247/ )
- Pituitary gland and hormones
- (https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/pituitary-gland#)
- Physiology, Exocrine Gland - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542322/)
- Histology, Thyroid Gland - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31869123/#)
- The role of iodine in human growth and development - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21802524/)
- Hypothyroidism in the older population - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6367787/)
- Physiology, Adrenal Gland - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK537260/ )
- Physiology of the Pineal Gland and Melatonin - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK550972/)
- Melatonin, the Hormone of Darkness: From Sleep Promotion to Ebola Treatment - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4334454/)