Last Updated on Dec 21, 2023
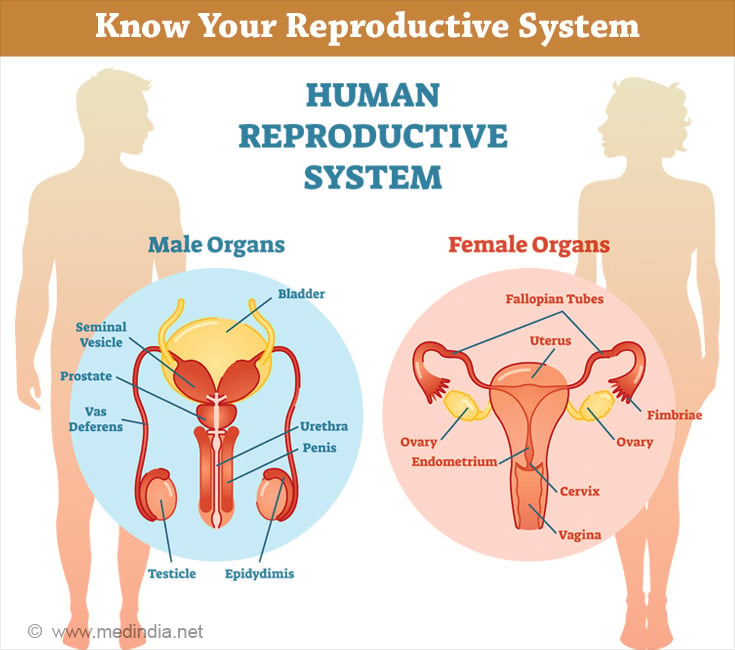
Female Reproductive Organs
-
The female reproductive organs include the vagina, uterus, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and external genital organs.
Male Reproductive Organs
-
The male reproductive organs include the penis, testicles, epididymis, vas deferens, and prostate gland (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Review: Introduction to the Reproductive System
Go to source).
Smallest and Largest cell
-
The ovum is the largest cell in the human body, with a diameter of 0.1 mm.
-
The sperm is the smallest cell in the human body (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Molecular Biology of the Cell
Go to source).
Lifespan of an Ovary
-
Female ovaries contain about 1-2 million eggs at birth, but only 300,000 ovaries make it to puberty (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Biological versus chronological ovarian age: implications for assisted reproductive technology
Go to source). -
An egg can have a lifespan of 12-24 hours after it is released from the ovary, while a sperm can have a lifespan of 36 hours (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Natural methods of family planning
Go to source).
Sperm Production
-
A healthy male testes can produce around 500 million sperm cells daily, and these testes can also release up to 75 million or more sperm cells during an ejaculation (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Semen analysis
Go to source). -
The process of sperm production (spermatogenesis) requires an optimal temperature that is around 2-3 ºC lower than the normal human body temperature; this is why the scrotum, which contains testicles, is present outside the body (6✔ ✔Trusted Source
The process of spermatogenesis liberates significant heat and the scrotum has a role in body thermoregulation
Go to source).
Advertisement
Male Hormone
-
Androgens are the hormones that are responsible for 'manly' characteristics in men. A deep voice, body hair, height, and muscle mass are some of these characteristics (7✔ ✔Trusted Source
Androgens and hair growth
Go to source).
Sexual Function
-
Alcoholism, smoking, and drug abuse greatly reduce sexual function, while exercise and a healthy diet can improve it (8✔ ✔Trusted Source
The risk of sexual dysfunction associated with alcohol consumption in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Go to source).
Ovulation
-
Ovulation is the process by which a mature egg is released from one of the ovaries during the menstrual cycle.
-
Ovulation usually occurs once a month, about two weeks before the start of next menstural period.
Fertilization
-
A zygote is a fertilized egg cell that is formed by the fusion of both the sperm and the ovum (9✔ ✔Trusted Source
Embryology, Week 1
Go to source). -
Fertilization is mostly possible when the female is in the middle of her menstrual cycle. This is when the hormones promoting pregnancy are at their peak (10✔ ✔Trusted Source
Menstrual Cycle Proliferative And Follicular Phase
Go to source).
Female Uterus
-
A female uterus is about 3 inches long and 2 inches wide normally, but during pregnancy, the uterus can expand up to 20 times its normal size. The uterus contains one of the strongest muscles in the female body (11✔ ✔Trusted Source
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Uterus
Go to source). -
Fallopian tubes are about 12 cm long and only as wide as a sewing needle (12✔ ✔Trusted Source
Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Fallopian Tube
Go to source). -
The cervix is a small, cylindrical, and conical canal that can be referred to as the “neck of the uterus.” (13✔ ✔Trusted Source
Physiology, Uterus
Go to source)
Pregnancy
-
At 8 weeks of pregnancy, vital organs like the brain, heart, skin, and stomach are all developed within the embryo, measuring only an adult’s thumb (14✔ ✔Trusted Source
Fetal Development: Week 8
Go to source)
References:
- Review: Introduction to the Reproductive System
- (https://training.seer.cancer.gov/anatomy/reproductive/review.html)
- Molecular Biology of the Cell - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK26914/)
- Biological versus chronological ovarian age: implications for assisted reproductive technology - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2764709/)
- Natural methods of family planning - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/3091823/)
- Semen analysis - (https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003627.htm)
- The process of spermatogenesis liberates significant heat and the scrotum has a role in body thermoregulation - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17011725/)
- Androgens and hair growth - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18844710/)
- The risk of sexual dysfunction associated with alcohol consumption in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10155345/ )
- Embryology, Week 1 - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK554562/)
- Menstrual Cycle Proliferative And Follicular Phase - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542229/)
- Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Uterus - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470297/)
- Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis: Fallopian Tube - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547660/)
- Physiology, Uterus - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557575/)
- Fetal Development: Week 8 - (https://www.michigan.gov/mdhhs/adult-child-serv/informedconsent/michigans-informed-consent-for-abortion-law/procedures/fetaldevelopment/fetal-development-week-8# )
Advertisement