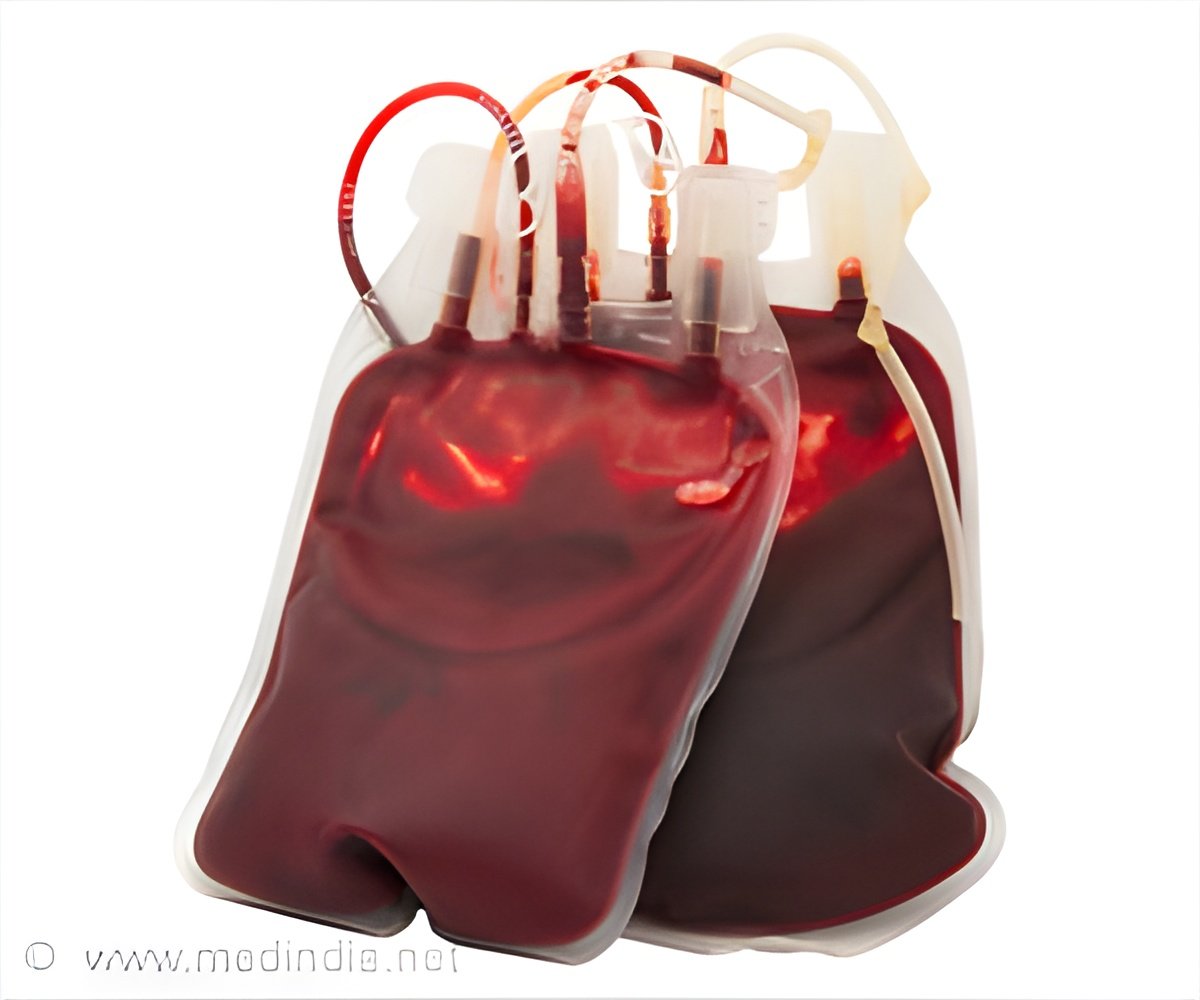
In Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh, where 14 children, who were undergoing blood transfusions, have tested positive for infections like Hepatitis B, C, and HIV.
‘A group of 14 children, ranging in age from 6 to 16, who underwent blood transfusions for thalassemia, have been found to test positive for both HIV and hepatitis infections. #bloodtransfusion #HIV #hepatitis #blooddisorder’





Arun Arya, head of pediatrics department at LLR and nodal officer for this centre, said this is a cause for concern and shows the risks blood transfusion involves.“We have referred the hepatitis patients to the gastroenterology department and the HIV patients to the referral centre in Kanpur,” he said.
Regular Screening and Blood Transfusions for Thalassemia Patients in Focus
At present, 180 thalassemia patients receive blood transfusion at the centre, which screens each of them every six months for any viral diseases.The 14 children had received blood transfusions at private and district hospitals, and in some cases locally, when they required it urgently.Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder caused when the body does not make enough of hemoglobin, an important part of red blood cells (1✔ ✔Trusted Source
Thalassemia
Go to source). It is a treatable disorder that can be managed with blood transfusions and chelation therapy. Arya said the blood transfusion took place during the window period.
“This seems to be the case because the children are already battling a serious issue and are now at a greater health risk.”According to him, when someone donates blood, the blood is tested to make sure it is safe for use. However, there is a period of time after someone was infected when the virus could not be detected by the tests -- this is called the “window period”.“At the time of transfusion, the doctors should have vaccinated the children against Hepatitis B,” he added.
The 14 children are aged between the ages of 6 and 16, are among the 180 patients. Of the infected children, seven tested positive for Hepatitis B, five for Hepatitis C and two for HIV, said Arya. The children come from different parts of the state, including Kanpur City, Dehat, Farrukhabad, Auraiyya, Etawah and Kannauj.
“District-level officials will trace the root of infection under the Viral Hepatitis Control Programme. The team will look for the place of infection, both for hepatitis and HIV,” said a senior official of the Uttar Pradesh National Health Mission.
Advertisement
- Thalassemia - (https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/thalassemia/index.html)
Source-IANS