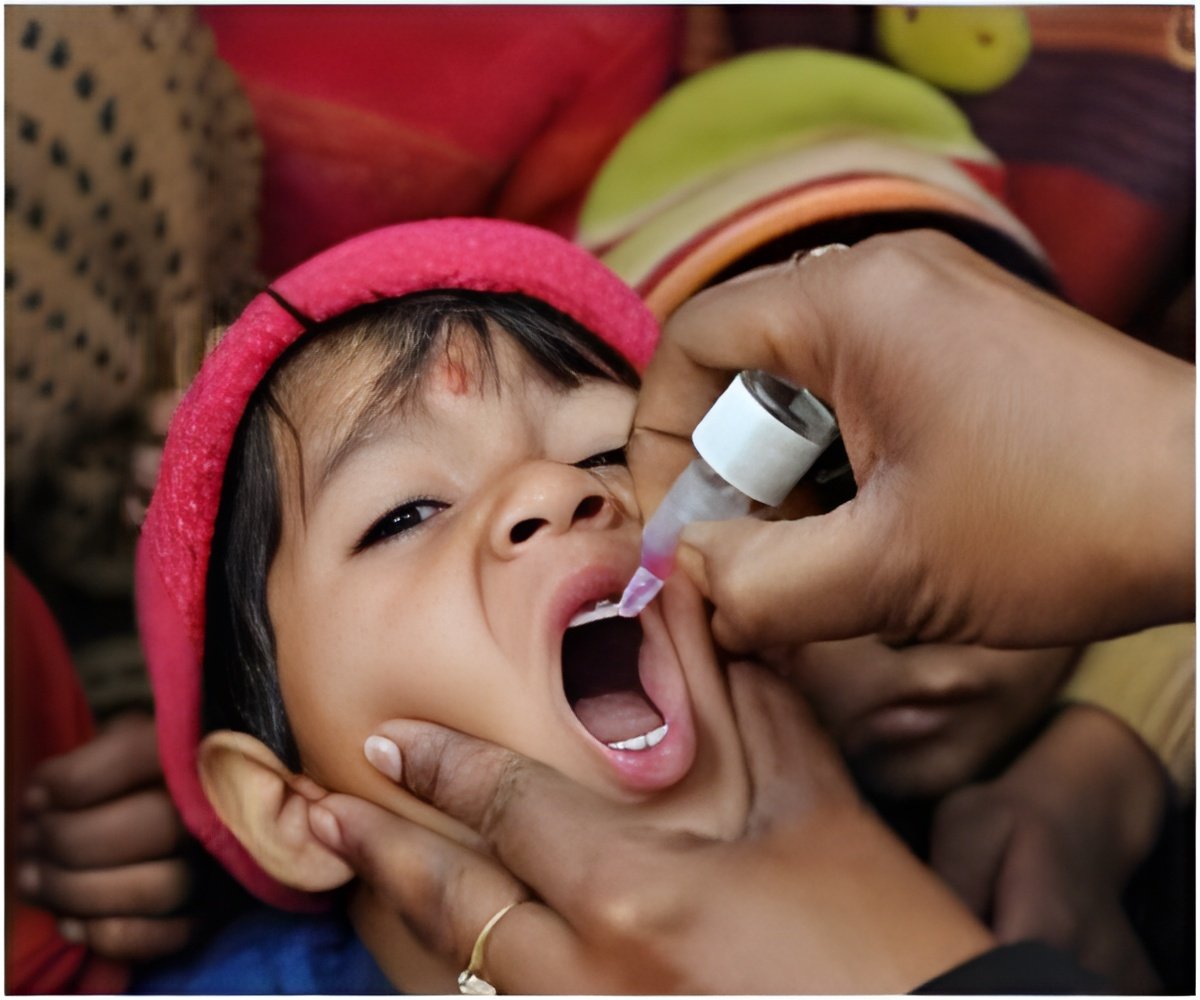
Access to immunization has decreased the number of deaths in children, specially in the endemic nations like Pakistan, Afghanistan, Nigeria.
‘Poor children are more likely to die before the age of five. Hence, immunization services must be provided to these poverty stricken communities.
’





"Almost 450 million doses (were) procured to children in Nigeria, 395 million in Pakistan and over 150 million in Afghanistan. Unicef is the lead procurement agency for the Global Polio Eradication Initiative," Unicef said, citing the figures released during World Immunization Week (April 24-30). According to the Unicef, access to immunization has led to a dramatic decrease in deaths of children under five years from vaccine-preventable diseases.
Between 2000 and 2015, globally deaths of under-fives due to measles declined by 85 per cent and those due to neonatal tetanus by 83 per cent.
Stating that in India the under-five mortality stands at 1.11 million deaths per year, the Unicef said pneumonia accounted for 13 per cent and diarrhea contributed to about 10 per cent of the total under-five deaths.
According to the global agency involved in immunization, an estimated 10 million children in India still miss out on full vaccinations every year.
Advertisement
Unicef India Representative Louis-Georges Arsenault said the organization was committed to ensuring closure of immunity gaps in every state in India.
Advertisement
Globally, the poorest children are nearly twice as likely to die before the age of five as compared to the richest.
Robin Nandy, Chief of Immunisation at Unicef headquarters in New York, said: "Since 1990, immunization has been a major reason for the substantial drop in child mortality, but despite this progress, 1.5 million children still die from vaccine preventable diseases every year."
By 2030, about one in four persons will live in urban poor communities, mainly in Africa and Asia, meaning the focus and investment of immunization services must be tailored to the specific needs of these communities and children, the Unicef said.
Source-IANS