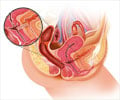
AHT is one of several methods based on breathing exercises and correction of body posture for urinary incontinence.

‘Abdominal hypopressive technique involves breathing in deeply through the diaphragm, and contracting the abdominal muscles after fully breathing out and holding the breath before relaxing.’





AHT is a breathing and corrective postural technique, which aims to lessen abdominal pressure, the theory being that this can involuntarily activate muscles in the abdominal wall and pelvic floor, so reducing urinary incontinence and pelvic organ prolapse. It was developed in the 1980s by a physical therapist, Dr Marcel Caufriez, and is widely known and used in Europe, and North and South America.
It involves breathing in deeply through the diaphragm, and contracting the abdominal muscles after fully breathing out and holding the breath before relaxing.
AHT is one of several methods based on breathing exercises and correction of body posture, which have been proposed as ways of preventing or treating prolapse and urinary incontinence. Others include Pilates and Tai Chi.
But the trial data indicate limited or "questionable" effects for these techniques, and in the case of AHT, no evidence at all, including when added to pelvic floor muscle exercises, for which there is strong evidence of effectiveness.
Advertisement
"However, to date, AHT lacks scientific evidence to support its benefits. At this stage, AHT is based on a theory with 20 years of clinical practice," they continue.
Source-Eurekalert