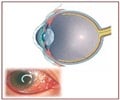
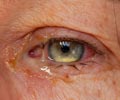
Eye inflammation in patients with non infectious uveitis can now be treated using non steroid alternative adalimumab
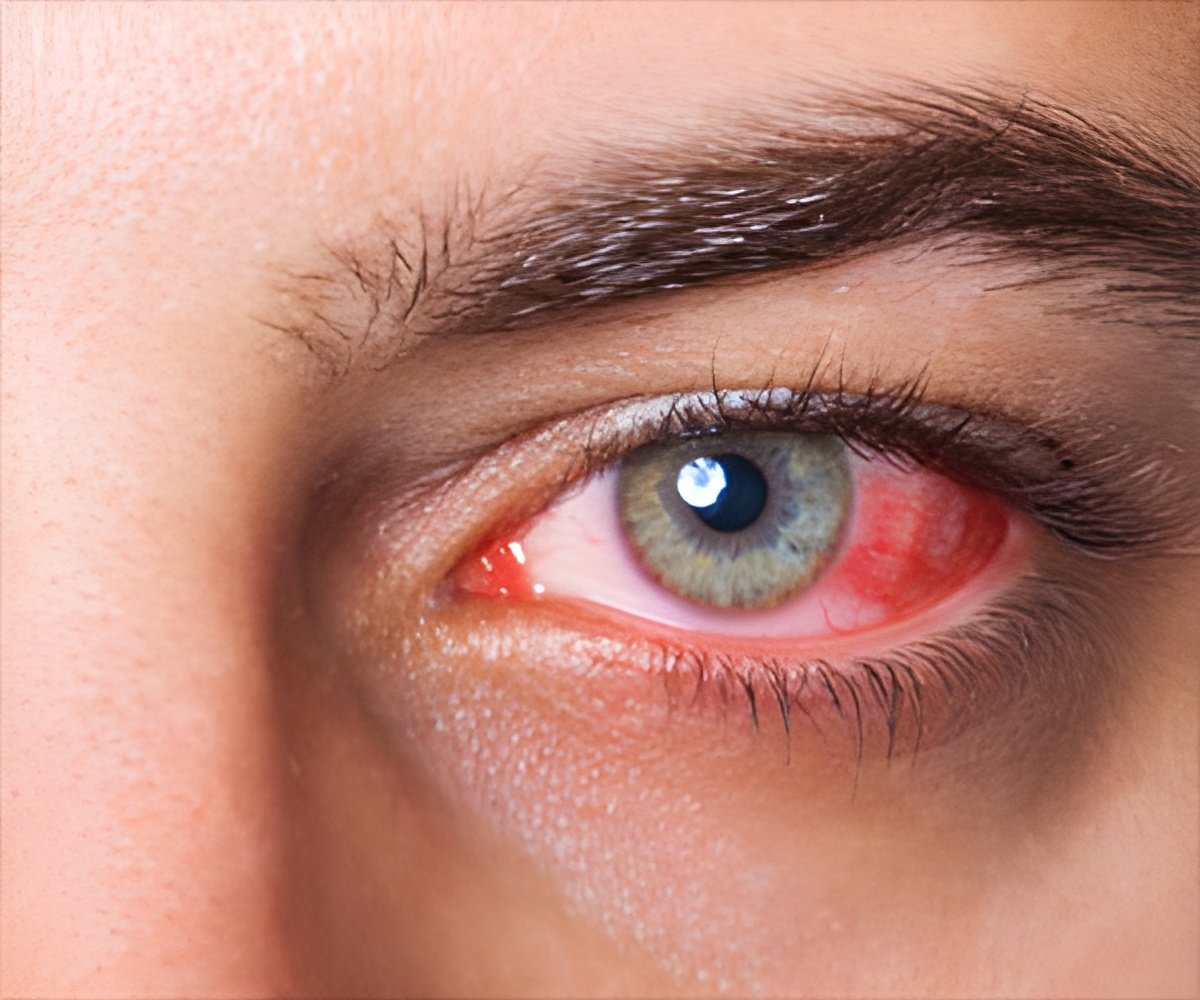
The FDA’s approval is limited to treatment of the three types of noninfectious uveitis that pose the greatest threat of vision loss.
Glenn Jaffe, M.D., a professor in the Department of Ophthalmology at Duke University School of Medicine, said adalimumab works to treat uveitis by targeting a protein that is thought to promote inflammation. Jaffe led one of two clinical studies that formed the basis of the FDA’s approval and was senior author of the study appearing Sept. 8 in the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM).
“Patients may have many unwanted side effects when taking steroids long-term, as many uveitis patients do,” Jaffe said. “The goal of these studies was to determine whether there was an alternative that could replace or minimize the use of steroids. The studies also looked at whether an alternative would be better tolerated or more effective, yet still safe.”
The study consisted of 217 adults who had active, non-infectious intermediate or posterior uveitis, or panuveitis. Participants were randomly assigned to a group that received either adalimumab or a placebo at the start of the trial and every two weeks thereafter. All participants also initially received standard doses of the corticosteroid prednisone, and continued to receive it in diminishing doses over the course of 15 weeks.
Advertisement
“It is the active inflammation, caused by the body’s immune system reacting against itself, that can potentially permanently decrease the patient’s vision and cause unwanted symptoms, such as eye pain and floaters in the field of vision,” he said. “The hope is that by delaying or eliminating recurrences, the symptoms will be minimized or eliminated.”
Advertisement
Jaffe said the study’s results are significant not only because they indicate adalimumab delays treatment failure, but also because the investigation considered several signs as causes for treatment failure.
“Using these multiple, possible endpoints was something unique to this study,” Jaffe said. “Since each of these signs can be associated with different types of uveitis, the study’s results broaden the applicability of treatment for patients.”
The study authors note, however, that patients in the adalimumab group reported serious adverse effects, such as respiratory tract infections and allergic reactions, more frequently than those in the placebo group.
In addition to Jaffe, co-authors include Andrew D. Dick, Antoine P. Brézin, Quan Dong Nguyen, Jennifer E. Thorne, Philippe Kestelyn, Talin Barisani-Asenbauer, Pablo Franco, Arnd Heiligenhaus, David Scales, David S. Chu, Anne Camez, Nisha V. Kwatra, Alexandra P. Song, Martina Kron, Samir Tari, and Eric B. Suhler.
AbbVie, the pharmaceutical company that manufactures and markets adalimumab as Humira, sponsored the study. Dr. Jaffe served as a consultant for AbbVie, and other study authors also report financial relationships with the company. Further author disclosures are available in the study’s manuscript.
Source-Newswise