Hypersensitivity to allergens is associated with the intensity of psoriasis. Therefore, controlling its exposure may reduce psoriasis symptoms.
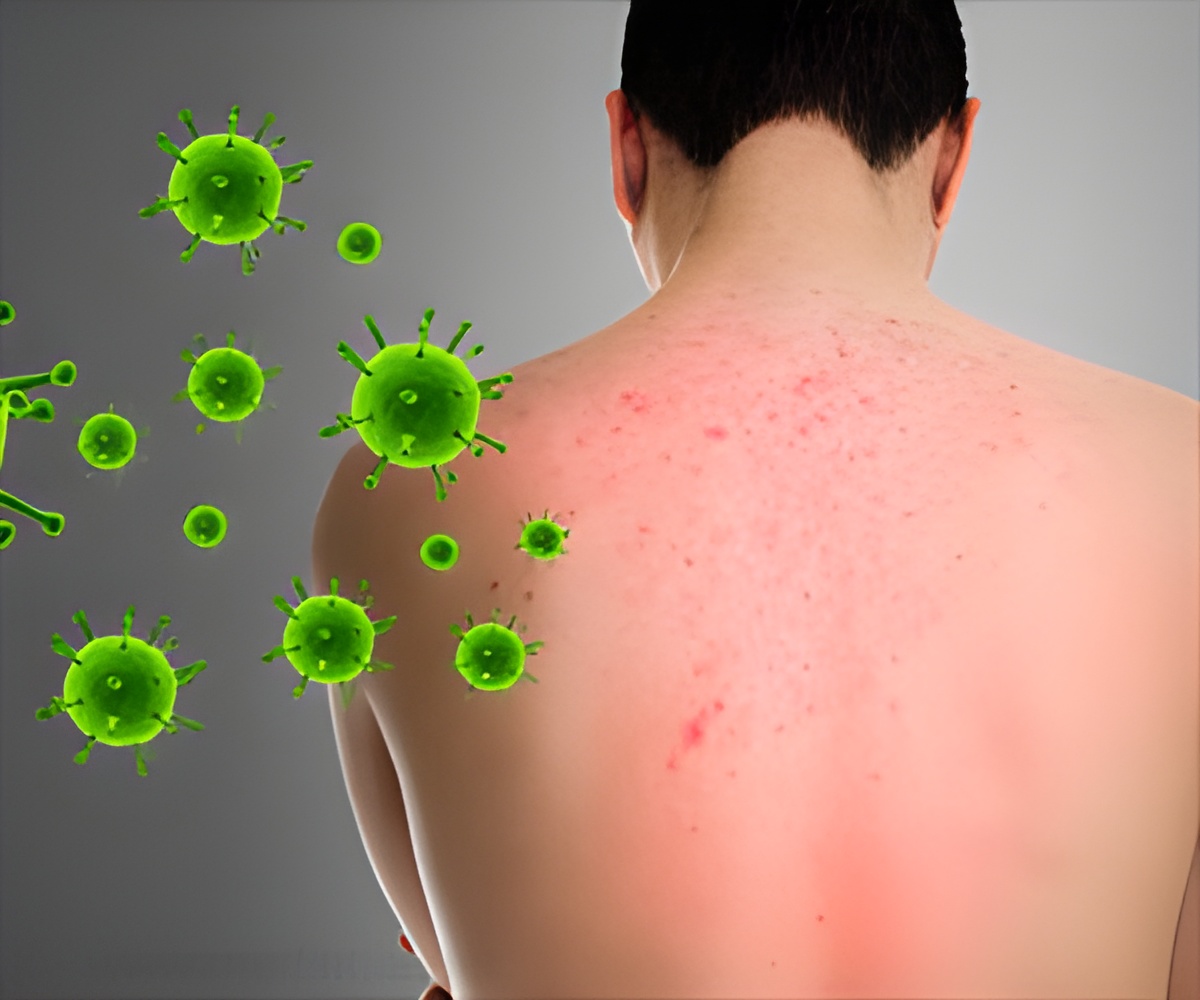
- Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory disease with an unknown etiology.
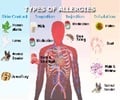
- Allergic disease is believed to co-exist with psoriasis.
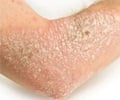
- Psoriasis that exists for a prolonged period leads to break in the epidermal barrier and increased exposure to allergens.
- Hypersensitivity to allergens is found to correlate with the intensity of disease symptoms.
- Genetic, immunologic and environmental factors play an important role in etiology.
- Immunological process plays an important role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
- Allergic reactions are believed to co-exist with psoriasis due to disease complexity.
- Prolonged disease leads to a breakdown in the epidermal barrier, resulting in the entry of allergens.
- Total IgE antibodies.
- Allergen-specific antibodies (asIgE).
- Standard epidermal tests.
- Atopic patch test- This contained allergen extract of dust mites, birch pollen, molds, fungus, pollen, hairs of dog and cat.
- The allergens that were tested included egg, wheat flour, soy, hazelnut , dust mites, cat, horse, cod, carrot, milk, potato, and dogs.
This study also highlighted that the concentrations of IgE antibody correlated with the intensity of disease progression in patients with psoriasis.
The suggested pathogenesis of psoriasis is due to the dendritic cells presenting T lymphocytes with self-antigens in individuals who have a genetic predisposition for psoriasis. Activated T lymphocytes derived from patients with psoriasis have been shown to induce psoriasis in mice but not those derived from healthy people. Moreover, the injected T-lymphocytes increased keratinocyte proliferation when injected.
Initially, it was believed that Th1 cells mediated the immune response that leads to psoriasis and other auto-immune disorders. However, recent studies have found that Th17 cells also aid in mediating the response.
Though immune reactions are triggered by both an allergy as well as psoriasis, the current study by Maria found a weak correlation of an allergic reaction with psoriasis pathogenesis. However, hypersensitivity correlates with the intensity of the disease symptoms.
This aids in controlling flare-ups in psoriasis patients by re-instating the need to control exposure to allergens.
Controlling Allergy in Psoriasis Patients
- Identify the allergen: Allergen identification is made using a patch test or by injecting the allergen into the skin and then waiting for an allergic reaction.
- Avoiding allergen exposure: Though there are some allergens which cannot be avoided, there are certain allergens like food allergens which can be avoided.
- Immediate treatment: When exposed to an allergen that could trigger a psoriasis flare-up, immediate treatment measures should be carried out.