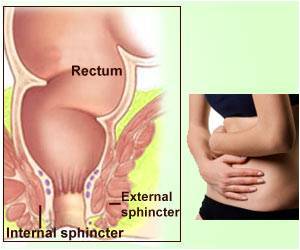
Engaging in the practice of anal intercourse may increase risks for bowel problems, including fecal incontinence and bowel leakage.
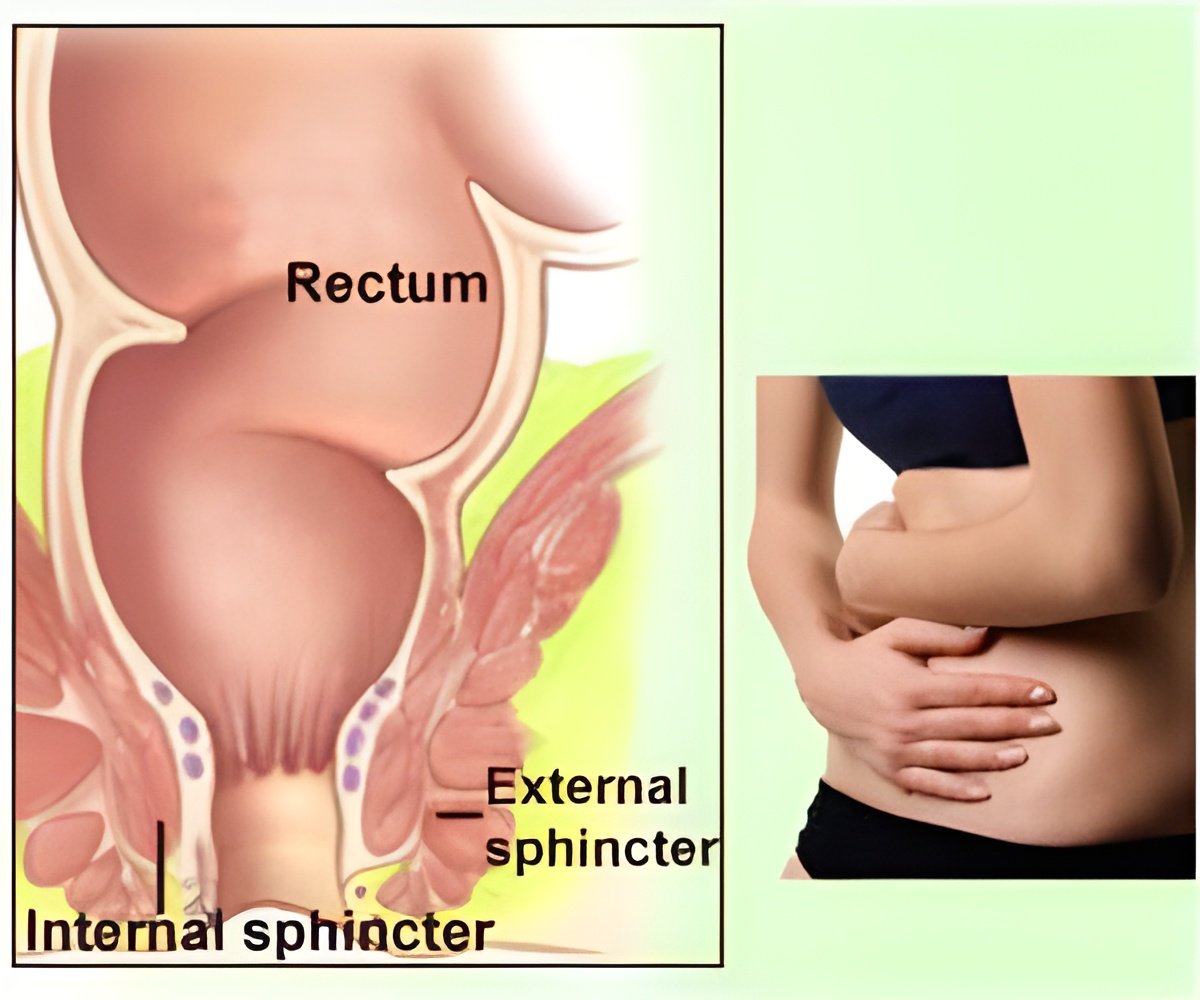
‘Engaging in the practice of anal intercourse may increase risks for bowel problems, including fecal incontinence and bowel leakage. There is heightened risk particularly among men who have intercourse with men.’





Markland said, "The study did not provide data on the frequency of the practice of anal intercourse and the impact of incontinence, but it did show a relationship between the practice of anal intercourse and fecal incontinence - more so among men than women. What we don't know is whether someone who has anal intercourse one or two times is at the same increased risk for fecal incontinence as someone who has anal intercourse regularly." Overall, 4,170 adults ages 20-69 (2,070 women and 2,100 men) completed sexual behavior questionnaires and responded to fecal incontinence questions as part of the NHANES surveys. Overall, 8.3% of women and 5.6% of men in the study had fecal incontinence. Fecal incontinence rates were higher among women (9.9%) and men (11.6%) reporting anal intercourse than among women (7.4%) and men (5.3%) not reporting anal intercourse.
Fecal incontinence was determined to have occurred by researchers who reviewed responses to survey questions about leakage of mucus, liquid or stool and occurred at least monthly. The study showed that most adults who experience fecal incontinence have only occasional bouts of diarrhea. However, fecal incontinence can be chronic; it is often caused by muscle and nerve damage around the rectum, constipation, certain diseases, surgical procedures, and childbirth.
Markland said, "Little is known about how anal intercourse might affect bowel function, even though the survey showed the practice is common among both heterosexual and homosexual couples. We really know very little about the connection between anal intercourse and fecal incontinence, especially among women. Older studies among predominately HIV-positive males showed that men who have anal intercourse with men may have impaired rectal muscle strength. But one thing I think this study does show is that it is important that both the patient and clinical provider need to be aware of the potential risks associated with anal incontinence and be willing to discuss what those risks may be."
Markland further added, "Previous clinical trials have shown that pelvic floor muscle or anal exercises can be an effective treatment for fecal incontinence. Those engaging in anal intercourse consider these exercises to help guard against decreased anal sphincter tone. These are also known as Kegel exercises. But, doing these exercises has not been studied as a preventive measure for lowering the odds of having fecal incontinence in a general population. All we can do is speculate."
Advertisement
Markland said, "I am always looking for potentially modifiable factors that may be related to bowel leakage. Anal intercourse has been understudied in our population in general, and anal incontinence and bowel incontinence were evaluated only in men who have sex with men in older studies. I thought we really needed to look at both men and women and assess the prevalence and associations between anal intercourse and fecal incontinence in both genders."
Advertisement