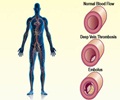
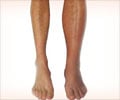
Research shows that individuals with anxiety and depression are at a higher risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
- Anxiety and depression are linked to an increased risk of DVT
- Inflammation, hypercoagulability, and immobility are potential factors contributing to this risk
- Screening and prevention strategies are crucial for individuals with anxiety and depression
Research Spotlight: Anxiety and Depression are Important Risk Factors for Dangerous Deep Vein Blood Clots
Go to source).
Studies have shown that people with anxiety and depression have a 40% increased risk of developing Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) #medindia #mentalhealthmatters’
The Link Between Anxiety and Deep Vein Thrombosis
Studies have consistently shown that individuals with anxiety disorders are at a higher risk of developing DVT. This may be due to several factors, including:- Increased inflammation: Anxiety has been shown to increase inflammation in the body, which can increase the risk of blood clotting.
- Hypercoagulability: Anxiety can cause changes in blood clotting factors, making it more likely for clots to form.
- Immobility: Individuals with anxiety may be more likely to be immobile, which can increase the risk of DVT.
The Link Between Depression and Deep Vein Thrombosis
Depression has also been linked to an increased risk of DVT. This may be due to several factors, including:- Inflammation: Like anxiety, depression has been shown to increase inflammation in the body, which can increase the risk of blood clotting.
- Lack of physical activity: Individuals with depression may be less likely to engage in physical activity, which can increase the risk of DVT.
- Poor health habits: Individuals with depression may be more likely to engage in poor health habits, such as smoking and poor diet, which can increase the risk of DVT.
The Importance of Screening for Deep Vein thrombosis
Given the link between anxiety, depression, and DVT, it is important for individuals with these conditions to be screened for DVT. This can include:- Physical examination: A healthcare provider can perform a physical examination to look for signs of DVT, such as swelling and redness in the legs.
- Medical history: A healthcare provider can take a medical history to identify individuals who may be at risk for DVT.
- Blood tests: Blood tests can be used to check for clotting factors and other signs of DVT.
Treatment and Prevention for Deep Vein thrombosis
If an individual is diagnosed with DVT, treatment typically involves anticoagulation therapy to prevent the clot from growing and to prevent new clots from forming. In addition to treatment, there are several ways to prevent DVT, including:- Stay Active: Regular physical activity can help prevent DVT.
- Managing anxiety and depression: Getting treatment for anxiety and depression can help reduce the risk of DVT.
- Practicing good health habits: Engaging in good health habits, such as a healthy diet and regular exercise, can help reduce the risk of DVT.
Reference:
- Research Spotlight: Anxiety and Depression are Important Risk Factors for Dangerous Deep Vein Blood Clots - (https://www.massgeneral.org/news/research-spotlight/anxiety-depression-risk-factors-blood-clots)
Source-Medindia