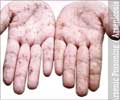
Inorganic arsenic exposure from rice consumption is associated with increased risk of cardiovascular diseases in the long-term and causes premature deaths. Low-level exposure to arsenic over an extended period of time can lead to arsenic poisoning and cause many health problems.

‘Natural arsenic found in rice can contribute to health problems including cancers and cardiovascular diseases, even if consumed at relatively low concentrations over an extended period of time. People should opt for rice varieties that have low inorganic arsenic contents.’
Read More..




Compared to other staple foods, rice tends to concentrate inorganic arsenic. Across the globe, over three billion people consume rice as their major staple and the inorganic arsenic in that rice has been estimated by some to give rise to over 50,000 avoidable premature deaths per year.Read More..
A collaborating group of cross-Manchester researchers from The University of Manchester and The University of Salford have published new research exploring the relationship, in England and Wales, between the consumption of rice and cardiovascular diseases caused by arsenic exposure.
Their findings, published in the journal Science of the Total Environment, shows that - once corrected for the major factors known to contribute to cardiovascular disease (for example obesity, smoking, age, lack of income, lack of education) there is a significant association between elevated cardiovascular mortality, recorded at a local authority level, and the consumption of inorganic arsenic bearing rice.
Professor David Polya from The University of Manchester said: "The type of study undertaken, an ecological study, has many limitations, but is a relatively inexpensive way of determining if there is plausible link between increased consumption of inorganic arsenic bearing rice and increased risk of cardiovascular disease.”
Professor Polya from The University of Manchester said "The study suggests that the highest 25 % of rice consumers in England and Wales may plausibly be at greater risks of cardiovascular mortality due to inorganic arsenic exposure compared to the lowest 25 % of rice consumers.”
Advertisement
While more robust types of study are required to confirm the result, given many of the beneficial effects otherwise of eating rice due to its high fibre content, the research team suggest that rather than avoid eating rice, people could consume rice varieties, such as basmati, and different types like polished rice (rather whole grain rice) which are known to typically have lower inorganic arsenic contents. Other positive behaviors would be to eat a balanced variety of staples, not just predominately rice.
Advertisement