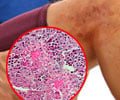
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania have revealed that air pollution may decrease the effectiveness of asthmatic inhalers.
Researchers at the University of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania have revealed that air pollution may decrease the effectiveness of asthmatic inhalers. The study involved 85 asthmatic children, ages 7 to 12, living in Mexico City.
Of the kids, 53 had mild intermittent asthma, while 20 had mild persistent asthma and 12 had moderate persistent asthma. The researchers found that in presence of high pollutants especially nitrogen dioxide and ozone; the inhalers did not function properly.Lead research Dr. Fernando Holguin said the findings "may explain why asthmatics are more symptomatic in relation to air pollution."
The details of the study appear in the journal Chest.
Source-Medindia
RAS