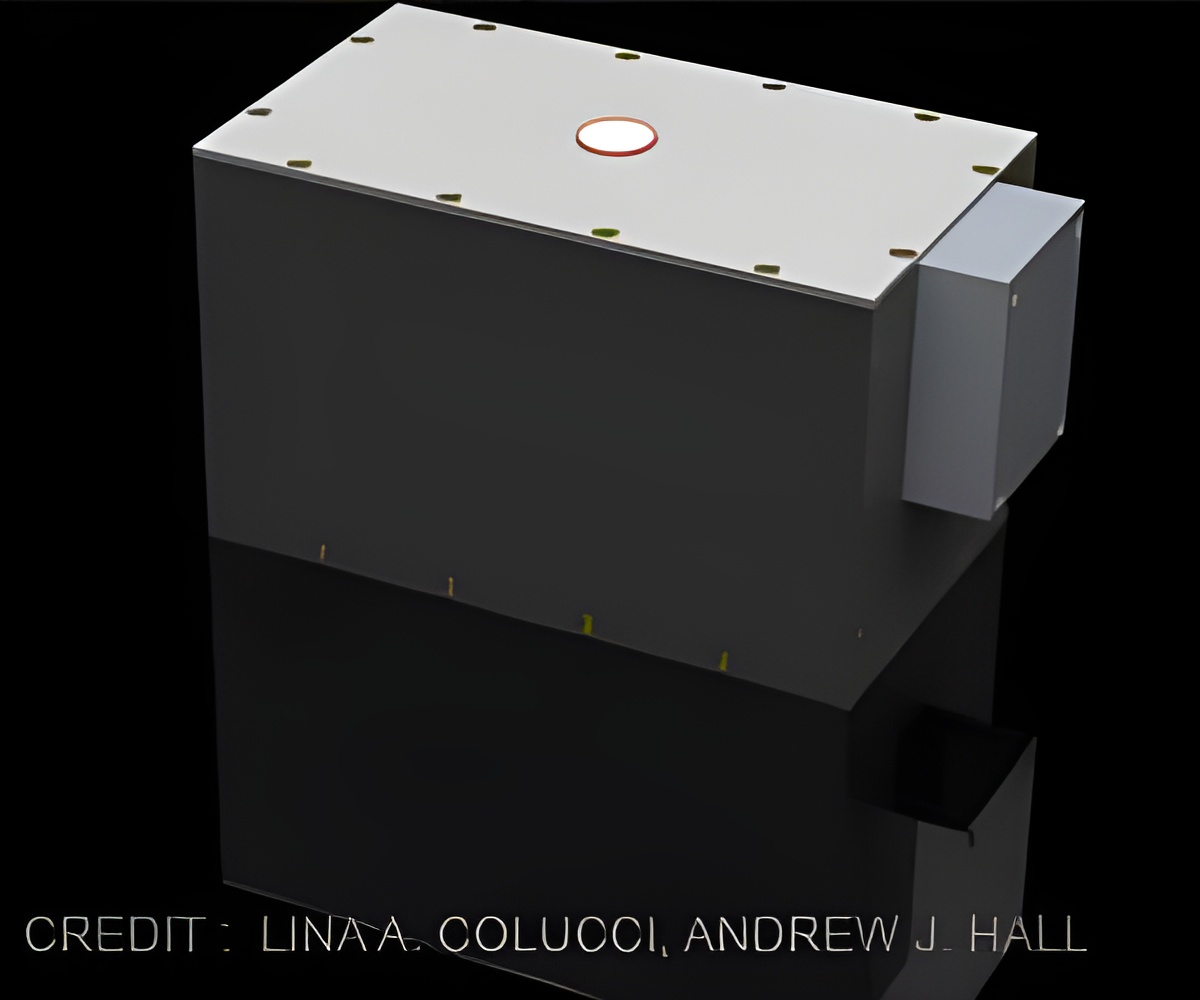
Scientists have created an alternative, non-imaging tool based on portable nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) sensors, which can noninvasively assess fluids and their environment.
‘Fluid buildup, which impacts over six million people in the U.S., occurs in conditions such as kidney and congestive heart failure and costs the U.S. more than $35 billion annually.’





Treating patients with fluid buildup requires striking a delicate balance; removing too little fluid leaves them at risk of hypertension and heart failure, while removing too much leads to muscle cramps and low blood pressure. Current imaging techniques such as MRI machines are expensive and can only be used in hospitals, making them impractical for routine use.
Lina Colucci and colleagues created an alternative, non-imaging tool based on portable nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) sensors, which can noninvasively assess fluids and their environment.
Their platform contains a single-sided NMR sensor harboring 180 individual magnets, and was found to provide accurate measurements of leg fluid buildup when applied to seven participants with end-stage kidney disease, which were matched by results from an MRI machine and an FDA-approved device that estimates body fat and muscle mass.
The authors believe their platform's portability and ease-of-use could allow clinicians to track fluid buildup at the bedside in a manner not possible with larger machines.
Advertisement