Researchers have made a breakthrough that could lead to a better understanding of a common form of arthritis that, until now, has eluded scientists.
Researchers have made a breakthrough that could lead to a better understanding of a common form of arthritis that, until now, has eluded scientists. The researchers are from the Western University.
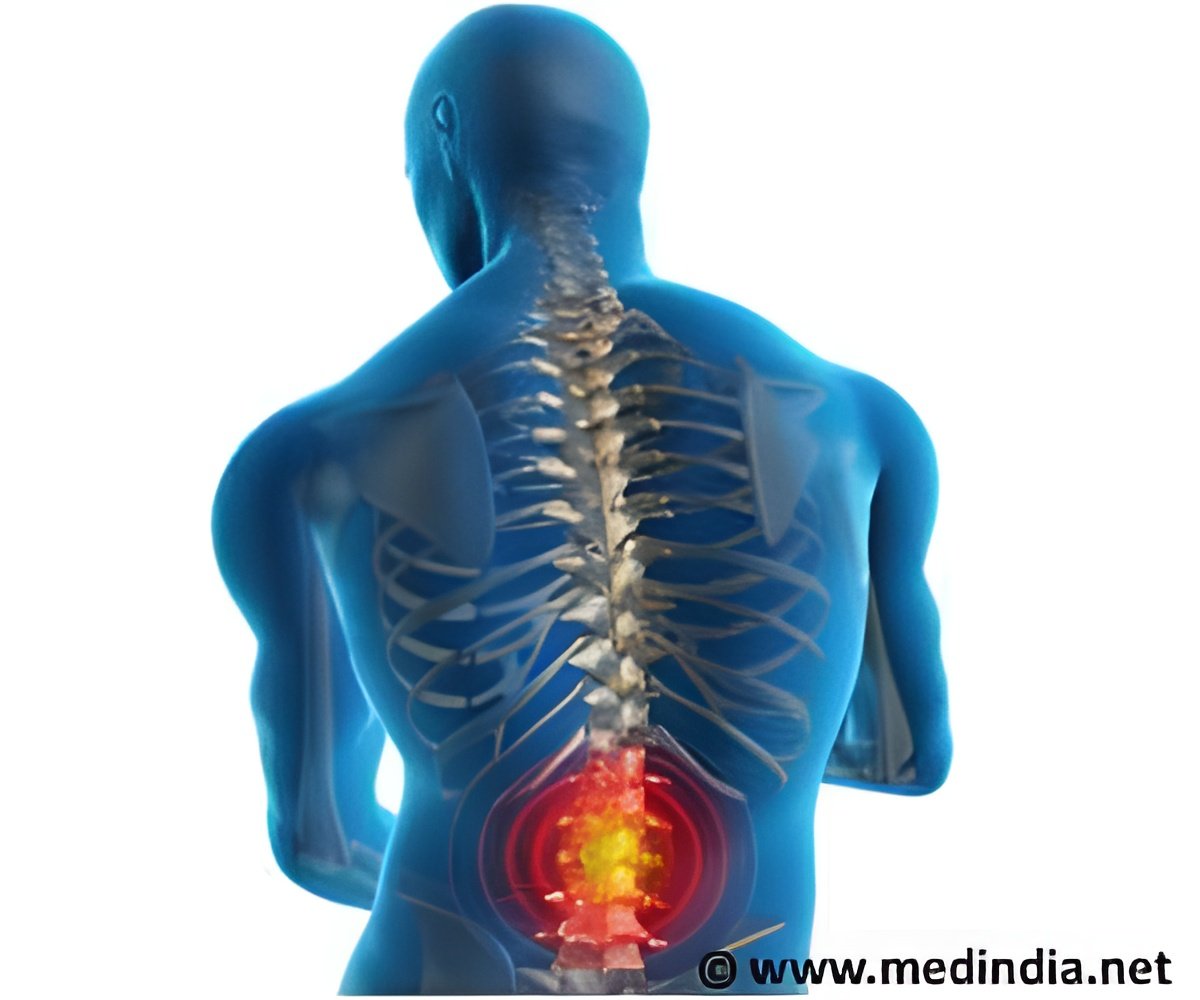
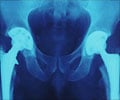
According to The Arthritis Society, the second most common form of arthritis after osteoarthritis is "diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis" or DISH. It affects between six and 12 percent of North Americans, usually people older than 50. DISH is classified as a form of degenerative arthritis and is characterized by the formation of excessive mineral deposits along the sides of the vertebrae in the neck and back. Symptoms of DISH include spine pain and stiffness and in advanced cases, difficulty swallowing and damage to spinal nerves. The cause of DISH is unknown and there are no specific treatments.
Now researchers at Western University's Bone and Joint Initiative, with collaborator Doo-Sup Choi at the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minnesota have discovered the first-ever mouse model of this disease. The research is published online in the
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
Source-Eurekalert