Women who breastfed their babies for a minimum of six months had decreased blood pressure and better body-weight recovery (BMI).
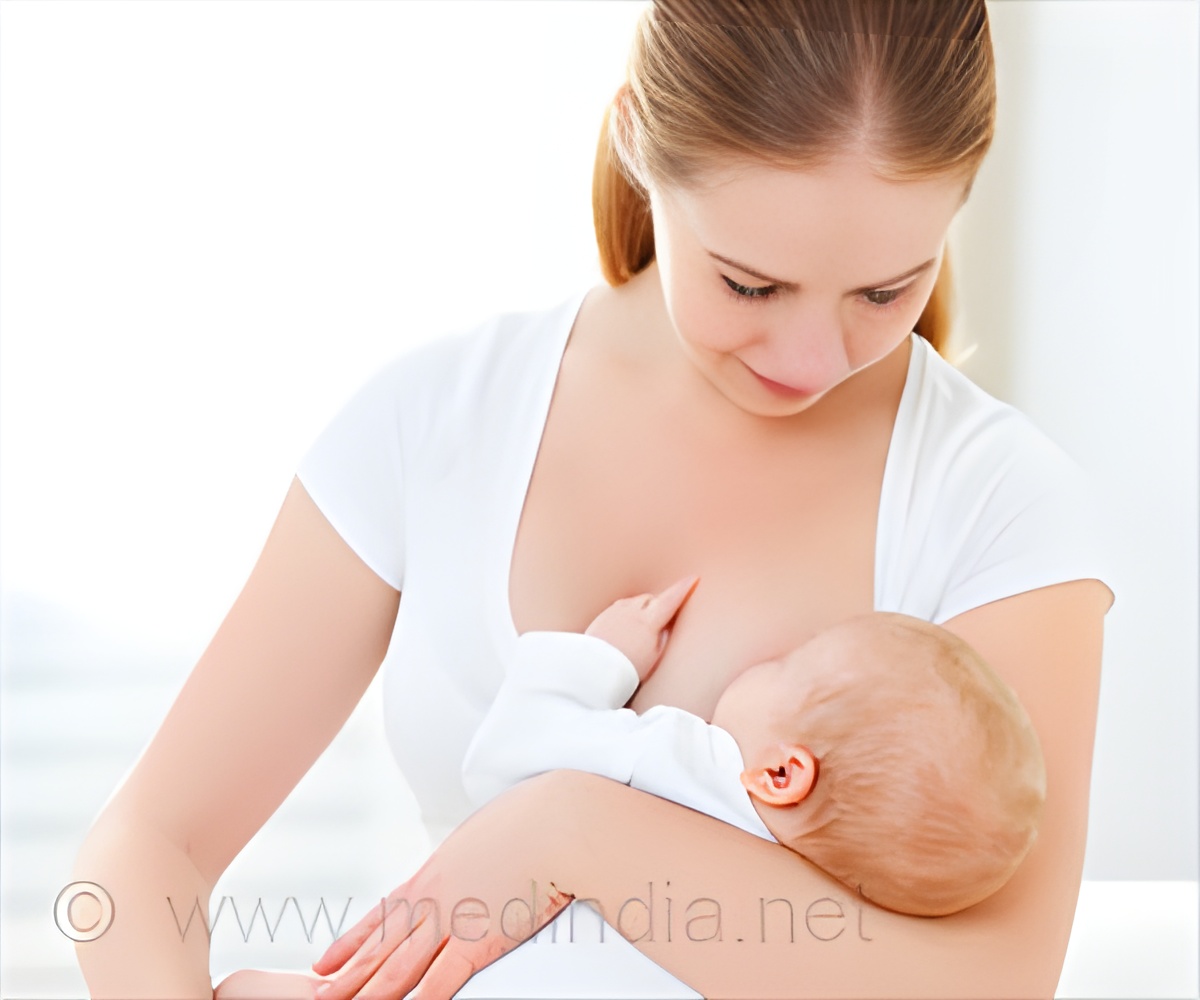

The association of breast feeding for at least six months with hemodynamic and metabolic health of women and their children aged three years
Go to source). The surprising cardio-metabolic benefit for maternal health is particularly important for women who experienced a complicated pregnancy, which can increase their chance of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) later in life.
‘Women who experienced at least one significant pregnancy complication, such as preeclampsia, gestational hypertension, or gestational diabetes, and breastfed for a minimum of six months, demonstrated lowered blood pressure, improved cholesterol levels, and reduced insulin levels. #breastfeeding benefits’





The new results – published this month in the International Breastfeeding Journal by experts from the University of Adelaide and Flinders University – stem from a long-running study of 160 breastfeeding mothers who took part in followup health checks after delivery of their babies. Senior author, Professor Claire Roberts, who leads the Pregnancy Health and Beyond (‘PHaB Lab’) research group at Flinders University, says the study was positive for women with pregnancy complications, as they recorded lower blood pressure and improved cholesterol measures at three years postpartum.
Breastfeeding Enhances Women's Cardio Metabolic Risk Factors
“That means that breastfeeding improves women’s cardio metabolic risk factors, which is good news for new mothers who might be at risk of developing future cardiovascular and metabolic diseases,” says Matthew Flinders Professor Roberts, from Flinders College of Medicine and Public Health.“Pregnancy complications are associated with later cardiovascular disease risk and their children are also at risk of impaired metabolic health earlier in life."
”Along with neurological and other health benefits for babies, the World Health Organization recommends breastfeeding exclusively for up to six months, and breastfeeding over 12 months to promote a significant reduction in both chronic hypertension and diabetes in women.”
The new South Australian study was led by University of Adelaide PhD Dr. Maleesa Pathirana and colleagues from the Robinson Research Institute, Lyell McEwin Hospital cardiology department and Flinders University, who conducted the follow-up of 280 women and their children from the Screening Tests to Predict Outcomes of Pregnancy (STOP) study between 2018 and 2021.
Advertisement
“These findings indicate an overall improvement in cardiovascular health.”
Advertisement
They also recommended more interventions that support breastfeeding in disadvantaged or low socioeconomic areas, particularly for women with pregnancy complications to reduce their lifetime risk of cardiovascular disease.
Reference:
- The association of breast feeding for at least six months with hemodynamic and metabolic health of women and their children aged three years - (https://internationalbreastfeedingjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13006-023-00571-3)