The mission of Axiom Space incorporated numerous experiments focusing on human stem cell aging, inflammation, and cancer within the laboratory situated in the low Earth orbit.

Cancer Drugs To Be Tested In Orbit During American Private Astronaut MissionThe mission of Axiom Space incorporated numerous experiments focusing on human stem cell aging, inflammation, and cancer within the laboratory situated in the low Earth orbit.
Go to source).
‘The Ax-2 mission, which launched at 5:37 p.m. EDT on Sunday (3:07 a.m. Monday IST) aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will investigate whether two inhibitory drugs can reverse the regeneration process in an organoid model of breast cancer. #Axiomspace #Cancer #Drug’





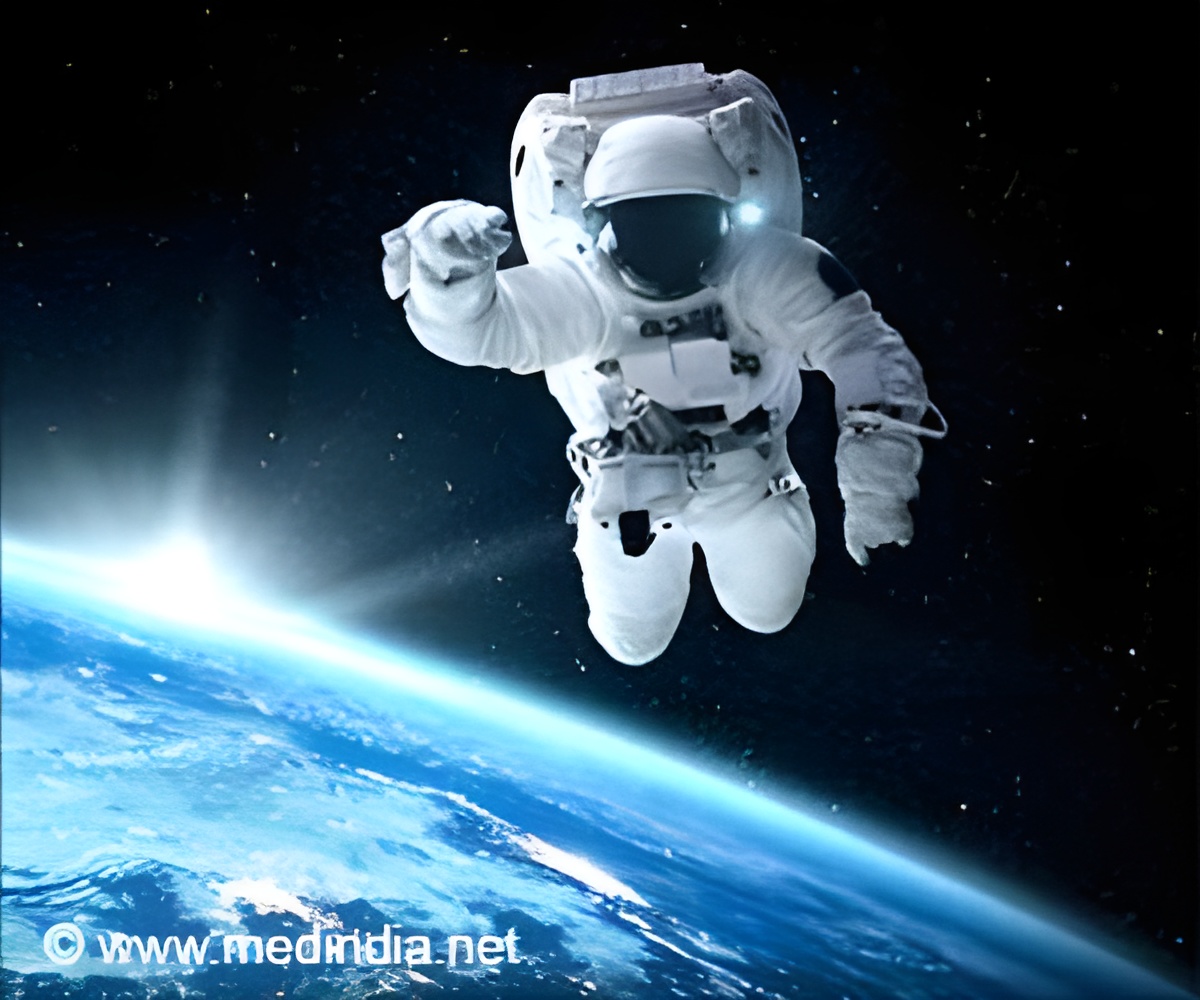
Understanding this process is not only helpful for keeping astronauts healthy - it could also teach us how to better treat cancer on Earth. The Axiom Mission 2 (Ax-2) lifted off at 5:37 p.m. EDT on Sunday (3:07a-am Monday IST) on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket with a multinational crew including the first woman from Saudi Arabia.
The Ax-2 mission will now determine if two inhibitory drugs can reverse the regeneration in an organoid model of breast cancer.
Experiments will Monitor Astronauts’ Blood Stem Cells in Space
Another line of experiments will track the health of astronauts' blood stem cells before, during and after spaceflight to evaluate the effects of the space environment on stem cell ageing, immune function and cancer stem cell generation.These projects are part of the NASA-funded Integrated Space Stem Cell Orbital Research (ISSCOR) Center, a collaboration between University of California-San Diego Sanford Stem Cell Institute, JM Foundation and Axiom Space.
The experiments will take place over 10 days in orbit, with subsequent data collection and analysis performed at UC San Diego.
Advertisement
"By conducting these experiments in low Earth orbit, we are able to understand mechanisms of cancer evolution in a compressed time frame and inform the development of new cancer stem cell inhibitory strategies," Jamieson added.
Findings will Guide Predictive Models, New Drugs for Cancer
The findings will inform the development of predictive models for cancer and immune dysfunction-related diseases and could lead to the development of new drugs to prevent or treat these conditions during space exploration and here on Earth.Advertisement
"Our mission is to improve life on Earth and foster the possibilities beyond by building and operating the world's first commercial space station," she added.
Axiom Space astronauts are expected to depart the space station May 30, pending weather, for a return to Earth and splashdown at a landing site off the coast of Florida.
Reference:
- UC San Diego First to Test Cancer Drugs in Space Using Private Astronaut Mission- (https://today.ucsd.edu/story/uc-san-diego-first-to-test-cancer-drugs-in-space-using-private-astronaut-mission)