Cell-replacement therapy involves differentiating stem cells into dopamine-signaling, neurons and transplanting them into Parkinson's patient’s brain. This therapy shows some promise as a treatment for Parkinson's
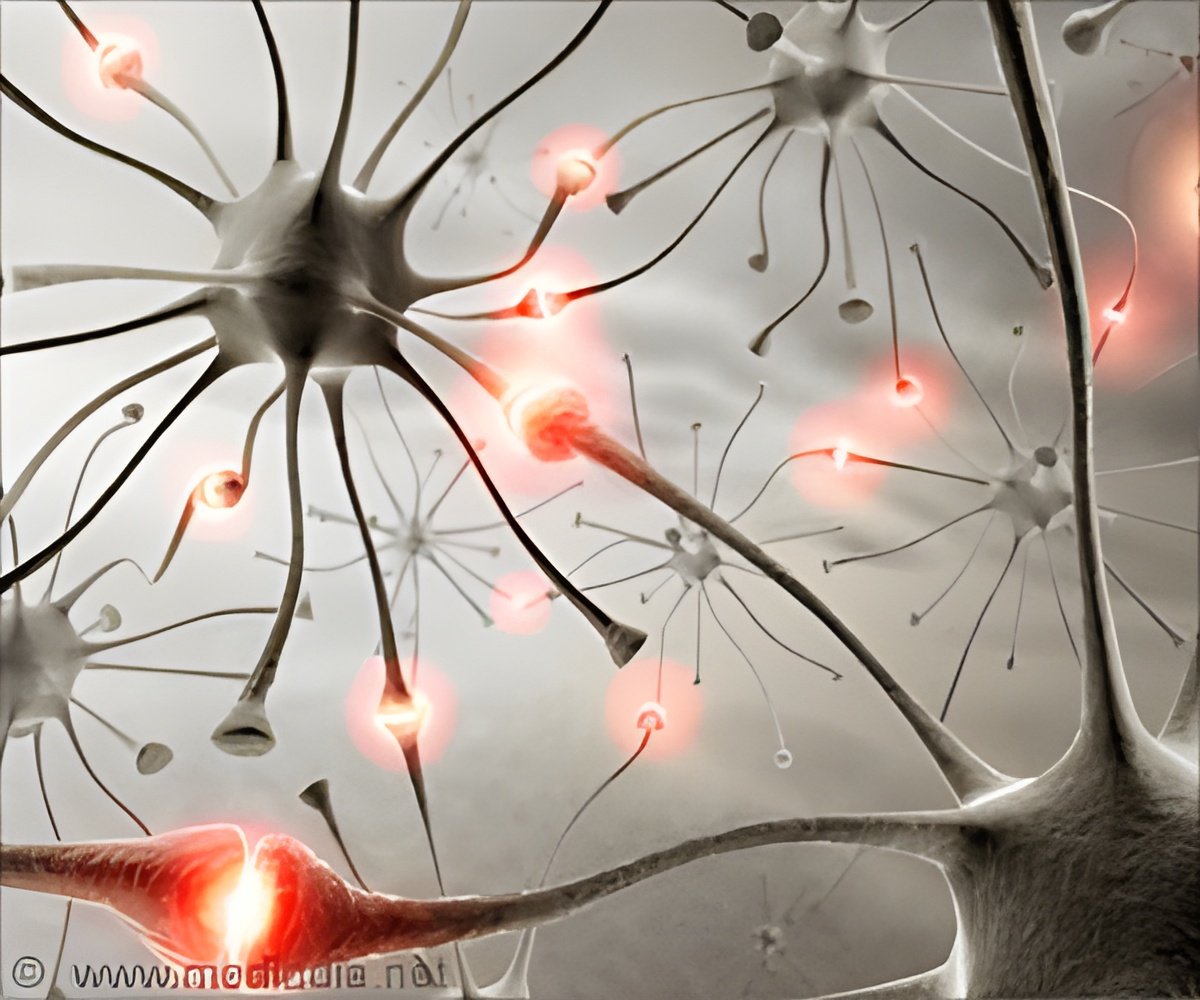
‘Cell-replacement therapy involves differentiating stem cells into dopamine-signaling neurons and transplanting them to replace dying neurons.’





In clinical trials in the 1990s, for example, such contamination gave some patients severe dyskinesia, uncontrollable jerky movements that were worse than the movement problems caused by Parkinson's disease.To avoid interference by unwanted cell types, researchers need a differentiation protocol that yields a more homogeneous population of dopaminergic neurons.
Researchers led by Hossein Baharvand, of Iran's University of Science and Culture in Tehran, and Ghasem Hosseini Salekdeh , of the Academic Center for Education, Culture and Research in Iran and Macquarie University in Australia, set out to develop such a protocol.
First, the team developed a special stem cell line that contains a green fluorescent protein, or GFP, reporter for a transcription factor involved in dopaminergic neuronal development.
In undifferentiated cells from this line, the fluorescent reporter is not expressed. When cells begin to make the transcription factor, the first step toward becoming a dopaminergic neuron, they also begin to make the GFP protein.
Advertisement
By selecting for one protein characteristic of dopaminergic progenitors, called contactin 2, they isolated progenitors and transplanted them into rats modeling Parkinson's disease.
Advertisement
Sorting the cells also reduced motor symptoms of Parkinson's compared with rats treated that received unsorted cells.
The team's isolation procedure uses may be an important step toward more successful cell-replacement therapy.
Source-Eurekalert









