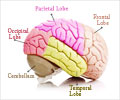
Neurons in the brain work like colonies of honeybees and show that colony decision time increases with the number of available nests, in agreement with the Hick-Hyman law of psychophysics, and decreases with mean nest quality, in agreement with Piéron’s law.

‘The function of neurons in the brain is like a colony of honeybees. Honeybee colonies adhere to the same laws as the brain when making collective decisions. The way in which bees communicate with each other and make decisions is similar to the way the numerous individual neurons in the human brain interact with each other.’





Previous research has shown that the brain of humans and other animals follow certain rules known as psychophysical laws. Single brain neurons do not obey the laws, but the whole brain does. Similarly, this study found that even if single bees do not obey these laws, the superorganism, i.e. the bee colony, does. The study, published in Nature: Scientific Reports, which has fundamentally found that superorganisms may obey the same laws as the human brain, is important because it suggests that the mechanisms that generate such psychophysical laws are not only happening in brains as previously thought. This discovery will enable scientists to better understand the basic principles that generate such laws by studying superorganisms such as bee colonies, which is much simpler than watching brain neurons in action when a decision is being made.
The study also helps us better understand and explore brain laws, including Pieron’s Law, Hicks Law and Weber’s Law.
Pieron’s Law is the law that suggests that the brain is quicker to make decisions when the two options to decide from are of high quality. The brain is slower when the two options are of lower quality. When studying the bee colony, the study found that the honeybee colony is quicker to make a decision between two high-quality nest-sites compared to two low-quality nest-sites.
Similarly, Hick’s Law finds that the brain is slower to make decisions when the number of alternative options increases. In this study, academics found that the bee colony was slower to make decisions when the number of alternative nest-sites increased.
Advertisement
This law can also be applied to changes in stimulus as well as quality, for example, light, sound or weight. An analogy could be: if you’re holding 1lb of rocks and add another 1lb of rocks, you’ll notice the difference immediately; but if you’re holding 30lbs of rocks and add another 1lb, the change is much less noticeable.
Advertisement
"The study also supports the view of bee colonies as being similar to complete organisms or better still, superorganisms, composed of a large number of fully developed and autonomous individuals that interact with each other to bring forth a collective response.
"With this view in mind, parallels between bees in a colony and neurons in a brain can be traced, helping us to understand and identify the general mechanisms underlying psychophysics laws, which may ultimately lead to a better understanding of the human brain. Finding similarities between the behavior of honeybee colonies and brain neurons is useful because the behavior of bees selecting a nest is simpler than studying neurons in a brain that makes decisions."
Source-Eurekalert