Penicillin and several other antibacterial medications commonly taken by pregnant women are not associated with many birth defects, reveals a new study.
Penicillin and several other antibacterial medications commonly taken by pregnant women are not associated with many birth defects, reveals a new study.
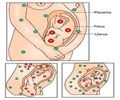
However, the study also showed that other antibiotics, such as sulfonamides and nitrofurantoins, may be linked to several severe birth defects and require additional scrutiny.Bacteria-fighting medications are among the most commonly used drugs during pregnancy. Although some classes of antibiotics appear to have been used safely during pregnancy, no large-scale studies have examined safety or risks involved with many classes of antibacterial medications.
Krista S. Crider, Ph.D., of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues analyzed data from 13,155 women whose pregnancies were affected by one of more than 30 birth defects (cases).
The information was collected by surveillance programs in 10 states as part of the National Birth Defects Prevention Study.
The researchers compared antibacterial use before and during pregnancy between these women and 4,941 randomly selected control women who lived in the same geographical regions but whose babies did not have birth defects.
Antibacterial use among all women increased during pregnancy, peaking during the third month.
Advertisement
"Reassuringly, penicillins, erythromycins and cephalosporins, although used commonly by pregnant women, were not associated with many birth defects," the authors said. No defects were associated with erythromycins (used by 1.5 percent of the mothers whose children had birth defects and 1.6 percent of controls), one with penicillins (used by 5.5 percent of case mothers and 5.9 percent of controls), one with cephalosporins (used by 1 percent of both cases and controls) and one with quinolones (used by 0.3 percent of both cases and controls).
The study has been reported in the November issue of Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine, one of the JAMA/Archives journals.
Source-ANI
ARU