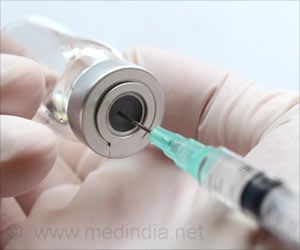
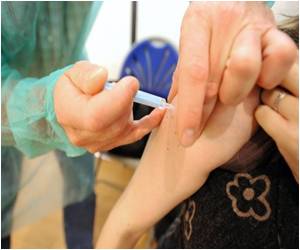
Despite studies showing the vaccine to be safe and effective, the number of children and young adults with autoimmune diseases receiving the HPV vaccination is profoundly low.
Autoimmune diseases, such as lupus and inflammatory bowel disease, are associated with increased rates of persistent infection with human papillomavirus (commonly called HPV) - the most common sexually transmitted disease and the primary cause of cervical cancer. In 2006 and 2009, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved two different HPV vaccines for use in people ages nine to 26 (both females and males). Studies show the HPV vaccine to be safe and effective in people with autoimmune diseases, and researchers in Boston recently investigated whether those with autoimmune diseases receive the vaccine more or less often than the general population.
"Our study demonstrated striking low uptake of HPV vaccination among patients both with and without autoimmune diseases," explains Candace Feldman, MD, MPH; rheumatology fellow; Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy, Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston and lead investigator in the study. "While increased efforts are necessary for the entire population, a particular focus should be paid to those at high risk for persistent infection. Further studies are needed to better understand this low uptake and to determine strategies for improved access."
Using a U.S. commercial insurance claims database, Dr. Feldman's team identified 29,255 children and young adults with autoimmune diseases and 117,020 without and reviewed their health care records. The average age of those studied was 19 years, and 59 percent were female. The team excluded patients with a history of malignant cancers or organ transplants. Those with autoimmune diseases were matched (based on age, sex and date they received an autoimmune diagnosis) and compared to those without. The team accounted for patients' characteristics, including co-existing diseases, use of health care treatments and geographic regions when assessing the vaccine uptake.
Dr. Feldman's team noted that those with autoimmune diseases had a higher number of physician visits, abnormal pap smears and sexually transmitted diseases when compared to those without autoimmune diseases. Few people in both groups actually received one or more of the three doses of HPV vaccination (8.5 percent in those with autoimmune diseases and 9.1 percent in those without). When looking specifically at females, the researchers noted 13.1 percent with autoimmune diseases and 14.1 percent without received at least one of the three doses, but less than five percent in both groups received all three of the doses - the full vaccination. In a subgroup of female patients who had at least two years of follow-up, 20.6 percent with autoimmune disease and 23.1 percent without autoiummune disease received at least one dose. And of those, 53.1 percent and 51.4 percent - respectively - completed the series.
Additionally, the researchers noted that vaccinations were equally distributed geographically, with the exception of the Northeast, which had a higher percent of those with autoimmune diseases receiving at least one dose.
Advertisement
The American College of Rheumatology is an international professional medical society that represents more than 9,000 rheumatologists and rheumatology health professionals around the world. Its mission is to advance rheumatology. The ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting is the premier meeting in rheumatology.
Advertisement
Abstract Number: 848
Human Papillomavirus Vaccine Uptake Among Children and Young Adults With Autoimmune Diseases
Candace H. Feldman1, Linda T. Hiraki2, Joyce Lii3 and Seoyoung C. Kim3, 1Division of Rheumatology, Immunology and Allergy, Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, 2Brigham and Women's Hospital, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, 3Brigham and Women's Hospital, Boston, MA
Background/Purpose: Autoimmune diseases such as lupus and inflammatory bowel disease are associated with increased rates of human papillomavirus (HPV), the most common sexually transmitted disease and the primary cause of cervical cancer. In 2006 and 2009 the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved two 3-dose series HPV vaccines for use in 9-26 year-old females and males. Studies show the HPV vaccine to be safe and efficacious in patients with autoimmune diseases. We investigated whether HPV vaccine uptake is higher among those with autoimmune diseases compared to the general population.
Methods: Using a U.S. commercial insurance claims database from 2005-2012, we identified children and young adults age 9-26 with ≥12 months of continuous enrollment and ≥2 autoimmune disease diagnosis codes ≥7 days apart. We defined the index date as the calendar month and year of the second autoimmune disease diagnosis code. We matched these individuals by age, sex, and index date to randomly selected controls without any autoimmune disease diagnosis codes (1:4 ratio). We excluded individuals with a history of malignancy or organ transplant. Vaccination was defined as ≥1 HPV vaccine code (CPT 90649 or 90650) following the index date, after 2006. Baseline covariates for stratified analyses included age, sex, region, healthcare utilization and comorbidities. We also examined vaccine uptake in the 21 states that passed HPV-related legislation from 2008-2012, compared to states that did not. We obtained p-values comparing proportions of HPV vaccine uptake in the two cohorts.
Results: We identified 29,255 children and young adults with autoimmune diseases and 117,020 without. The mean age was 19 years (SD 5); 59% were female. The autoimmune disease cohort had a higher number of physician visits, abnormal pap smears, and sexually transmitted diseases (all p-values<0.01). Both cohorts had low percentages of HPV vaccine uptake overall, with 8.5% with autoimmune diseases and 9.1% without receiving ≥1 vaccine (p=0.34) (Table). Among females, 13.1% with autoimmune diseases and 14.1% without received ≥1 vaccine (p<0.01); <5% of females in both groups completed a 3-dose series (p=0.57). Vaccinations were equally distributed geographically except for the Northeast which had a higher percent with autoimmune diseases receiving ≥1 HPV vaccine (p=0.02). In states with HPV-related legislation, 7.1% with autoimmune diseases and 7.5% without received ≥1 vaccine, compared to 6.5% with autoimmune diseases (p=0.04) and 7.4% without (p=0.5) in states without legislation.
Conclusion: HPV vaccine uptake is profoundly low among children and young adults both with and without autoimmune diseases despite its known efficacy. Heightened public health efforts are necessary for the general population and for those with autoimmune diseases given their increased risk of persistent HPV infection.
Source-Newswise