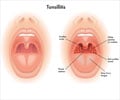
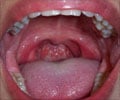
A new study has found that the risk of complications following tonsillectomy is higher among children who come from lower income families.

"Surprisingly, despite all children having a relatively uniform health status before surgery, we found significant differences in the numbers of children requiring revisits after their tonsillectomies," said co-author Dr. Nina Shapiro, director of pediatric otolaryngology at Mattel Children's Hospital UCLA and a professor of head and neck surgery at the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA.
To conduct the study, Shapiro and Dr. Neil Bhattacharyya, professor of otolaryngology at Harvard Medical School, examined the complication rate in close to 80,000 children who had tonsillectomy surgeries in an outpatient setting (with or without an adenoidectomy) in four states — California, Iowa, Florida and New York. They reviewed ambulatory surgery databases from 2010 and 2011 and linked them to emergency room and inpatient databases. The revisit rates and diagnoses in the 14 days after tonsil removal surgery were analyzed with respect to gender, race and median household income level.
Among all cases reviewed in the study, approximately 8 percent of the children saw the doctor within two weeks following surgery for complications that included bleeding, pain and dehydration/fever.
However, they found that compared to those in the highest income group, children in the lowest income households had a one-and-a-half times greater likelihood of needing a doctor visit after surgery, and a one-and-one-third times greater likelihood of bleeding after surgery. They also found that black and Hispanic children were more likely to suffer from a complication than white children.
The importance of the research stands out if the rates of postoperative complications found in the study were applied to the 500,000 annual tonsillectomies performed in the United States. This would be equivalent to 3,000 additional children from lower-income families and beyond that 1,700 additional Hispanic children requiring a doctor's visit after their tonsillectomy compared to children from higher-income families and white children, Shapiro said.
Advertisement
The authors believe several factors may have contributed to the disparities.
Advertisement
Bhattacharyya noted that the data was taken from surgeries that took place before the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA). "Since this type of surgery is so common, the next stage of this research will look at the impact of the ACA on post-surgical complications based on demographic variables," he said. "Furthermore, these data have important implications as the public gains access to more transparent data regarding surgical complications."
Source-Eurekalert