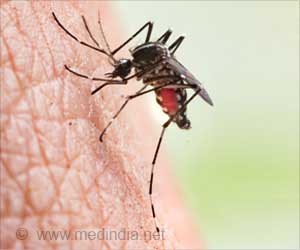
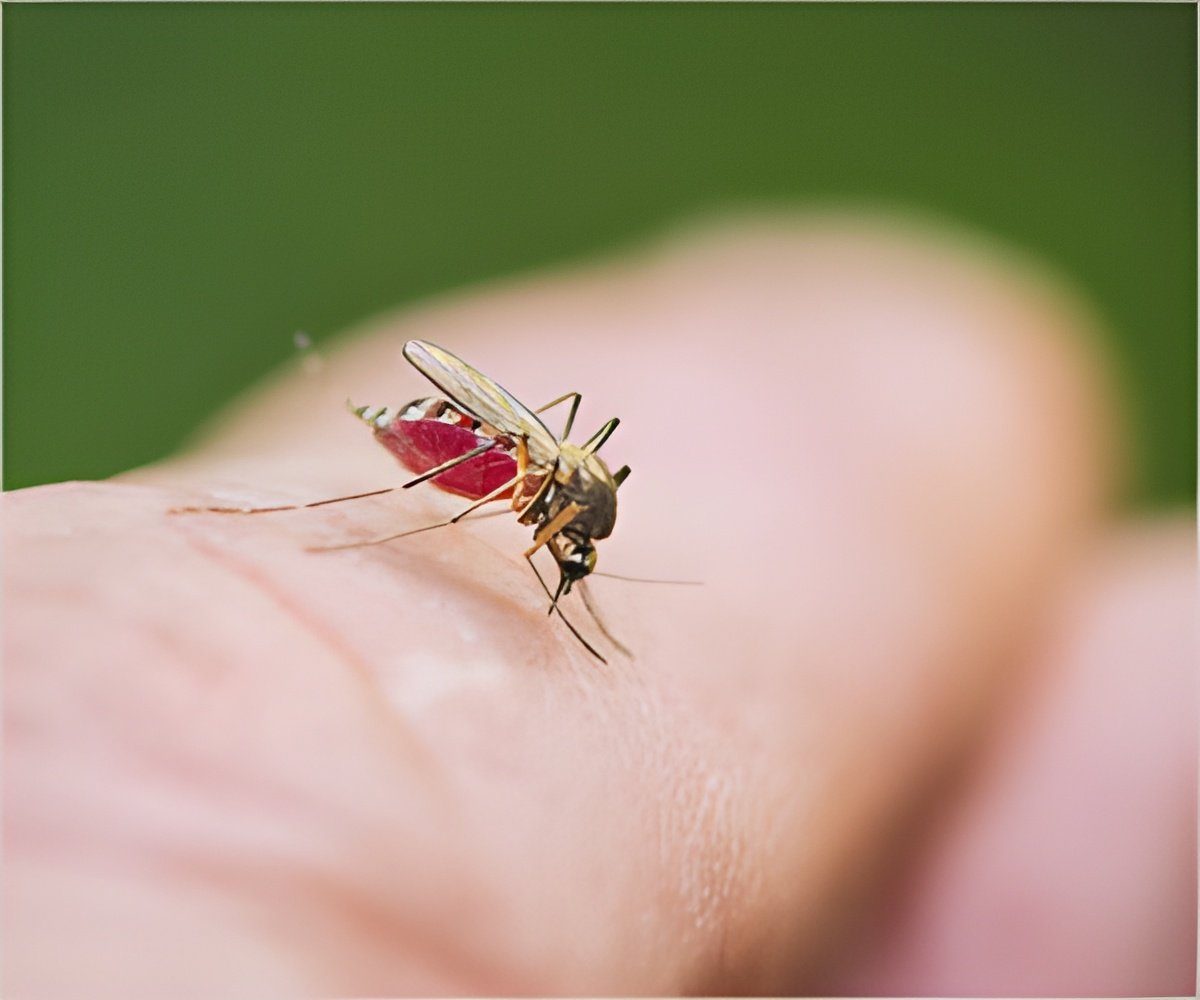
Regardless of the exact transmission pattern China is facing a substantial dengue threat, with potential invasion into broader areas of the country.
Rubing Chen, evolutionary virologist at University of Texas Medical Branch- Galveston, said, "We now have compelling evidence that dengue can persist in China - in some cases up to six to eight years. We found a surprisingly complex and diverse mix of viral subtypes represented in China, a factor that can mean greater risk of epidemic dengue in the future."
Chen further added, "The new research provides one of the most extensive analyses to date and could be a critical tool in adjusting dengue prevention and control efforts to protect millions of people in China."
The researchers evaluated all dengue virus sequences from China available in the public database GenBank. They found 50 individual variants and multiple variants during the 2014 Guangdong outbreak.
Chen said, "Even within the same year, a person can catch dengue more than once if distantly related variants are circulating in the same region."
The authors said, "Regardless of the exact transmission pattern China is facing a substantial dengue threat, with potential invasion into broader areas of the country. Sporadic cases have been identified in several provinces in recent years. The combination of a hot, humid climate ideal for breeding mosquitoes and large population centers in southern China combine to make this area a particular concern for public health officials."
Advertisement
Source-IANS