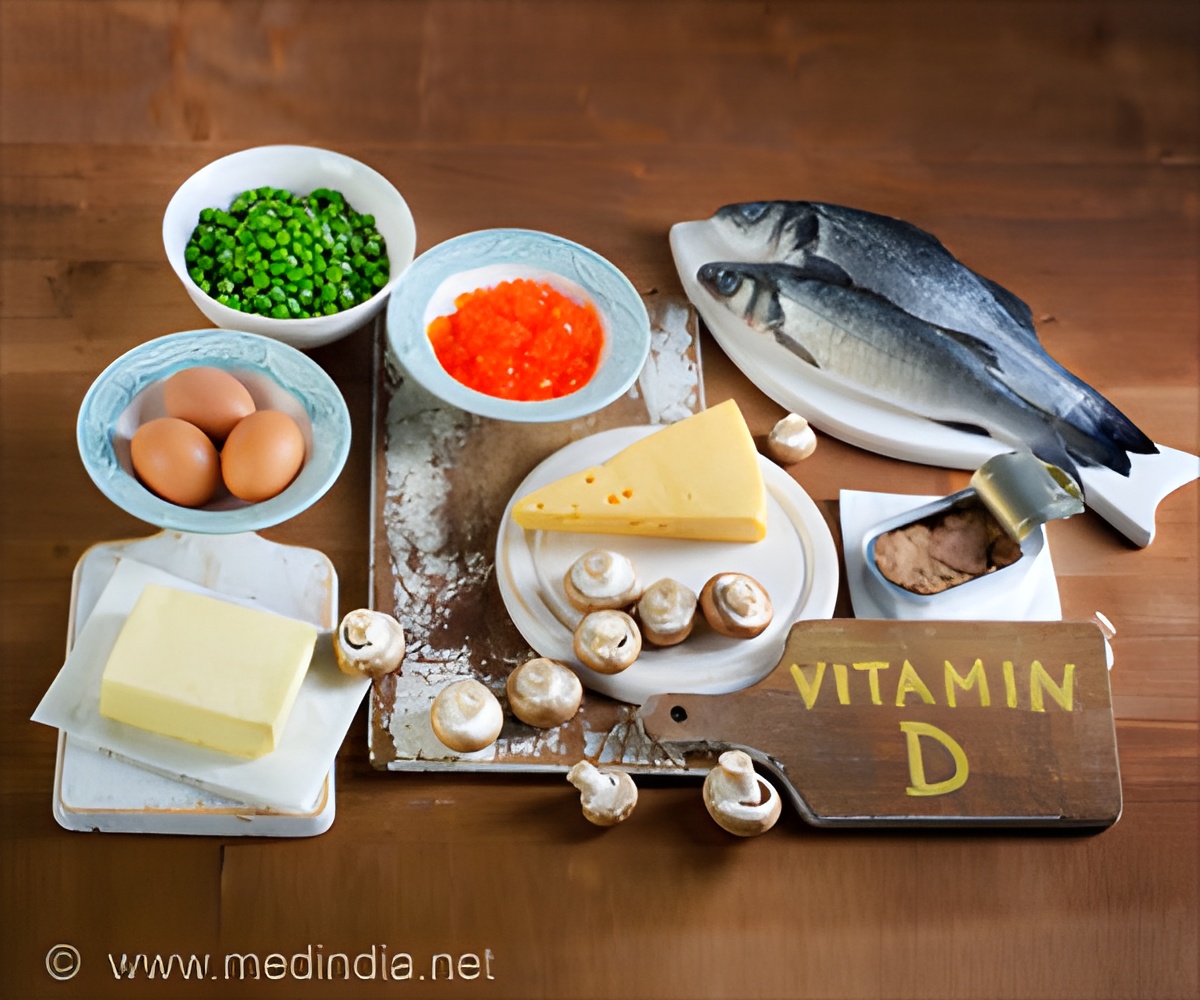
Excess consumption of vitamin- D rich foods can lead to elevated calcium levels and dangerous health consequences.

‘Vitamin-DD overdose can lead to hypercalcaemia resulting in fatigue, muscular weakness and renal stones.’
Read More..




If persistent, hypercalcaemia can lead to kidney stones, kidney calcification and, ultimately, to a loss of renal function.Read More..
Even without exposure to sunlight, a daily consumption of 20 £gg of vitamin D is adequate to meet the body's needs for this vitamin for the vast majority (97.5%) of the population.
The European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) has set a UL value (tolerable upper intake level) of 100 £gg for vitamin D. According to the latest scientific research, if adults and children aged eleven and older consume a daily quantity of no more than 100 £gg, any impairments to health are unlikely.
This UL value includes the intake of vitamin D from all sources, and thus includes intake from supplements, normal dietary intake and intake from food that has been fortified with vitamin D. If high-dose vitamin D preparations are also consumed, this figure may be exceeded in combination with other sources of the vitamin.
From the perspective of nutritional science, the daily consumption of vitamin D preparations containing a 50 £gg or 100 £gg dose is not necessary. On the other hand, the BfR considers it unlikely that impairments to health will result from the occasional consumption of such high-dose preparations.
Advertisement
The BfR notes that, given an adequate length of time spent outdoors with corresponding exposure of the skin to sunlight, plus a balanced diet, an adequate supply of Vitamin D can be achieved by individuals without having to take vitamin D preparations.
Advertisement
This opinion does not constitute a decision as to whether or not a product should be classified as a foodstuff, nor should it be interpreted as such.
Source-Eurekalert