It is a well known fact that every new edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders stirs up a host of questions and controversies and the next DSM is no exception.
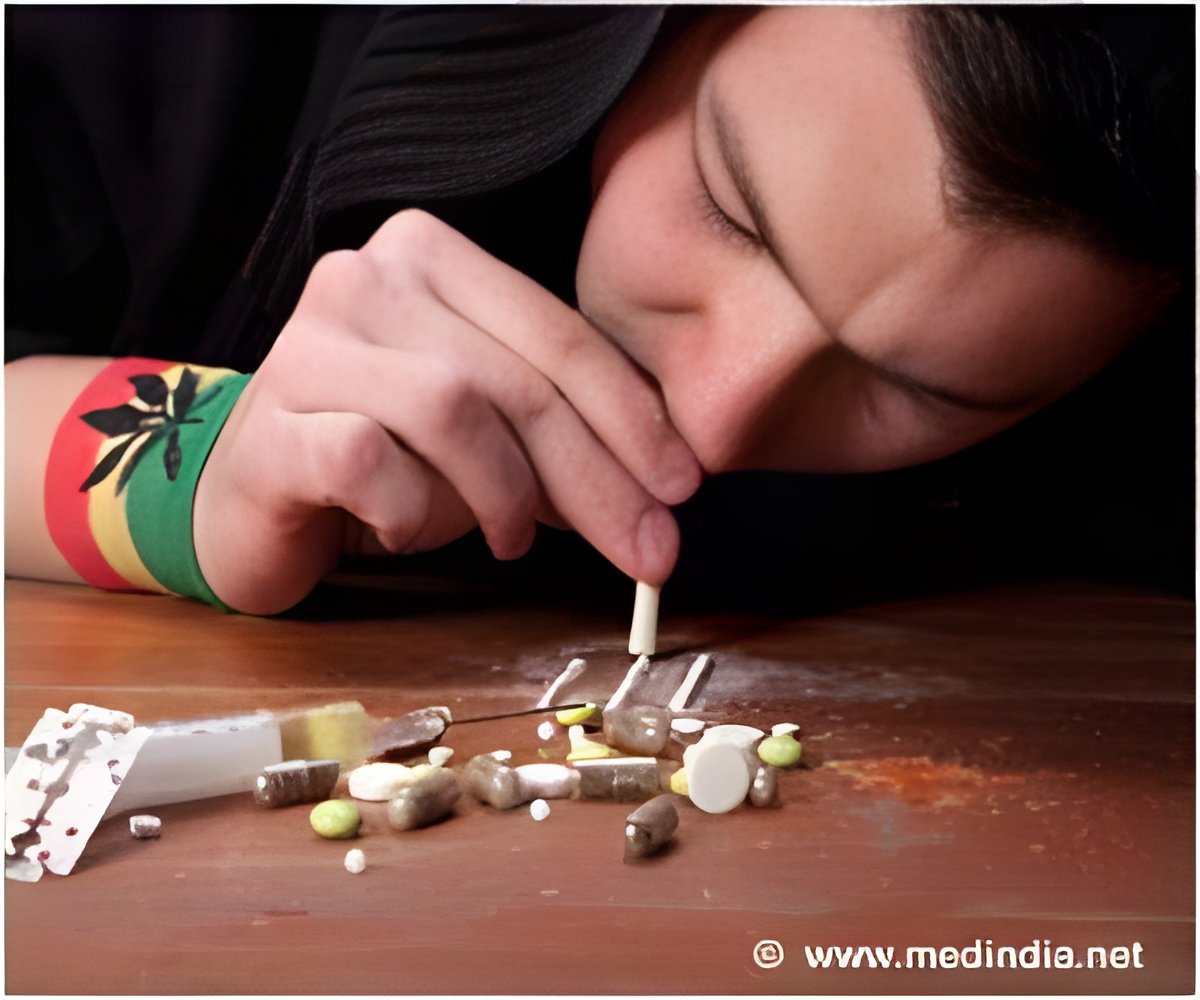

Therefore, one of the biggest changes is the decision to meld the separate abuse and dependence categories into a single diagnosis in which a person has to meet two or more items for a diagnosis. With the DSM-5, a person can have an "alcohol use disorder" or a "drug use disorder" but not specifically abuse of or dependence on alcohol or other drugs.
"Our goal was to try to make the criteria easier for the usual clinician to use, and so we're no longer asking them to remember one criteria set for abuse and a separate set for dependence," says Schuckit.
But the proposed changes have received significant criticism. Griffith Edwards, D.M., in a letter to the editor in the same issue of JSAD, writes that there is "no convincing case" for the proposed changes. "The impression is given of a field in disarray," Edwards continues. "Revisions are sometimes necessary, but unnecessary revisions are likely to be without benefit."
Edwards writes that experience working with patients has shown that there is, in fact, an intermediary step of disruptive drinking, such as alcohol abuse, that does not meet the higher threshold for dependence. Further, he states, the new, single category would deviate significantly from the diagnostic criteria set out by the World Health Organization in its diagnostic manual, the International Classification of Diseases. "The consequence may be that the DSM comes to be seen as enshrining an American point of view, whereas the ICD would be the international currency," Edwards concludes.
On the other hand, according to Schuckit, factor analyses performed on the group of 11 criteria have shown that these symptoms currently used to diagnose abuse and dependence statistically constitute approximately 1.2 disorders—not exactly one group, but certainly closer to one group than to two. Proponents of the change to a single, combined diagnosis also argued that it is simpler for both lay people and clinicians to understand.
Advertisement
A recent article in The New York Times (May 11, 2012) suggested that this change could result in many more people being diagnosed as having a substance use disorder than was seen using the DSM-IV and may strain health care resources. In response, Schuckit says the committee evaluated data on more than 100,000 cases using both the current abuse-and-dependence approach in DSM-IV and the proposed substance-use-disorder approach in DSM-5, which combines abuse and dependence. The committee found that the number of people diagnosed did not change much across the two diagnostic schemes.
Advertisement
Schuckit concludes that although people are often resistant to change, it's a healthy process.
"Science marches forward, so it makes sense that every decade or so, people who are using the science in order to best diagnose disorders should reevaluate what's happened over that decade," says Schuckit. "The DSM is reflecting what we know now that we didn't know 10 years ago."
Source-Eurekalert