Gamma delta Intraepithelial lymphocytes, disappears early in Crohn’s disease, potentially triggering inflammation.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Go to source).
‘Did You Know?
A missing immune cell might be the key to Crohn’s disease! #crohnsDisease #inflammatory bowel disease #guthealth #inflammation #immunesystem #healthcare #medindia’





A missing immune cell might be the key to Crohn’s disease! #crohnsDisease #inflammatory bowel disease #guthealth #inflammation #immunesystem #healthcare #medindia’
Advertisement
Role of Gamma Delta IELs(Intraepithelial lymphocytes) in Gut Health
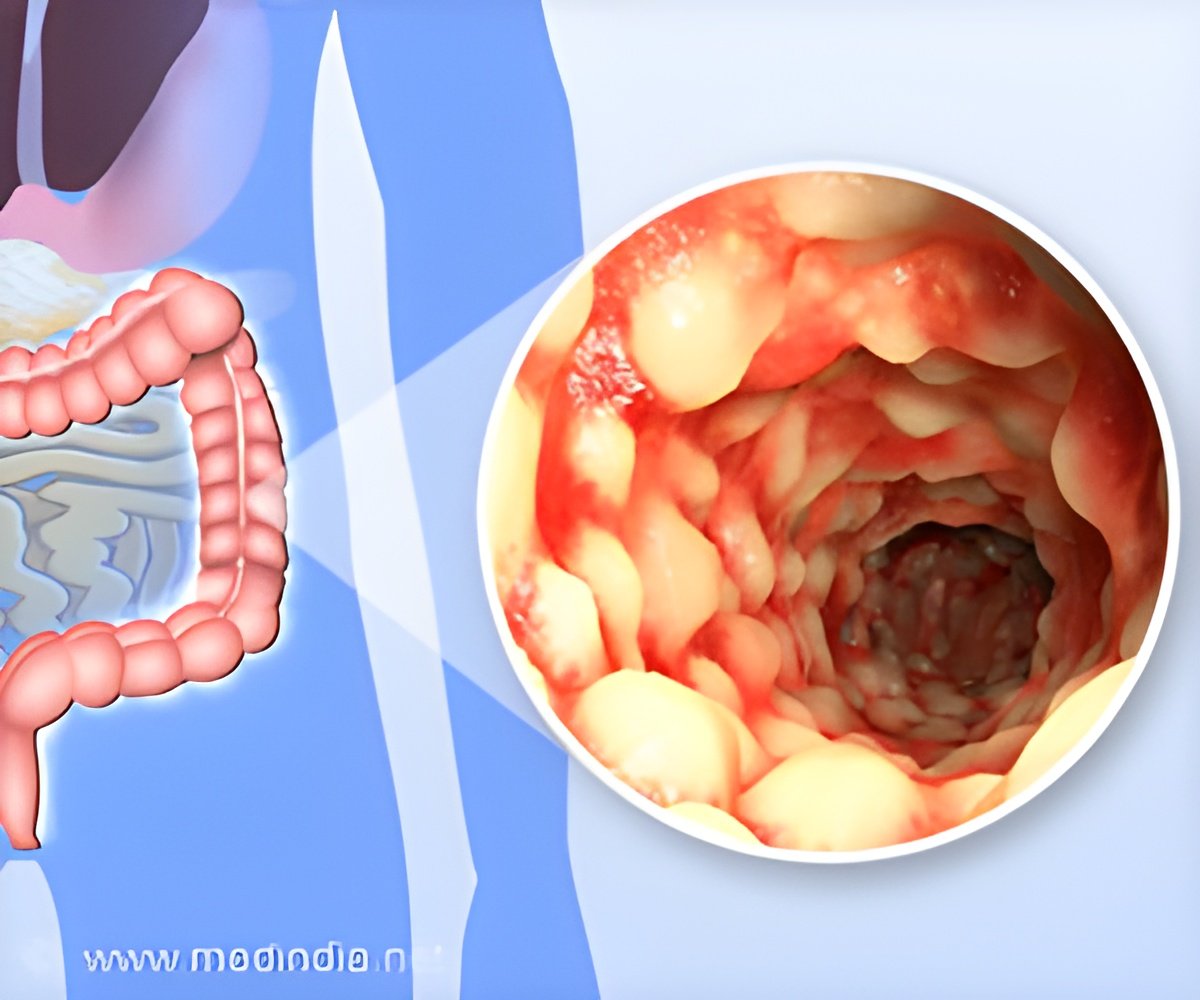
Crohn’s disease is a long-term condition that causes inflammation in the digestive tract, leading to symptoms like stomach pain, diarrhea, weight loss, and fatigue. While inflammation helps the body fight infections, too much can harm healthy tissues. Certain immune cells called gamma delta IELs (intraepithelial lymphocytes)protect the gut, but they are often lower in people with active Crohn’s disease.Advertisement
How Their Loss May Trigger Crohn’s Disease
Gamma delta IELs(intraepithelial lymphocytes) prevent gut inflammation, but they decrease weeks before Crohn’s symptoms appear. In a mouse model, inflammation disrupted these cells, weakening gut protection and allowing harmful immune cells to cause damage, possibly triggering the disease.Advertisement
Implications for Diagnosis and Treatment
The loss of gamma delta IELs may predict Crohn’s relapse or treatment response. Future therapies boosting these cells could help maintain remission or prevent the disease. The study was supported by major research institutions and funding agencies.Reference:
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease - (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29262182/)
Source-The Mount Sinai Hospital / Mount Sinai School of Medicine