Ebola hemorrhagic fever is a disease caused by a Ebola virus via direct contact with body fluids or infected blood. Congo's health minister has declared an end to the Ebola epidemic.
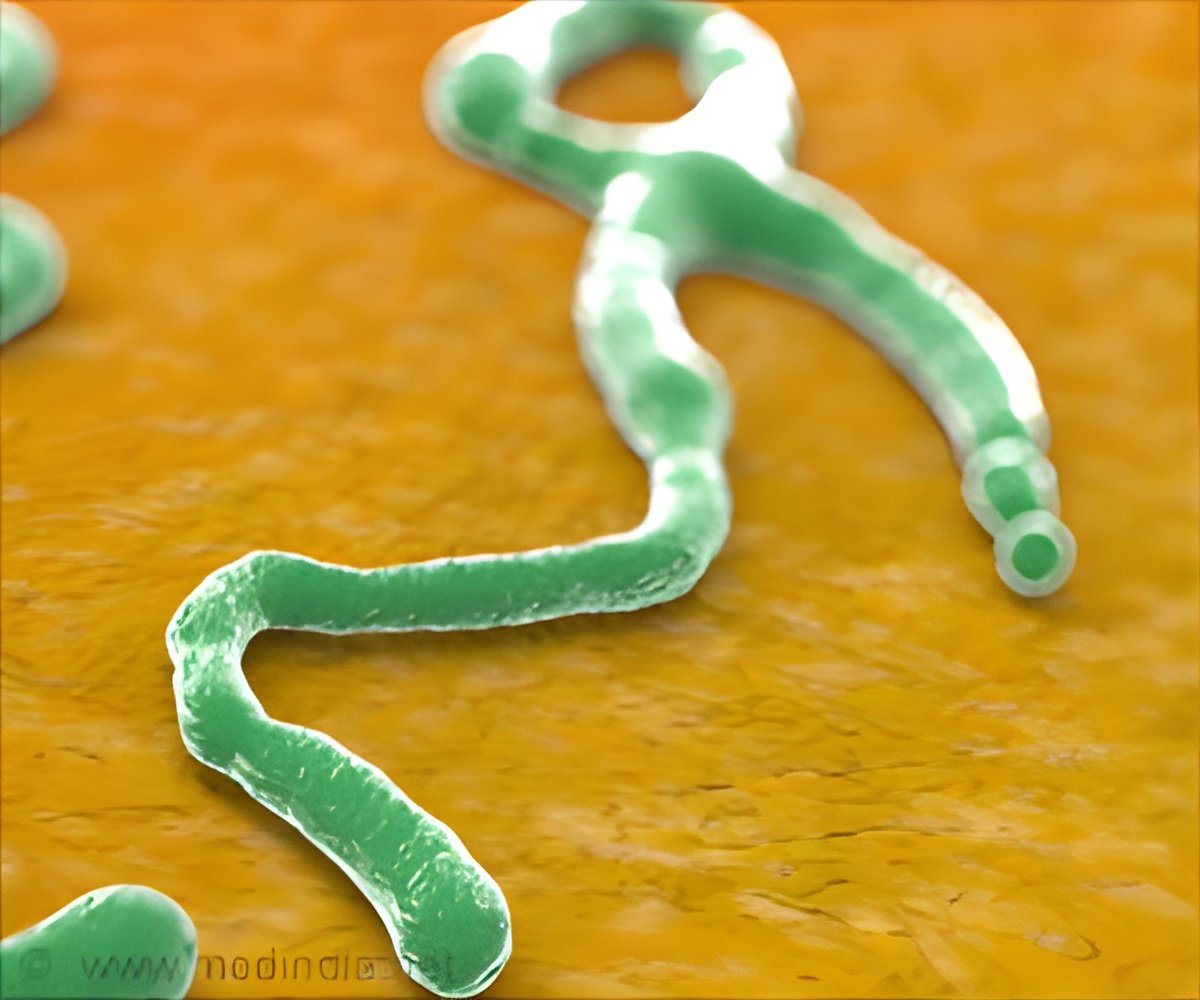
‘The World Health Organization declared an end to the Ebola Virus Disease (EVD) in the Democratic Republic of the Congo.’





The announcement comes 42 days after the last confirmed Ebola patient in the affected Bas-Uele province tested negative for the disease for the second time. "Enhanced surveillance in the country will continue, as well as strengthening of preparedness and readiness for Ebola outbreaks," the WHO said.On 11 May 2017, the WHO was notified by the Ministry of Public Health of the virus among a cluster of undiagnosed illnesses and deaths with haemorrhagic signs in Likati Health Zone.
This was DRC's eighth outbreak of EVD since the discovery of the virus in the country in 1976. According to WHO, around 600 people who had close contacts with affected individuals were registered and monitored closely for the duration of the outbreak.
Shortly after the WHO announced the end of the outbreak, Dr Oly Ilunga Kalenga, Congo's Minister of Health said, "I urge that we now focus all our efforts on strengthening the health system in Bas- Uele province, which has been stressed by the outbreak. Without strengthening the health system, effective surveillance is not possible."
Advertisement