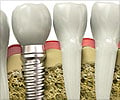
Customizable strontium-filled implant surfaces form an effective soft-tissue seal around the dental implant, helping it heal faster.
- Dental implant success depends on effective tissue attachment in the mouth following placement
- This can be achieved by modifying the implant surfaces and placing tissue for effective seal formation
- Materials compatible with bone have been developed to support attachment and healing after implant placement
Strontium-loaded hydrogel scaffolds to promote gingival fibroblast function
Go to source).
Read More..
Dental Implant Healing: What you Need to Know
Dental implants are the most realistic tooth replacement option in modern dentistry. It functions and looks like a natural tooth, so you can regain the confidence in your smile. The process of placing this implant undergoes various healing stages. Although the initial healing stage takes as little as two weeks, in some patients it can be placed immediately after tooth removal. But the complete healing takes between six to twelve months.Therefore, the success of dental implants is dependent on the adhesion of soft tissues and bone to the implant surface. For this, implant surfaces present facing the mouth tissue can be modified to improve cellular adhesion and function leading to the formation of an effective soft-tissue seal during healing (2✔ ✔Trusted Source
Dental Implants: What You Should Know
Go to source).
In this healing process, fibroblasts present in the gum are prominent cells to migrate to repair wounds and are crucial for the development of connective tissue rich in cells that gives structural support.
Previous research has found that strontium, a bone-seeking element that improves bone density and strength, also supports soft tissue function. Strontium can promote the function of fibroblasts, a type of cell that forms connective tissues and plays a critical role in wound healing (3✔ ✔Trusted Source
Osseointegration effects of local release of strontium ranelate from implant surfaces in rats
Go to source).
Strontium in the Bone-Implant Interface: Success Mantra for Dental Implant
In the current study, the research team developed a strontium-loaded hydrogel platform that can be customized to any size and shape of implant collar or healing screw through the creation of reusable, ring-shaped templates and molds.The strontium ions are then released from the scaffold in an initial burst over 24 hours, followed by a sustained dosage over four days. According to the researchers, this process involves minimal toxicity for the patients.
The laboratory tests also showed that the strontium ions released from the scaffold effectively stimulated fibroblast activity in the gums and thus promoted wound healing. In addition, tests showed that the hydrogel scaffold alone had only a minimal effect on the tissue.
Having proven that strontium-loaded scaffold displays good biocompatibility and functionality, researchers feel it has great potential for promoting wound healing processes following implant placement.
Scaffold materials have been explored to promote bone and skin wound healing, but adaptations for the oral cavity are limited. This novel scaffold might be a system for effective strontium release in the oral cavity.
Tips for Faster Healing After Dental Implant Surgery
Having dental implants placed can make you feel both excited and nervous at the same time. At the same time, it is important to be cautious about the recovery period following surgery.To make your recovery even faster and easier, here are some tips to help you heal faster after dental implant surgery (4✔ ✔Trusted Source
Health, Maintenance, and Recovery of Soft Tissues around Implants
Go to source):
Take Rest
: One of the best things you can do to help your body heal itself is simply to rest. This is especially important in the days immediately after surgery. Even when you start to feel better, it is recommended to avoid strenuous activities.Eat Soft, Nutritious Food
: It is recommended to avoid hot or spicy foods for 48 hours after implant placement surgery since they can cause bleeding and/or irritate the surgical site. After that, the general rule is to only eat soft foods. Do not use a straw, since suction can disturb the surgical site. Instead, use a spoon (5✔ ✔Trusted Source
Dietary Strategies to Optimize Wound Healing after Periodontal and Dental Implant Surgery: An Evidence-Based Review
Go to source).Stay Hydrated
: Staying hydrated allows your body to flush out toxins that could otherwise slow your recovery process. Along with drinking plenty of water, you should also avoid drinking caffeine and alcohol, at least for two weeks.Use Ice Packs
: Using an ice pack is an easy and effective way to decrease swelling and provide pain relief after implant placement surgery. You should also only use ice for about 20 minutes, then remove it for 20 minutes before starting again.Rinse with Salt Water
: Saltwater rinses not only decrease the number of bacteria inside the mouth without irritating the surgical cut, but they are soothing as well.Don’t Smoke
: Smoking after having dental implants placed can severely affect your chances of a successful recovery as it restricts oxygen flow to your bones and oral tissue.Practice Good Oral Hygiene
: Even though dental implants are not natural teeth, they still require proper oral hygiene. This will reduce the chances of developing an infection around the surgical site.
References:
- Strontium-loaded hydrogel scaffolds to promote gingival fibroblast function - (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/jbm.a.37439)
- Dental Implants: What You Should Know - (https://www.fda.gov/medical-devices/dental-devices/dental-implants-what-you-should-know)
- Osseointegration effects of local release of strontium ranelate from implant surfaces in rats - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6790188/)
- Health, Maintenance, and Recovery of Soft Tissues around Implants - (https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/cid.12343)
- Dietary Strategies to Optimize Wound Healing after Periodontal and Dental Implant Surgery: An Evidence-Based Review - (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3681034/)
Source-Medindia