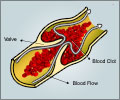
Scientists launched a new model to detect pediatric patients at risk for developing blood clots or venous thromboembolisms (VTEs).
‘Kids with increased risk of developing blood clots should be reviewed by a hematologist, and a personalized prevention plan should be implemented.’
Read More..




Walker noticed that blood clot development was on the rise in kids.Read More..
"The reason children get blood clots is very different from adults," said Walker, who worked with mentors Allison Wheeler, MD, MSCI, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Pathology, Microbiology and Immunology, and C. Buddy Creech, MD, MPH, director of the Vanderbilt Vaccine Research Program and associate professor of Pediatric Infectious Diseases.
"There was no standardized protocol for preventing clots in pediatric patients. As we noticed that the rate of blood clots was going up and recognized that the adult strategy wasn't going to work for our patients, we wanted to look at each patient's individual risk factors and see how we could focus our attention on targeted blood clot prevention."
The study, set to be published in Pediatrics, explains how they validated a predictive model that can be automated to run within the electronic health record of each patient admitted to the hospital.
The model includes 11 risk factors and was based on an analysis of more than 110,000 admissions to Children's Hospital and has been validated on more than 44,000 separate admissions.
Advertisement
After calculating the risk score, patients are randomized, so in half of the patients, elevated scores are reviewed by a hematologist, and then discussed with each patient's medical team and family to determine a personalized prevention plan. All patients, regardless of randomization, continue to receive the current standard of care.
Advertisement
"We are, in real-time, assessing the use of this model as a clinical support tool. We saw a clinical opportunity of something we could improve and have moved forward with building the model -- to identify high-risk patients and are currently performing the CLOT trial, which will run through the end of the year."
Walker's study was possible with the help of the Advanced Vanderbilt Artificial Intelligence Laboratory, or AVAIL.
"AVAIL served as a catalyst, in this instance by bringing experts in a complex trial development into proximity so that a great synthesis could happen," said Warren Sandberg, MD, PhD, executive sponsor of AVAIL, along with Kevin Johnson, MD.
"What is unique about this particular project is that we were not only able to predict complications but also able to test the model in a rigorous, pragmatic, randomized, controlled trial to see if it benefits patients," said Dan Byrne, senior biostatistician for the project and director of artificial intelligence research for AVAIL.
"The future of this kind of work is unlimited," he said. "We can hopefully use this approach to predict and prevent pressure injuries, sepsis, falls, readmissions or most any complication before they happen.
At Vanderbilt, we are raising the bar when it comes to the science of personalized medicine and application of artificial intelligence in medicine in a way that is both ethical and safe."
Source-Medindia