In rare cases, differentiated thyroid carcinoma can widely infiltrate the larynx, making total laryngectomy unavoidable
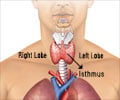
The proximity of the thyroid gland to the larynx, trachea, pharynx, and cervical esophagus allows thyroid cancer to invade these structures. Invasion of the larynx by differentiated thyroid gland carcinoma is uncommon, but causes serious morbidity and mortality when present.
A recent article, which appears in the July issue of The American Journal of Surgery, reports on 5 differentiated thyroid carcinomas in which a total laryngectomy was included in the surgical procedure with special emphasis on the histologic intralaryngeal tumor spread.In the study, the clinicopathologic characteristics of 5 patients in which a total laryngectomy had to be performed for differentiated thyroid carcinoma were analyzed. Special reference was paid to the histologic intralaryngeal tumor spread, which was evaluated on whole-organ section.
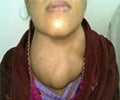
All patients presented with hoarseness and/or dyspnea. Two patients are alive at 44 and 115 months. One patient died of intercurrent disease 2 months and 2 patients with disease 6 and 14 months after surgery. In all cases, intralaryngeal tumor spread was observed. Invasion of the larynx occurs by direct extension or by posterior tumor growth around the edge of the thyroid cartilage.
Thus, in rare cases, differentiated thyroid carcinoma can widely infiltrate the larynx, making total laryngectomy unavoidable. The diagnosis of intralaryngeal tumor spread is done by imaging and endoscopy.
The authors claim that to the best of their knowledge, this is the first article analyzing the histologic growth pattern of thyroid carcinoma invading the larynx on whole-organ slices.
Medindia on Cancer:
Cancer, in simple terms, occurs when cells divide in an uncontrolled manner for no apparent reason. In time, they form a mass of extra tissue and become big enough to be noticed as a growth or tumor.