Report on the highlights of Scientific Program of the 2009 American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO).
Report on the highlights of Scientific Program of the 2009 American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO).
The highlight include Pan-American Association of Ophthalmology (PAAO) Joint Meeting include: John T. Flynn, MD, Columbia University School of Medicine, discussing the ever-tougher challenges Eye M.D.s face in caring for the vision of the tiniest premature babies; and a report by Bradford W. Lee, MD, Stanford University School of Medicine, on barriers to glaucoma follow-up as perceived by patients in an urban, culturally diverse clinic.The AAO-PAAO meeting is in session October 24 through 27 at the Moscone Center, San Francisco, CA. As the largest, most comprehensive ophthalmic education conference in the world, it offers United States and international Eye M.D.s more than 2,000 scientifically-based, peer-reviewed presentations, including instruction courses, skills transfer labs, "Breakfast with the Experts" roundtables and 900 research papers and posters.
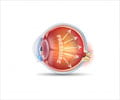
Saving Sight in Tiny Babies: the Past, Present and Future of ROP Treatment
Due to astonishing progress in neonatal medicine, younger and smaller babies than ever before are being saved: they often weight less than one pound and may be born 10 to 14 weeks early. Paradoxically, this medical progress has generated new healthcare challenges, including retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) a potentially blinding disease. ROP is more likely to occur in such tiny infants and to be severe and hard to treat successfully even with laser therapy, today's method of choice. In a key lecture at today's Pediatric Ophthalmology symposium John T. Flynn, MD, Columbia University School of Medicine, relates the history of ROP to today's escalating treatment challenges and the search for new solutions.
From the 1970s onward, pediatric ophthalmologists have been increasingly able to reduce or cure ROP by adapting treatments developed for adult diabetic retinopathy. In the extremely premature infants saved today, though, all treatment parameters are more difficult and vulnerable to failure.
"It is time for pediatric ophthalmologists to reassess how best to screen and treat their smallest, frailest patients," said Dr. Flynn.
Advertisement
In the first study of its kind in the US, researchers asked San Francisco General Hospital (SFGH) glaucoma clinic patients about their reasons for missing follow-up appointments with their ophthalmologists. Poor glaucoma follow-up is a widespread problem–especially among medically underserved groups–that leads to unnecessary vision loss. The study also investigated whether barriers were linked to ethnicity. Bradford W. Lee, MD, Stanford University School of Medicine, led the joint project by Stanford and University of California, San Francisco, Department of Ophthalmology.
Advertisement
The most vexing issues were long clinic wait times and appointment-scheduling difficulties, according to the 152 SFGH clinic patients surveyed from August 2008 to January 2009. Seventy-five percent of patients cited long wait times as a significant barrier. And even though SFGH provides medical interpreting services, 37 percent of Latino-ethnicity and 32 percent of Asian-ethnicity patients cited language and interpreter issues as significant barriers. The researchers say new strategies to streamline appointment procedures for non-English speaking patients, and resolving wait time and interpreter issues should be top priorities for SFGH and similar glaucoma clinics.
Source-Eurekalert
ARU